Calculation of the heating system: how to choose the right
Heating the house in the climate in Russia is not a luxury, but a vital necessity. If in urban conditions you don’t need to think about it - there are heat stations, heat and power plants, district boiler houses that will fully provide housing for heating, then in your own house you need to think about everything yourself.
In this case, a dwelling should be equipped with an autonomous heating system. Before installing the network, it must be designed and calculated. This is what we will lose in this article.
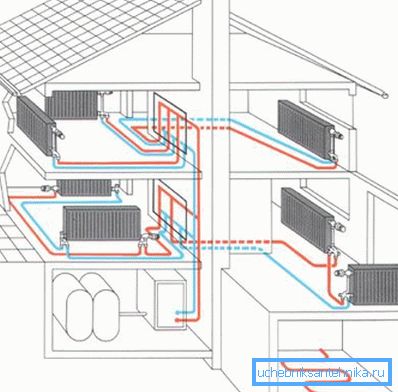
Calculation of heating devices
As a heat carrier, usually ordinary water is selected in its own houses. And the heating system itself can be closed or open.
Kind of boiler

The type of heat generator you need to select, given the type of energy that is most accessible and cheap in your area.
Below the category of devices by type of fuel used.
- Electric boilers. Heating a house based on them is not very popular with us, because electricity is expensive, and it can be supplied with interruptions or voltage drops. And for reliable operation of such a device requires a stable power supply system.
- Solid fuel appliances. The simplest units. The Russian market represents many of their models, both with manual and automatic loading of fuel. The price of the latest analogues, of course, is higher.
- Gas aggregates. These devices have high efficiency. Their current models have fully automated work cycles. They are compact with a high level of performance. Such a device is optimal if your home is connected to a central gas supply network.
Note! Making the calculation of feeding the heating system, note that the cost of gas increases all the time. Therefore, it is desirable to equip the heating network on it with systems of energy saving and automation.
- Liquid Fuel Devices. These boilers work on diesel, kerosene, fuel oil, oil-working. They are highly productive, practical, such fuel is available and cheap.
Similar generators of heat can be put at dachas, in cottages and country houses. However, liquid fuel is fire and explosive. Therefore, for tanks with it you need to allocate separate rooms and carefully adhere to safety precautions.
Some points to consider
- Fuel oil boilers for heating systems have one important advantage. Their burner can be exchanged for a gas analogue, and the unit will be able to work on the appropriate energy carrier.
- From solid fuel appliances it is best to put your own pyrolysis counterparts. They are the most economical, their efficiency, thanks to an improved design, reaches 85%. Such units have two fireboxes. In the first of them, the fuel slowly smolders and emits thermal energy, as well as combustible (pyrhoslic) gas. The latter, together with air, then enters the second fire chamber, where it is burned, generating additional heat.

- Conventional solid fuel boilers have a significant disadvantage - they can not be equipped with efficient automation systems. Proceeding from this, it is necessary to lay the fuel in them manually, every 4/6 hours.
There are models of units to which you can connect the bunker. Fuel from it enters the boiler automatically.
However, it lasts no more than 1.5 days. Then you need to load the capacity manually.
Calculation of characteristics
After selecting the type of heat generator, carrying out the design and calculation of heating systems, it is necessary to determine its capacity and general characteristics of the system.
To carry out a preliminary calculation, it is enough to multiply the area of the room by the coefficient of climatic power of the heat generator. The result of the calculation is further divided by 10.
This is the simplest formula suitable for living conditions. With its help, it is possible to carry out an approximate calculation and design of heating systems with a small number of known factors.
A little more about these calculations.
