Aluminum radiator section: technical features of a sectional
Convectors of heating from non-ferrous metals are becoming increasingly popular. We want to consider the main structural element of such a radiator - a section, and find out how many watts are in one section of an aluminum radiator, what are its dimensions and other characteristics. We will also tell you how to calculate the number of sections of the aluminum radiator necessary for heating a specific room.

Technical features of a sectional radiator
Design

Sectional batteries have almost the same design. They are a system of two horizontal reservoirs connected by vertical channels. On the vertical tubes outside there are plate fins, which form channels for the movement of convection currents and increase the area of thermal interaction.
The distance between the plates is chosen so that the convection currents are not laminar, but turbulent. This increases the intensity of air interaction with the surface of the housing.

The design is divided into equal parts. One such part includes a vertical channel and two collector elements, one from the top, the other from the bottom. The collector element with the vertical channel forms a T-shaped connection, two open holes of which are adapted to be combined with other similar collector holes.
The parts are connected using a special nipple with a gasket.
If the part is installed with an edge, then the hole is closed with a plug or used to connect the supply, return or air valve.

Consider the operation of a battery with a similar design:
- The parts are assembled into a single battery, a coolant supply pipe is connected to one of the holes, a waste liquid outlet pipe is connected to another, a Mayevsky valve is used to drain excess air to the third, the fourth hole is closed with a plug;
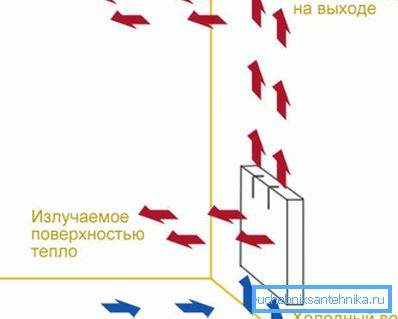
- The coolant enters the collector and gradually fills the entire device. Aluminum has a high thermal conductivity, about four times higher than steel. Therefore, the body starts to warm up quickly;
- The heated surface of the convector begins to emit thermal energy. The share of radiation of heat in the infrared range accounts for about 50 - 60% of the total heat transfer of the device;
- The air in contact with the surface of the body begins to heat up due to direct heat transfer. Under the action of gravity, the heated masses begin to move upwards through the channels formed by the edges of the convector, and new portions of cold air are drawn into the battery from below;
- The device begins to work as a gravity pump. Airflows passing through the channels take on a vortex character, which increases the heat transfer of the plates due to mixing.
Note! The main advantage of the sectional design is the ability to change the power and size of the device with your own hands.
Characteristics and features

The main technical characteristic of any heater is its thermal power. This is the amount of heat that the device transmits to the environment per unit of time. Measured in kcal / hour or watts.
Power depends on many factors, among which the main ones are considered:
- device surface area;
- coolant temperature;
- channel capacity (how many liters in one section of the aluminum radiator);
- thermal pressure;
- material thermal conductivity;
- housing design;
- connection method feed and return.

Since the maximum number of sections in the aluminum radiator is not installed, and different devices have different sizes, it is more convenient to consider the parameters of one separate part, and then determine the characteristics of the battery by adding the values of each of its parts.

Consider the technical specifications in more detail:
| Specifications | Parameter values |
| Height (center distance) | 250, 300, 350, 400, 450, 500 mm. The most common sizes are 350 to 500 mm. Vertical models can reach 1 - 2 meters in height. |
| Depth | For standard models 80 - 140 mm |
| Width | For most products 80 mm |
| Capacity | 0.25 - 0.5 liters |
| Wall thickness | 2 - 3 mm |
| Heat transfer area | 0.4 - 0.6 m? |
| Power | 80 - 220 W, more often 140 - 160 W |
| Maximum temperature of the heat carrier | 130? C |
| Operating pressure | 6 - 24 atm. |

Note! For connection to the centralized coolant supply systems, models with a maximum (pressing) pressure of at least 45 atm should be selected. and a working pressure of at least 16 atm.
Determining the number of sections

It is often asked how much one section of a convector heats, how to calculate the number of sections, etc. Detailed and accurate calculation of heat loss will be very difficult, but the instruction allows you to use simplified formulas.
According to the norms of SNiP, for heating one square meter of a room with a ceiling height of 2.4 - 2.8 meters, about 100 W of thermal energy is required. That is, if we multiply the area of such a room by 100, we obtain the necessary heating capacity.

Then we will be able to find a suitable device in terms of parameters, design and quality and see its passport characteristics. There will be indicated sectional power.
We divide the previously found heating power of the room into a sectional capacity, the result is rounded up and we get the number of sections required for a particular room.

Note! It should be noted here that the indicated power is often overestimated due to the fact that the supply of heat carrier with a temperature of 100? C is assumed, which is unlikely in real conditions. Should be guided by the fact that the actual power is usually in the range of 140 - 160 watts.
Conclusion
Aluminum heating batteries confidently occupy positions in the construction market. These units have a convenient sectional division, which simplifies their selection, assembly and installation. Watch the video in this article and find out more about this topic.