Calculation of the heating system of a private house:
What parameters need to be calculated when designing an autonomous heating system? How is the calculation of the heating system of a private house in each case? In the article we will provide the reader with all the necessary formulas, reference data and accompany the calculations with examples.

What we think
What are the stages of the calculation of the heating system for a private house?
What exactly do we have to count?
- The total need for heat and the corresponding power of the heating boiler.
- Thermal energy demand of a separate room and, accordingly, the power of the heater in it.
Note: we have to touch on the methods for determining the heat output for various heating devices.
- Expansion tank capacity.
- Parameters of the circulation pump.
In this order, and move on.
Thermal power
It is possible to roughly estimate the need for home heat in two ways:
- By area.
- By volume.
Area calculation
This technique is extremely simple and is based on SNiP half a century ago: one kilowatt of thermal power is taken per 10 square meters. Thus, a house with a total area of 100 m2 can be heated with a 10-kilowatt boiler.
The scheme is good because it does not require to climb into the wilds and calculate the thermal resistance of walling. But, like any simplified calculation scheme, it gives a very approximate result.
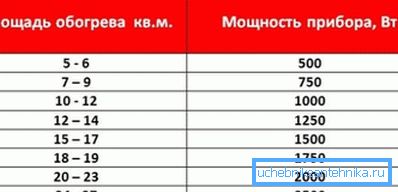
There are several reasons:
- The boiler heats the entire volume of air in the room, which depends not only on the area of the house, but also on the height of the ceilings. And this parameter in private housing can vary in the widest limits.
- Windows and doors lose much more heat per unit area than walls. If only because it is much more transparent for infrared radiation.
- The climate zone also greatly affects the heat loss through the building envelope. An increase in the temperature delta between the room and the street will double in two times the increase in heating costs.
Volume calculation with regional coefficients
It is for these reasons that it is better to use a slightly more complicated calculation scheme, which gives a much more accurate result.
- 60 watts of heat per cubic meter of the volume of the heated room are taken as the base value.
- Each window in the outer wall adds 100 watts to the calculated heat output, and 200 to each door.
- The result is multiplied by the regional coefficient:
| Climate zone | Coefficient |
| Krasnodar region, Crimea | 0.7 - 0.9 |
| Moscow, Leningrad region | 1.2 - 1.3 |
| Irkutsk, Khabarovsk Territory | 1.5 - 1.6 |
| Yakutia, Chukotka | 2.0 |

Let's take as an example the same house with an area of 100 square meters.
However, this time we will specify a number of additional conditions:
- The height of its ceilings is 3.5 meters.
- The house has 10 windows and 2 doors in the external walls.
- It is located in the city of Verkhoyansk (the average January temperature is 45.4 C, the absolute minimum is 67.6 C).
So, let's calculate the heating of a private house for these conditions.
- The internal volume of the heated room is 100 * 3.5 = 350 m3.
- The basic value of thermal power will be equal to 350 * 60 = 21000 watts.
- Windows and doors exacerbate the situation: 21000+ (100 * 10) + (200 * 2) = 22400 watts.
- Finally, the refreshing climate of Verkhoyansk will force us to increase the already large heat capacity of heating by another two times: 22400 * 2 = 44800 watts.

It is easy to see that the difference with the result obtained by the first method is more than four times.
Heating appliances
How to calculate the heating in a private house for individual rooms and choose the heating devices appropriate for this power?
The very method of calculating the need for heat for a single room is completely identical to the one above.
For example, for a room of 12 m2 with two windows in the house described by us, the calculation will look like this:
- The volume of the room is 12 * 3.5 = 42 m3.
- Base thermal power will be equal 42 * 60 = 2520 watts.
- Two windows will add 200 more to it. 2520 + 200 = 2720.
- A regional coefficient will double the heat demand. 2720 * 2 = 5440 watts.
How to recalculate the resulting value in the number of sections of the radiator? How to choose the number and type of heating convectors?
- Manufacturers always indicate heat output for convectors, plate radiators, etc. in the accompanying documentation.
- For sectional radiators, the necessary information can usually be found on the websites of dealers and manufacturers. In the same place it is quite often possible to find the calculator for recalculation of kilowatts in section.
- Finally, if you use sectional radiators of unknown origin, with their standard size of 500 millimeters along the nipple axes, you can focus on the following average values:
| Section type | Thermal power per section, watts |
| Cast iron with internal fins | 160 |
| Cast iron without fins | 140 |
| Bimetallic | 180 |
| Aluminum | 200 |
In an autonomous heating system with its moderate and predictable parameters of the coolant most often used aluminum radiators. Their reasonable price is very pleasantly combined with a decent appearance and high heat dissipation.
In our case, aluminum sections with a capacity of 200 watts will require 5440/200 = 27 (rounded).

As always, there are a couple of subtleties.
- With a side-mounted multi-section radiator, the temperature of the latter sections is much lower than the first; accordingly, the heat flux from the heater drops. A simple instruction will help to solve the problem: connect radiators according to the scheme from the bottom to the bottom.
- Manufacturers indicate heat output for a temperature delta between the coolant and a room of 70 degrees (for example, 90 / 20C). When it decreases, the heat flux will fall.
A special case
Often, home-made steel registers are used as heating devices in private homes.
Please note: they attract not only low cost, but also exceptional tensile strength, which is very useful when connecting the house to the heating main. In an autonomous heating system, their attractiveness is negated by the unassuming appearance and low heat emission per unit volume of the heater.