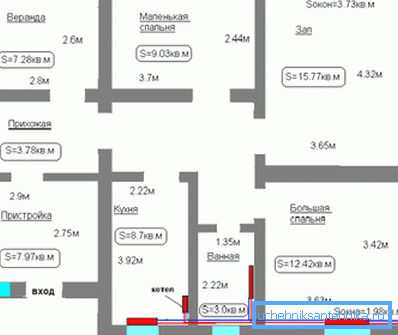
- With regard to the heated area, it is often taken its sum for all areas of the house. This is a mistake, because As a rule, only those rooms of the building in which at least one wall is external are heated. This heat engineering calculation is correct, in which only rooms with external walls are taken into account. At the same time, a small margin of productivity for the boiler is added to the results of the calculations. It is necessary for a situation when the winter will be too harsh for your area.
- The coefficient of climatic power is very important for practical calculations of heating. Its value depends on the area in which the house is located.
- So, for the Center of the Russian Federation the figure is 1.3 / 1.6 kW;
- for the South - 0.8 / 0.95;
- for the North of Russia - 1.6 / 2.2.
An example of the calculation of the heating system (boiler power) for a building of 100 m2 for the Central regions of the Russian Federation:
Vк = 100 • 1.2: 10 = 12 kW
The number of battery sections

The instruction notes that a competent heating project is impossible without determining the necessary number of radiator sections. This parameter can be calculated by the simplest formula: the area of the premises is multiplied by 100, the resulting figure is divided by the power of one section of the radiator.
Let us examine the positions of the formula in more detail.
- Heated area. The power of heating devices is calculated for each specific room. Therefore, the formula should also include the area of one room. However, there is an exception. If you want to be warm in the adjacent room, with the one in which there will be radiators, then the area of both rooms is summed up.
- The number 100 is taken from SNiPa. It means that for 1 m2 of living rooms 100 W of thermal power of batteries is necessary.
- The performance of one radiator section may be different and depends on the material of its manufacture and design features. When you cannot find out this parameter precisely, you can operate with a value of 200 watts. It is equal to the average power of each section of modern radiators.
We give a specific example of calculation. Let the floor space be 20 square meters. The power of one section of the selected radiators is 170 W for it. Determine the number of sections needed:
N = 20 • 100: 170 = 11.7 = 12.
Note! If the room is angular or end, then having made the calculations, their total should be multiplied by a coefficient of 1.2. So you get the number of sections of the radiator, taking into account the increased heat loss of the room.
Specific professional calculations in formulas
Consider how the calculation and installation of heating systems by professionals.
What is hydraulic calculation?
The tasks of the overall hydraulic calculation of the system include the following.
- Determination of the cross section of the pipeline and in connection with this - the calculation of the volume of water in the heating system.
- Finding the magnitude of the pressure (working pressure) in different parts of the network.
- Calculation of pressure drops / head.
- Accurate binding of all points of the network in dynamic and static modes. This is necessary to ensure the allowable pressure and the desired pressure in the system.
Basic computational dependencies

The heat-shielding properties of enclosing structures are characterized by their resistance to heat transfer (Ro).
- This is expressed in the formula: Ro = Rвн + Rк + Rв. The symbol Rвн is the resistance to heat transfer of the inner part of the fence, which, in turn, is described as (m • 2 • ° C): Bm.
- Rвн = 1:? C. Here? In is the coefficient of thermal return of the inside of the enclosing structures, it is equal to 8.7 • (m • 2 • ° C): Bm.
- RK is the thermal resistance of the enclosing structure with sequentially placed layers. Rc = R1 + R2 + ... + Rn + Rt of external air.
- R1 =? / ?. Here? means layer thickness in millimeters, eh? - is the coefficient of thermal conductivity, which is described as Bm: (m • 2 • ° C).
- Rb is the resistance to heat transfer from the outside of the enclosure.
- Rв = 1:? Н. ? n is the coefficient of thermal return of the outer part of the fence, it is expressed as 23 • Bm: (m • 2 • ° C).
- The heat transfer coefficient k is calculated according to the formula: k = 1: Ro.
So, before calculating the heating system, the thickness of the main insulation layer is calculated.
We give a specific example.
