Calculation of heating in an apartment building and
This article is addressed to the reader, who will be living in an apartment in a state after the builders. As a rule, it implies running into the apartment and muffled branches from the risers of the heating system. We have to learn how to calculate the thermal power of heating devices, and at the same time get acquainted with the recommendations on their selection and installation.

Tasks
Let's start with the formulation of tasks.
We have the following:
- Calculate the amount of heat required to maintain a comfortable temperature in the apartment.
- Choose the type of heaters and their size depending on the need for heat.
- Decide on the size and material of pipes.
- Select stop valves.
In addition: if in your apartment the only input of heating for horizontal wiring, it would be strange not to use it and not to install a heat meter. He is able to provide very tangible savings on utilities in the heating season.
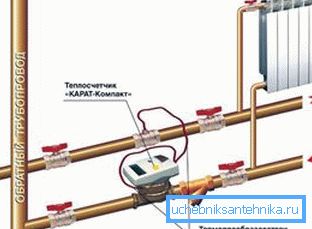
Thermal power calculation
It is possible in two ways.
Area calculation
A simpler scheme in which the thermal power of one kilowatt is taken per 10 m2 of floor space. In addition, regional coefficients are used:
| Region | Coefficient |
| Crimea, Krasnodar region | 0.7 - 0.9 |
| Moscow, Leningrad region | 1.2 - 1.3 |
| Siberia, the Far East | 1.5 - 1.6 |
| Chukotka, Yakutia | 2.0 |
So, for an apartment with an area of 74 m2 in the Yalta new building, the need for heat output will be 7.4 * 0.7 = 5.18 kW.
Alas, simplicity is not always accompanied by high accuracy of calculations.
The proposed scheme gives considerable errors for several reasons:
- The variation in the height of the ceilings will give a change in the volume of the room with its constant area. It is clear that to heat the increased volume will need more heat.
- Both windows and doors are much more heat permeable than walls.. It is logical to assume that each additional window will increase heat loss.

- The location of the apartment also can not be ignored.: at the corner and end apartments a larger number of walls will be common with the street.
Calculation by volume
That is why a more accurate value of thermal power can be obtained by a somewhat complicated method:
- 40 watts of heat is taken per cubic meter of heated volume.
- 100 watts is added to each window. At the front door - 200.
- For apartments located in the butt of the house and having additional, in addition to the facade, the walls with the street, a factor of 1.2 is used.
- Finally, the regional coefficient mentioned above also applies in this case.
As an example, let's calculate the heat demand for a two-room apartment for the following conditions:
- Its area is 58 square meters.
- Ceiling height - 3 meters.
- The total number of windows - 4. Entrance door - one.
- The apartment is located at the end of the house.
- The house itself is located in the town of Komsomolsk-on-Amur of the Khabarovsk Territory of the Russian Federation.

So:
- The volume of the room is 58 * 3 = 174 m3.
- The base value of thermal power is 40 * 174 = 6960 watts.
- Four windows and the door will add 600 watts (100 * 4 + 200) to it. 6960 + 600 = 7540.
- Additional total wall with the street will force to multiply this value by 1.2. 7540 * 1.2 = 9048.
- Since the winters in Komsomolsk are rather severe, we take the regional coefficient equal to 1.6. 9048 * 1.6 = 14476.8 watts.
The choice of heating devices
In the stores of heating equipment you can find the following main types of heaters:
| Type of | Minimum section price, rubles | Average heat flow per section | Operating pressure, kgf / cm2 | Operating temperature, C |
| Cast iron sectional radiator | 400 | 160 | 9-12 | 110 |
| Aluminum sectional radiator | 280 | 200 | 8-16 | 110 |
| Bimetallic (steel + aluminum) sectional radiator | 450 | 180 | 20-100 | 130 |
| Steel register | - | - | 16-25 | 150 |
| Steel plate radiator | - | - | 8-12 | 110 |

