4 methods for calculating the area heating radiator
A preliminary calculation of the capacity of heating radiators over the area makes it possible to create the most comfortable microclimate in the equipped room. You can avoid as well as unnecessary costs, and lack of performance. You can use one of three ways to get the numbers you need, which we'll analyze in this article.

Calculation methods
Installation of the heating system is an incredibly serious task. All sections have their own power index, and exactly how much you install them will determine the convenience of a winter stay in your own house or apartment. At the same time, the entire wall should not be hung with batteries either, since, firstly, it will be very expensive, and secondly, it is inexpedient.
That is why you should know in advance by calculating the number of sections on the radiator being installed that is necessary for your home. To carry out this task, you can use the following methods, each of which has its own characteristics:
Method # 1: Standard

In accordance with the SNiP, the calculation of sections of heating radiators by area is performed from the argument that about 100 W of power of the heating system is needed per square meter of housing. In this case, all mathematical operations are performed using several formulas using the following notation:
| Designation | Explanation |
| S | Area of the room, m2 |
| P | Power of one radiator section, W |
| H | Ceiling height, m |
| TO | Number of sections required |
- If no additional conditions are observed, then we use the formula K = S? 100 / P. Then, for example, the calculation of aluminum radiators over an area of 25 m2 will look like this: K = 25? 0.72 = 18 sections;
Tip: Batteries with the number of sections obtained are preferably mounted under window openings. This is how thermal barriers are formed on the path of cold air, allowing to reduce the amount of condensate that falls on the glasses.

- If the room in which the installation of the system is carried out is located in the end or corner of the building, the instruction requires the value obtained above to be multiplied by an increase factor of 1.2. We consider: K = 18? 1,2 = 21.6, which should be rounded to the nearest whole number, and we get 22;

- If we are talking about a room in which the height of the ceiling exceeds three meters, then it will also need to be taken into account, because such a space is much more difficult to heat.. Thus, when removing the ceiling by three and a half meters, the formula takes the following form: K = S? H? 40 / P = 25? 3.5? 0.23 = 23.4, which is rounded to 25.
Tip: you also want to perform the calculation of the area of the radiator before its acquisition and compare the resulting value with a free space on the wall. Otherwise, you can get into an uncomfortable situation when a new battery is simply nowhere to be installed. It is enough to multiply the height and length of the structure.
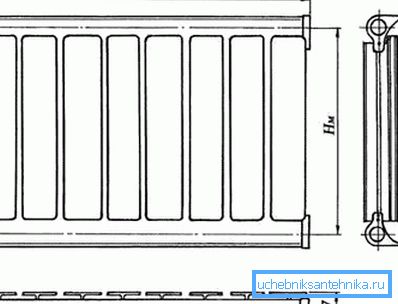
| Designation on the diagram | Parameter name |
| L | Length |
| H | Height |
The result: all the values are fairly accurate, but you have to work a little with the calculator, and you will need to know the formulas.
Method # 2: approximate

A simplified calculation of the number of heating radiators per area is performed from the following considerations:
- One section of a standard battery can heat 1.8 m2;
- For a normal room with one outer wall and one window, one kilowatt of radiator capacity per 10 m2 is enough to create a favorable microclimate;
- For corner rooms, it is considered sufficient when using this method of 1.3 kW.
But the cost of error in performing such calculations is very high, so they are used very rarely and only for small rooms. The bottom line: simple and fast, but with accuracy is problematic.
Method number 3: volumetric
In this case, the volume of the heated room is taken into account. To do this, multiply the width and length of the room with the height of its ceiling. Further, taking into account that a section with a power of, for example, 200 W can properly heat five cubic meters of space, we can perform the necessary mathematical calculations.
For example, take a room with the following parameters:
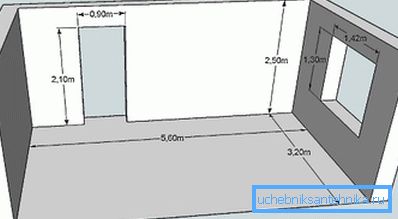
| Parameter | Value, m |
| Ceiling height | 2.5 |
| Length | 5.6 |
| Width | 3.2 |
So: 2.5? 5.6? 3.2 = 44.8, which means K = 44.8 / 5 = 8.96, which is rounded off to 9. It is also customary to increase the obtained value by 20% in order to avoid possible errors: 9+ 9/100? 20 = 10.8, and the new rounding gives 11.

Bottom line: the results are quite accurate, but you need to know how much air the battery of your choice can heat.
Method # 4: Online
It is also worth noting that today there is such a convenient option as an online calculator for calculating heating radiators by area:

Advice: when installing heating equipment in especially large premises, it is recommended to resort to the services of specialists, as they may have many additional factors that you unknowingly simply do not pay attention to, and the results will turn out to be erroneous because of them .
When choosing a suitable program, please note that the calculator for calculating steel heating radiators differs in area from the calculator for calculating aluminum or bimetallic products.
Bottom line: simple enough, but requires knowledge of all the necessary parameters of the room and the selected batteries, as well as the availability of the Internet.
Conclusion
It doesn’t matter whether you choose the online calculator for calculating aluminum radiators by area, decide to use special formulas or find the desired value through the volume of the room, the main thing is to do it before purchasing batteries. Only in this way you can be sure that the microclimate in your house or apartment will be comfortable enough for you to live.

The video in this article will introduce you to additional materials. Be careful while doing math calculations.