Antifreeze for heating systems - headache or panacea
Water used as a coolant in most cases becomes the main source of concern for the average person in harsh winters. Bursting pipes, damaged floors and furniture - who has not encountered such a picture? Before you choose antifreeze for heating systems, you must be familiar with the information on the properties of this substance and the rules for its use.
The question of the advisability of using antifreeze is up to you.

Water or antifreeze
Considering the feasibility of using antifreeze, you need to know the disadvantages of the coolant, which this additive is designed to eliminate.
The classics of the genre - water, which is used to heat a home, is different:
- availability and low price;
- high enough heat capacity;
- low viscosity;
- inertness to many substances;
- environmental friendliness.
Even with these advantages, water can gradually:
- cause metal corrosion;
- deposited in the form of scale on the walls of heat exchangers, this process is accelerated depending on the hardness of the water;

- to break pipes of any thickness, if for any reason the heating system fails and freezes (water in the solid state significantly increases in volume).

It is the latter fact that most often explains the use of additives that do not allow force majeure. Antifreeze for heating systems that do not freeze at low temperatures transfer this property to the coolant, protecting the integrity of the system.
At the same time, water acquires other qualities not characteristic of it, with the ensuing consequences.
These different non-freezers
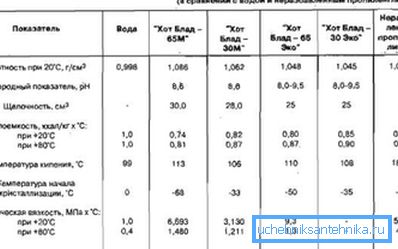
Known antifreezes for heating systems are aqueous solutions of alcohol and glycerin. Created to achieve one good goal - to protect all elements of the system from corrosion, destruction and prolong its service life, the samples can differ greatly from each other in physical and chemical properties and "behavior" in extreme conditions.
We give a comparative description of the main additives used in the heating system at home.
Operational safety
Ethylene glycol antifreeze is an oily, colorless liquid with a sweetish aftertaste and peculiar odor. The main disadvantage of ethylene glycol is its high toxicity, which threatens human health when carelessly handling. For this reason, this substance is strictly prohibited to use in a double-circuit boiler.

100 ml is enough for a person to cause an irreparable thing - according to statistics, 60% of all cases of ethylene glycol poisoning end in death. Since the ingress of a substance from the heating into the water supply circuit may still occur, it is better to choose a different antifreeze for heating.

For the same reason, it is unacceptable to use this non-freezing in an open heating system, because volatile ethylene glycol vapors are also poisonous. Vaporizing from the open expansion tank, they can enter living rooms and cause poisoning. Namely, irritation of the mucous membrane of the eyes, hemolysis of the blood, pulmonary edema is possible.
Note! Due to its danger, the liquid must not be poured onto the ground or into the sewage system. The instructions on the packaging strongly recommends that you hand over the waste material for disposal by a specialist.

Propylene glycol is a viscous, colorless substance with a slight characteristic odor, is not harmful to human health and does not have the above limitations on use. The same applies to glycerol based coolant - a colorless, viscous liquid with a sweet, odorless taste. The price of safe substances is higher by about 70%.
Reaction to critical temperatures
As it approaches a critical temperature, antifreeze changes its physicochemical parameters. These metamorphoses can sometimes radically change its properties, which, in turn, will acquire new qualities. Ethylene glycol antifreezes are sensitive to overheating.
If at some part of the system the temperature approaches the maximum permissible, the antifreeze for the heating system will begin to decompose into solid elements and acids. The resulting solid precipitates tightly stick around the surfaces of the heating elements, forming carbon deposits, which impair heat transfer and, in turn, provoke the formation of new deposits.