Specify: we show the average values in the framework of the statistics available to the author. The actual characteristics of the heater can be found in the accompanying documentation or on the manufacturer's website.
About these heaters useful to know a few things.
- A common disease of cast iron batteries - intersectional leaks after several years of operation. Paronit gaskets between sections gradually lose elasticity. It is necessary to cool the radiator - and the concomitant lowering of temperature changes the linear dimensions of the sections causes the appearance of droplets.
- Aluminum forms a galvanic couple with copper. Water, thanks to the salts dissolved in it, is an electrolyte. It is necessary to combine aluminum radiators with copper pipes in a common circuit - and the ion migration process occurring in it will cause rapid electrochemical corrosion of batteries.
Hint: in a central heating system, you never know what type of pipes are used when installing your liner by your neighbors.
- The main drawback of registers (which include tubular steel radiators) is a depressingly low heat flux per unit volume. It is associated with a fairly moderate thermal conductivity of steel: it does not make sense to supply it with developed finning simply because the ends of the fins will be noticeably cooler than the coolant.
- Lamellar radiators have a too short lifetime (mostly not more than 10 years). Most of the inexpensive heating devices of this type are made of non-corrosive steels; when airing or dumping the heating system for the summer, they corrode from the inside out.
What conditions will have to work heating devices? The standard parameters of the central heating station are as follows: pressure - 3-4 kgf / cm2; the temperature is limited by the existing SNiP and in any engineering system of a residential building can not exceed 95 C.
It is curious: in preschool institutions, the temperature of the coolant is altogether limited at 37 C.

It would seem that with such parameters you can use absolutely any batteries: the operating temperatures and pressures in all cases exceed those given by us. However, it is worth considering that in real conditions both the temperature and the pressure of the central heating system can be significantly higher.
Under what circumstances?
Let's give a couple of examples.
- In severe cold with low heating parameters in the apartments is set unacceptably low temperature. One of the practicing ways to solve this problem in critical situations is the work of an elevator assembly without a nozzle, with a muffled choke.
- The heating system does not receive the coolant mixture from the direct and reverse pipelines, but water directly from the feed line; at the same time, the temperature can reach 150 ° C, and the pressure - 7 kgf / cm2.
- When starting the heating system, it is recommended to open the house valve on the return pipe first. The latch must open extremely slowly; it is brought to the fully open position only after equalizing the pressures in the track and contour. Only after it opens the valve on the pitch.
- It is necessary for the locksmith to hurry and open any of the valves quickly - and a so-called hydraulic hammer will arise in a practically incompressible aqueous medium. At the front of the water filling the circuit, the pressure can no longer reach 3-4, but all 20-25 atmospheres.

That is why for the central heating system it is possible with a light heart to recommend only two types of heaters:
- Bimetallic radiators. They are a core of corrosion-resistant steel with an outer shell of aluminum. Steel provides mechanical strength and resistance to electrochemical corrosion, aluminum - developed finning with high thermal conductivity.
- If you can afford to allocate a significant amount of space for heating devices, you can use steel registers.

Calculation of heating devices
How to choose the optimal number of radiator sections for a room? How to calculate the heat capacity of the register?
The calculation of the room heat demand is the same as for the whole apartment. Nuance: the calculation should take into account the volume of premises without heating appliances (hallway, bathroom, toilet).
So, if the room, for heating which requires 2 kW, adjoins the hallway, for which the calculation gave the value of the heat flow of 400 watts, you should worry about buying a radiator with a capacity of 2400 watts.
Radiator
To recalculate this power in the number of sections of a bimetallic battery, it is enough to divide it by the heat flux specified in the documentation for one section. With a power section of 180 watts, the 2400-watt radiator should have 2400/180 = 14 (rounded) sections.
Here, however, there are a couple of subtleties.
- Manufacturers indicate heat flux for a temperature delta between the coolant and air at 70 degrees. If you need to maintain + 20C in the room, the radiator should be heated to 90. If the delta temperature is half as much - obviously, the heat output of the device will fall by half, and it will have to be compensated for by additional sections.
- With a long sectional radiator, its outer sections will be noticeably colder than the first ones from the liner. A simple instruction will help to solve this problem: connect the device according to the scheme from the bottom to the bottom.

