Calculation of the diameter of heating pipes: formulas and
How is the calculation of the diameters of the heating pipes at a known boiler power? How to calculate the minimum diameter for a separate section of the contour? In this article we have to get acquainted with the formulas used in the calculations, and accompany the acquaintance with examples of calculations.

Why do you need it
And in fact - why is it necessary to calculate the diameter of the heating pipes? Why simply don’t take the obviously oversized pipes? After all, by this we will protect ourselves from excessively slow circulation in the circuit.
Alas, this approach has several serious drawbacks.
- Consumption of materials and, accordingly, the price per meter increases in proportion to the square of the diameter. The costs will not be a penny.
Note: to maintain the same working pressure with increasing pipe diameter it is necessary to increase the wall thickness, which further increases the consumption of materials.
- Equally important, the increased diameter of the pipeline means an increase in the volume of coolant. and, accordingly, increased thermal inertia of the system. It will warm up longer and cool longer, which is not always desirable.
- Finally, with the open laying of thick heating pipes, they will not really decorate the room, and when hidden, they will increase the depth of the strobe in the walls or screed thickness on the floor.

Formulas
Since we, dear reader, do not encroach upon obtaining a diploma of a heating engineer, we will not climb into the jungle.
A simplified calculation of the diameter of the heating pipeline is performed according to the formula D = 354 * (0.86 * Q / Dt) / v, in which:
- D is the required diameter value in centimeters.
- Q - thermal load on the corresponding section of the circuit.
- Dt is the temperature delta between the supply and return lines. In a typical autonomous system, it is about 20 degrees.
- v is the flow rate of the coolant in the pipes.
It looks like we need some data to continue.
To calculate the diameter of pipes for heating, we need:
- Find out at what maximum speed the coolant can move.
- Learn how to calculate the thermal power of the entire system and its individual sections.
Coolant speed
It must meet a pair of boundary conditions.
On the one hand, the coolant should turn around in the circuit about three times per hour. Otherwise, the cherished temperature delta will noticeably increase, making the heating of radiators uneven. In addition, in severe cold, we get a very real possibility of defrosting the coldest parts of the circuit.

On the other hand, excessively high speed will generate hydraulic noise. To fall asleep to the rumble of water in the pipes is a pleasure, let's say, for an amateur.
Valid is the range of flow rates from 0.6 to 1.5 meters per second; at the same time, the maximum permissible value of 1.5 m / s is usually used in the calculations.
Thermal power
Here is a diagram of its calculation for the normalized thermal resistance of the walls (for the center of the country - 3.2 m2 * C / W).
- For a private house, 60 watts per cubic meter of room are taken for base power.
- They add 100 watts to each window and 200 watts to each door.
- The result is multiplied by the regional coefficient depending on the climate zone:
| Average January temperature | Coefficient |
| -40 | 2.0 |
| -25 | 1.6 |
| -15 | 1.4 |
| -five | one |
| 0 | 0.8 |
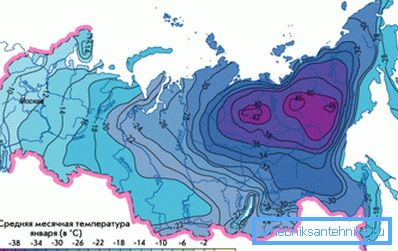
Thus, a 300 m2 room with three windows and a door in Krasnodar (the average January temperature is + 0.6 ° C) will require (300 * 60 + (3 * 100 + 200)) * 0.8 = 14,800 watts of heat.
For buildings whose thermal resistance of walls differs significantly from the normalized one, another simplified scheme is used: Q = V * Dt * K / 860, where:
- Q is the heat demand in kilowatts.
- V is the volume of heated space in cubic meters.
- Dt is the temperature difference between the room and the street at the peak of the cold.
It is useful: it is better to take the temperature in the room with the appropriate sanitary standards, the street temperature - the average minimum over the past few years.
- K - coefficient of insulation of the building. Where to get its values? The instruction will be found in the next table.
| Insulation coefficient | Description of enclosing structures |
| 0.6 - 0.9 | Foam or mineral wool coat, insulated roof, energy-saving triple glazing |
| 1, -1.9 | Brick laying in one and a half brick, single-chamber double-glazed windows |
| 2 - 2.9 | Brickwork, windows in wooden frames without insulation |
| 3-4 | Laying in half-brick, glazing in one thread |
Where to take the load for a separate section of the circuit? It is calculated by the volume of the room, which is heated by this section, one of the above methods.
Calculation example
So, in theory, we know how to calculate the diameter of the heating pipe.
Let's confirm the theoretical knowledge with practice and do the calculation for the following conditions:
- We need to calculate the diameter of the filling in a private house of 100 square meters.
- The height of the ceiling in the house is 2.8 meters.
- The walls are a tub of 40-cm-thick D600 brand concrete blocks with an outer foam coat 150 mm thick.

- The house is located in Komsomolsk-on-Amur of the Khabarovsk Territory (the average minimum temperature in January is -30.8 C). The internal temperature is taken equal to +20 C.
First, we calculate the need for thermal power.
Insulation clearly provides thermal resistance better than normalized, which will force us to turn to the second of the above calculation schemes.
- The internal volume of the house is 100 * 2.8 = 280 m3.
- Delta temperature between the street and the house in the worst case for us will be equal to 50 degrees.
- The coefficient of heat insulation is assumed to be 0.7.
- The estimated capacity of the domestic heating boiler must be at least 280 * 50 * 0.7 / 860 = 11.4 kW.
It remains to perform the actual calculation of the diameter of the pipe for heating. It will be equal to 354 * (0.86 * 11.4 / 50) / 1.5 = 2.4 cm, which corresponds to a steel VGP pipe DN 25 or a polypropylene pipe with an outer diameter of 32 mm.

Conclusion
Let us remind ourselves that we have given extremely simplified schemes of calculations. As always, the reader can find additional subject information in the video attached to the article. Successes!