- The outer wall of concrete:? = 2400 kg / m? /; ? 1 = 1.92 W / m • ° C; ? 1 = 100 millimeters.
- Warming from polyurethane foam:? = 2400 kg / m ?; = 1.92 W / m • ° C; ? = Ro-1:? C-1:? N-? 1:? 1.
System power
Thermal power of the heating system, in watts, is given by the formula: Qc = Qo + Qi-Qb.
Here:
- Qo is the heat loss in watts through the enclosing structures;
- Qi is the heat loss to warm the infiltrating air that goes through the doors, windows, slots (W);
- Qb - heat input from household appliances, also in watts.
Hydraulic calculation of the pipeline
The calculation of the volume of the heating system is impossible without hydraulic calculations of the diameter of the pipeline. They are carried out at the already determined thermal loads and the calculated pressure (circulation) in the system.
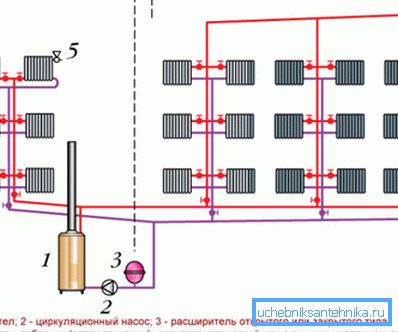
For example, in a two-tube type of network, the main circulation ring is mounted in case of a dead-end type of pipe distribution. In other words - through the lower radiator of the most loaded and most remote from the heat center of the riser.
In this situation, you can use the calculator for calculating the heating system located on the Internet, or carry out the calculations yourself.
For this it is necessary to determine the auxiliary parameter - the average value of the specific pressure loss, due to friction (Rav, in Pa / m), per meter of pipes. The formula looks like this:
Rcp =? • pp: L; in pa / m
In it, the symbols mean:
- ? - this is a coefficient that takes into account pressure losses, due to local resistances, of the total calculated pressure (circulation pressure), for networks with forced circulation, this parameter is 0.65;
- pp is the available pressure in the designed heating system, in pascals;
- L is the total length of the circulating ring, in meters.
Room heat loss
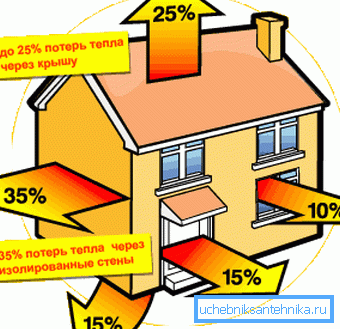
The main heat loss Qо (in watts), through the building envelope, is found according to the formula Qо = f • k • (tv-tвн) • n.
Here:
- k is the thermal transfer coefficient of the enclosure;
- f is the calculated area of the enclosing structure, in square meters;
- tv is the air temperature in the room, in degrees;
- tвн - temperature of external air, in degrees;
- n is a coefficient that depends on the location of the outer surface relative to the outside air.
The choice of radiators, based on their characteristics
Before you calculate the amount of water in the heating system, you should select the type of radiators that you will use. Below is a table of the characteristics of all the varieties currently being produced.
| Radiator | Pressure: working, pressure testing, maximum | Fencing, Ph | Corr. action O2 | Corr. Action free currents | Corr. Action electric steamer | Power sections, watts | Warranty |
| tubular steel | 6/129/18 27 | 6.5 / 9 | there is | there is | weak | 85 | 1 year |
| cast iron | 6/912/15 20/25 | 6.5 / 9 | not | not | not | 110 | 10 years |
| aluminum | 10/2015/30 30/50 | 7/8 | not | there is | there is | 175/199 | 3/10 years |
| bimetal | 3557 75 | 6.5 / 9 | there is | there is | weak | 199 | 3/10 years |
Conclusion
Long-term operation of the heating system is possible only with its proper calculation and subsequent proper installation. Therefore, the design of the network should be taken very seriously. The video in the article will complement the information.