By the way: with such a connection scheme, you will not have problems with silting of the radiator. The flow of coolant through the lower manifold will carry all deposits.
Register
How to calculate the register if your choice is on it?
The heat flux from one horizontal pipe is calculated by the formula Q = Pi * Dn * L * k * Dt, in which:
- Q - the desired value in watts.
- Pi is the number pi taken to be 3.1415.
- DN - the outer diameter of the pipe in meters.
- L is its length (also in meters).
- k - coefficient of thermal conductivity, taken for a steel pipe equal to 11.63 W / m2 * C.
- Dt - the same temperature delta between the coolant and the air in the room.
Since the heating is usually used multi-section horizontal registers, you need to consider that the upper sections will give heat to the upward flow from the lower pipe. Since its temperature is slightly higher than ambient air, the heat flux from these sections will be less. Therefore, for all sections except the first, an additional factor of 0.9 is used in the calculations.
As an example, let's do our own hands the calculation of the power of the register with four sections with a diameter of 159 mm and a length of 3.2 meters at its temperature of 70 degrees and the air temperature in the room is +18 C.

- The heat flux from the first section will be equal to 3.1415 * 0.159 * 3.2 * 11.63 * (70-18) = 967 watts (rounded to an integer value).
- The heat flux from each of the following sections is equal to 967 * 0.9 = 870 watts.
- The total heat output is 967+ (870 * 3) = 3577 watts.
Pipes
Material
Which pipes should you prefer when installing a central heating system?
From the above considerations, it is better to abandon all types of plastic and metal-plastic pipes for heating.
In the dry residue - only three options:
- Black steel pipes on welding.
- Galvanized steel on the threads.
- Corrugated stainless steel with pipe fittings.
Add a few comments to the list.
Black steel with welded joints is the most popular solution. In fact, it is much easier to weld the contour sections than to fiddle with threading and adjusting the size of the nozzles.
It seems that pipes should not rust: the heating system must be filled all year round, which guarantees that the internal surface of the pipes does not come into contact with atmospheric oxygen.

It was not there.
If in the majority of apartments there are cast-iron radiators, sooner or later the leaks between their sections become widespread. The leaks start only after the heating stops: during the heating season, the heated pig-iron sections reliably squeeze the paronite gaskets.
Guess what is easier to do for a locksmith - have a big and bright feeling every day with a battery overhaul in apartments or just reset the entire circuit for the summer?
But the galvanization of cast-iron threaded fittings has no problem of rusting.
There is an opinion that de zinc coating reacts with technical water and quickly collapses. The author dares to note that he repeatedly opened galvanized risers in stalinks after half a century of operation. Their condition was no different from new pipes.

Finally, stainless corrugated pipes attract two properties:
- Simple installation using a pair of adjustable wrenches.
- The possibility of easy disassembly of fittings and system configuration changes.
There are no specific problems or deficiencies in the stainless steel. Manufacturers declare the readiness of pipes to withstand a hydraulic shock up to 60 atmospheres and heating up to 150 C.
Diameter
Usually, a hydraulic calculation is performed to select the diameter of the pipeline, taking into account the pressure in the system and restrictions on the speed of the coolant. However, we are talking about an apartment where the maximum length of the contour is limited to a value of 30-40 meters. If so, we can recommend quite specific values.
| Contour plot | Do |
| Lead to radiator (up to 10 sections) | 15 |
| Lead to radiator (over 10 sections) | 20 |
| Horizontal wiring between radiators | 20 |
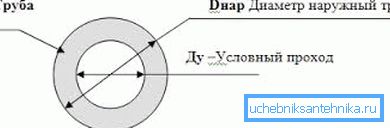
Attention: do not confuse the remote control (conditional passage) with the outer diameter. For steel pipe DN 15, the outer diameter is approximately equal to 20 mm.
Valves
What should it be?
- At the entrance to the apartment on both threads put ball valves, completely cut off from her risers.
- After the valve in the feed does not interfere with a sump (coarse filter). It will not allow sand or scale to clog thin channels in your batteries.
- Each radiator is equipped with a supply valve and a choke or thermal head on the return pipe. Throttling will help reduce the cost of heat, to bring them into line with your needs.
- With the lower connection, one of Mayevsky's valves is put into one of the upper radiator plugs, which allows to release air.

Conclusion
We hope that our recommendations will be useful to the reader in the design and construction of heating in their own apartment. As usual, the video attached to the article contains additional thematic materials. Successes!