However: how to estimate the thermal capacity of a register of a known size?
For a single horizontal round pipe, it is calculated by the formula of the form Q = Pi * Dn * L * k * Dt, in which:
- Q - heat flow;
- Pi is the number pi taken to be 3.1415;
- DN - the outer diameter of the pipe in meters;
- L is its length (also in meters);
- k is the coefficient of thermal conductivity, which is taken to be 11.63 W / m2 * C;
- Dt - delta temperature, the difference between the coolant and the air in the room.
In the multisection horizontal register, the heat transfer of all sections, except the first, is multiplied by 0.9, since they give off heat to the upward flow of air heated by the first section.

Let's calculate the heat transfer of a four-section register with a section diameter of 159 mm and a length of 2.5 meters at a coolant temperature of 80 C and an air temperature in the room of 18 C.
- The heat output of the first section is 3.1415 * 0.159 * 2.5 * 11.63 * (80-18) = 900 watts.
- The heat output of each of the other three sections is equal to 900 * 0.9 = 810 watts.
- The total heat output of the heater is 900+ (810 * 3) = 3330 watts.
Expansion tank
And in this case there are two methods of calculation - simple and accurate.
Simple circuit
Simple calculation is extremely simple: the volume of the expansion tank is taken equal to 1/10 of the volume of coolant in the circuit.
Where to get the value of the volume of coolant?
Here are a couple of simple solutions:
- Fill the contour with water, bleed the air, and then drain all the water through the sealer into any measuring dish.
- In addition, roughly the volume of a balanced system can be calculated at the rate of 15 liters of coolant per kilowatt of boiler power. So, in the case of a 45 kW boiler, the system will have approximately 45 * 15 = 675 liters of heat carrier.
Therefore, in this case the expansion tank for the heating system of 80 liters (rounded up to the standard value) will be a reasonable minimum.
Exact scheme
More precisely, you can do your own hands to calculate the volume of the expansion tank using the formula V = (Vt x E) / D, in which:
- V - the desired value in liters.
- Vt is the total volume of the coolant.
- E is the coefficient of expansion of the coolant.
- D is the coefficient of efficiency of the expansion tank.
Obviously, the last two parameters need comments.
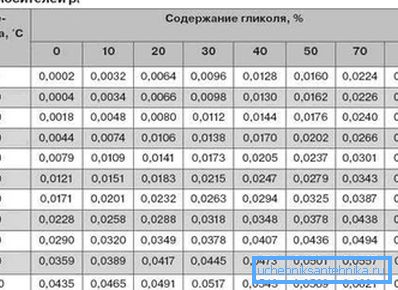
The coefficient of expansion of water and poor water-glycol mixtures can be taken from the following table (when heated from the initial temperature of + 10 ° C):
| Heating, C | Expansion,% |
| thirty | 0.75 |
| 40 | 1.18 |
| 50 | 1.68 |
| 60 | 2.25 |
| 70 | 2.89 |
| 80 | 3.58 |
| 90 | 4.34 |
| 100 | 5.16 |
The tank efficiency ratio can be calculated using the formula D = (Pv - Ps) / (Pv + 1), in which:
- Pv is the maximum pressure in the circuit (the opening pressure of the safety valve).
Hint: it is usually taken as 2.5 kgf / cm2.
- Ps- static pressure of the circuit (it is also the pressure of charging the tank). It is calculated as 1/10 of the differential in meters between the level of the tank and the upper point of the circuit (an overpressure of 1 kgf / cm2 raises the water column by 10 meters). A pressure equal to Ps is created in the air chamber of the tank before filling the system.
As an example, let's calculate the tank requirements for the following conditions:
- The height difference between the tank and the upper point of the contour is 5 meters.
- The power of the heating boiler in the house is 36 kW.
- The maximum water heating is 80 degrees (from 10 to 90C).
So:
- The tank's efficiency ratio will be (2.5-0.5) / (2.5 + 1) = 0.57.
- The volume of heat carrier at the rate of 15 liters per kilowatt is equal to 15 * 36 = 540 liters.
- The coefficient of expansion of water when heated at 80 degrees is 3.58%, or 0.0358.
- Thus, the minimum volume of the tank is (540 * 0.0358) / 0.57 = 34 liters.
Circulation pump
How to choose the optimal parameters of the circulating pump for the heating system?
Two parameters are important for us: the pressure created by the pump and its performance.

With pressure, everything is not simple, but very simple: the contour of any reasonable length for a private house will require a pressure of no more than 2 meters minimum for budget devices.
Help: a drop of 2 meters makes the heating system of a 40-apartment building circulate.
The simplest way to choose performance is to multiply the volume of coolant in the system by 3: the circuit should turn around three times in an hour. Thus, in a system with a volume of 540 liters, a pump with a capacity of 1.5 m3 / hour (rounded) is sufficient.
A more accurate calculation is performed using the formula G = Q / (1.163 * Dt), in which:
- G - performance in cubic meters per hour.
- Q is the power of the boiler or circuit section, where it is necessary to ensure circulation, in kilowatts.
- 1.163 is a coefficient related to the average heat capacity of water.
- Dt is the delta of temperatures between the flow and return of the circuit.
Hint: for the autonomous system, the standard parameters are 70/50 C.
With the notorious heat output of the boiler of 36 kW and a delta temperature of 20 ° C, the pump capacity should be 36 / (1.163 * 20) = 1.55 m3 / h.

Conclusion
We hope that we have made available to the reader all the necessary materials. Additional information on how to calculate heating in a private house can be found in the attached video. Successes!