Calculation of the expansion tank for heating: simple and
This article is about how to calculate the expansion tank for heating in your private home. We present the necessary formulas for the calculations and some additional data that the reader may need. So go.

Tank device
Before we begin the calculations, it is worth understanding one subtlety. The total volume of the expansion tank and the expansion of the coolant are two values that are interrelated, but not at all equal to each other.
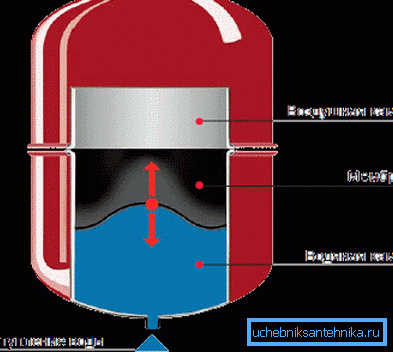
This directly follows from the scheme of operation of the device that we investigate:
- Its capacity is divided into two parts by an elastic rubber membrane.. One part of the tank is designed to be filled with coolant, while the second is filled with air with some overpressure.
- The part of the container intended for the heat carrier is supplied with a branch pipe for connection to the circuit. The air chamber, in turn, is completed with a nipple, which allows to relieve pressure or increase it with a manual or electric pump.
Important: when the heating is started, an overpressure equal to hydrostatic pressure is created in the expansion tank chamber. Simply put, when the height of the top point of the circuit above the tank installation level is five meters, it is adjusted to a pressure of 0.5 kgf / cm2 (a pressure of 1 kgf / cm2 corresponds to a head of 10 meters).
Thus, the volume indicated by the manufacturer should contain both the water displaced by thermal expansion and the air, which, when the excess pressure drops, will force it back into the circuit.
Payment schemes
Simple
The simplest formula is as follows: the expansion tank is taken equal to 10% of the total amount of coolant. If filling the circuit requires 600 liters of water, you need a 60-liter product; if you fill in the heating 800 liters - 80 and so on.
Like all simple schemes, this one has a big margin of error. The cost of a big mistake is a small overpayment for excess dimensions, but if the result is too low for what is needed, we will receive a constant response of the safety valve.
How to do a more accurate calculation with your own hands?
Accurate
More precisely, the value we need is calculated by the formula V = (Vt x E) / D, in which:
- V is the desired value.
- Vt - the total amount of heating - radiators, pipes, boiler, etc.
- E is the coefficient of expansion of the coolant.
- D is the coefficient of efficiency of the membrane expansion tank.
To continue, we clearly lack several reference values.
Volume of coolant in the system
How can you find out the full capacity of your heating system?
- Fill it with water and completely drain into a measuring container.
- Noting changes in the water meter readings when filling the system from the cold-water circuit.
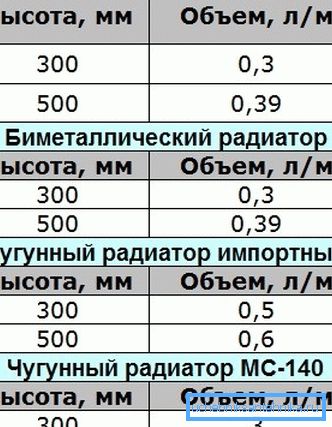
- Putting the capacities of all heating devices (data can be found in the documentation for them) and all pipelines (for each diameter they are calculated using the formula V = Pi * R ^ 2 * H, where Pi = 3.1415, R is half the internal diameter of the pipe, and H is its length).
- Finally, the capacity of a balanced heating system can be estimated at the rate of 15 liters per kilowatt of heat output of the boiler. Thus, a 24 kW boiler is usually connected to a circuit filled with 24x15 = 360 liters of water.
Expansion ratio
In most cases, ordinary water is used as a coolant. Here is the coefficient of its expansion for different temperatures during heating from a starting value of + 10 ° C.
| Heat, degrees Celsius | Expansion,% |
| thirty | 0.75 |
| 40 | 1.18 |
| 50 | 1.68 |
| 60 | 2.25 |
| 70 | 2.89 |
| 80 | 3.58 |
| 90 | 4.34 |
| 100 | 5.16 |
Note: the addition of antifreeze - ethylene or propylene glycol increases the thermal expansion, but not so much. So, with a delta temperature of 100 degrees and a glycol content in the coolant equal to 30%, the expansion will increase by only 0.45%.

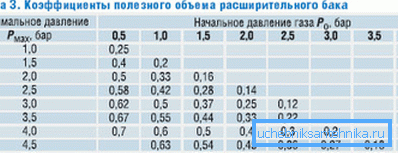
Tank efficiency ratio
Instructions for calculating the value of the effectiveness of the tank is also quite simple.
Here we use the formula of the form D = (PV - PS) / (PV + 1). In it:
- D is the desired coefficient;
- Pv is the maximum working pressure (that for which the safety valve has tripped).
- Ps - tank charging pressure. It, as we found out earlier, corresponds to the hydrostatic pressure in the heating circuit.
Calculation example
Let's perform the calculation on the more accurate of the schemes for the following conditions:
- We have to heat a two-story house, the top of the heating system in which rises above the expansion tank at 5 meters.
- The total area of the house with standard insulation is 240 meters. Let us estimate the need for boiler heat power using the simplest formula: 240/10 = 24 KW.
- The maximum heating of water used as a coolant, we take equal to 80 degrees.
So:
- The standard maximum working pressure for autonomous systems is 2.5 kgf / cm2.
- 5 meters of contour height give us a hydrostatic pressure of 0.5 kgf / cm2.
- The tank's efficiency ratio will be (2.5 - 0.5) / (2.5 + 1) = 0.57.
- The coefficient of expansion when heated at 80 degrees can be taken equal to 0.036 (according to the table it is equal to 3.58%).
- The total volume of the circuit, calculated by the power of the boiler, is assumed to be 24 x 15 = 360 liters.
- So, the minimum volume of the tank is equal to (360 x 0.036) / 0.57 = 22.7 liters (rounded to the nearest standard value - 24-25 liters).
It is easy to see that a more complicated calculation scheme in this case helped us save relatively simpler 11 - 12 liters of capacity.
Conclusion
Whether to spend time on an exact calculation or use a simple scheme - the reader will have to decide on his own. As always, the attached video will offer his attention to additional thematic information.
Successes!