Acids react with metallic elements, causing them to corrode. The density of rubber and paronite seals is reduced, as a result of which they begin to leak. Also, as a result of overheating, antifreeze can foam, causing the system to air.
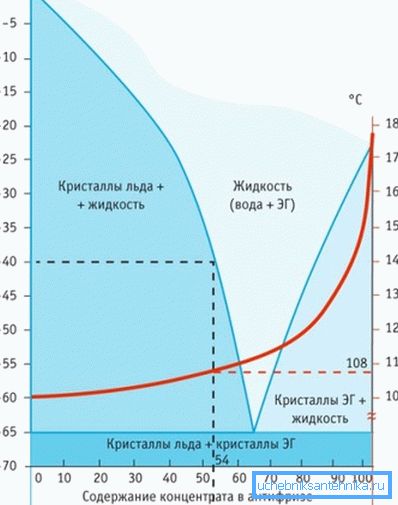
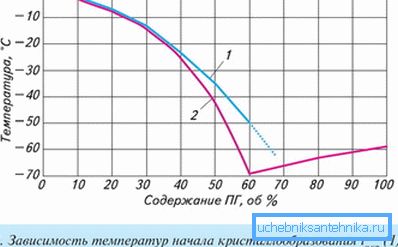
Evaporation of water leads to freezing of ethylene glycol already at -13 ° C, glycerol at +17 (!), Which does not happen with propylene glycol. This is the only antifreeze in the heating system that withstands the reduction of temperature to -60 ° C during “dehydration”.
The transformation of the fluid occurs gradually - single crystals, expanding, form a sludge (ice crumb) and harden. At the same time, the volume of the mass increases by only 0.1% (in ethylene glycol this figure is 1.5%).
In antifreeze based on glycerol, viscosity rises with a decrease in temperature, with increasing it decomposes into volatile and carcinogenic corrosive substances. When cured, they clog up the system with deposits that impede normal heat dissipation. The same ingredient as acrolein can cause asthmoid symptoms.
Note! Experienced users warn about undesirable long-term downtime of the system with glycol antifreeze. Lack of circulation can lead to their separation. Reverse mixing is unlikely to result in the same non-freezing.
Antifreeze survival in the aquatic environment
Let's start with the fact that when designing boilers the manufacturer takes into account the physical properties of the water - the coolant. It is this fact that becomes the starting point when calculating the working parameters of the boiler, the operation of automation and safety devices, the magnitude of the conditional water passages, etc.
The desire to use antifreeze in the heating system begins to materialize already at the design stage and has some inconveniences that radically change the user's plans:
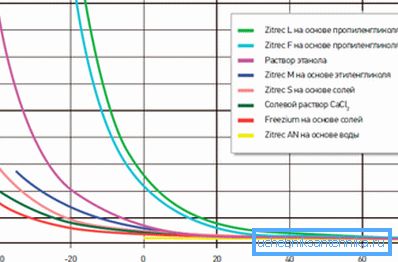
- since the heat capacity of antifreeze is 15–20% lower compared to water, more heating radiators from metal will be needed by 20% increased heat transfer;
- heating radiators for antifreeze should have a volume exactly half the volume of water analogues;
- increase the volume of the expansion tank due to the 40-60% increase in the antifreeze-water mixture;
- given the increased viscosity of the antifreeze pump, it should be more powerful, given the mandatory 10% margin of the design flow rate;
- solder fittings to conduct copper and silver hard solder;
- great value.
Note! The heating system includes elements made of different metals. In order for heating radiators for steel / cast iron / aluminum antifreeze, copper or plastic pipes, copper fittings to serve for a long time, it is necessary to use multicomponent coolants that are gentle on all metals in the complex.
It is important to observe the concentration of antifreeze in the system in the range from 20 to 50%, so as not to provoke the formation of precipitation from salts dissolved in water. In case of violation of these rules, you must add additional additives, as required by the manufacturer.

In the future, it is necessary to strengthen the control of the filters - the first cleaning no later than 2 weeks after the first filling of the heating system with antifreeze occurred. If you want to switch to water heating without impurities, you will need to thoroughly flush the system to completely eliminate unpleasant moments, especially after there was ethylene glycol in the system.
Glycolic antifreeze reduces the surface tension of water, which makes it more fluid. This condition makes it look like an indicator that detects leaks in detachable connections with microscopic defects.
Pour antifreeze
Filling antifreeze into the system with your own hands is a simple procedure and will require a small number of devices:
- capacity for diluted antifreeze;
- hose;
- a pump with a bottom fence for pumping water with antifreeze (suitable, for example, "Kid" or "Stream");

- pressure gauge;
- hose clamps;
- rope / cord, stick are important tools.
The process itself consists of 3 stages:
- Pre-cleaning the internal surfaces of the system.
- Filling the system with coolant.
- Pressure testing - check for tightness of the joints.
Before filling the heating system with antifreeze, it is necessary to dilute the coolant with water in accordance with the instructions.
- Connect one end of the hose to the pump, the second to the filling valve.
- Secure hoses with hose clamps.
- Pour heat carrier into bucket.
- Tie a cord to the pump and hook it to the stick that lies across the bucket. The unit should hang on this device 3-4 cm from the bottom of the tank.

- Open the priming valve and turn on the pump for short periods of time so that the antifreeze does not pump too fast, taking air with it.
- Monitor the level of liquid in the bucket, periodically adding it.
- With a pressure of 2 atmospheres stop the pump. The coolant spread through the system and partially went into the expansion tank.
- Before pumping antifreeze into the heating system completely, you must bleed the air manually if Mayevsky's taps are installed or wait if the valves are automatic.
- Repeat these actions until no air remains in the system, and the pressure acquires the necessary parameters.
- The remaining antifreeze is drained into the canister until the next time.
Note! Pressure testing is safe to conduct with water. Before filling the heating system with antifreeze, you need to be sure that the connections are tight. After elimination of leaks, the water is drained and the working coolant is finally pumped.

Summarizing
Only the manufacturer can guarantee the marvelous quality of the non-freeze, so try to shop at the appropriate stores. It is worth knowing that, for example, with the first drop of antifreeze falling into the depths of your heating system, the warranty on the water boiler is automatically canceled (see also the article Gas heating is cheap, effective, reliable).
Ask yourself if you are ready and ready to be constantly at risk, using dangerous ethylene glycol in the water heating system of your home? In comparison, the vigil for the amount of coolant in the system will seem trivial. It is logical to choose a safe version of the coolant and give yourself the opportunity to fully enjoy the benefits of civilization.
If you have never dealt with pouring antifreeze into the heating system, the video in the article will help you.