Classification of heating systems: from the usual to the
The topic of this article is the classification of heating systems for various buildings. We investigate the sources of heat energy used in them, methods of heat transfer, configurations of coolants movement and wiring of heating devices.
So go.

Heat source
In this role can be:
- Gas. Gas heating boilers provide the minimum cost of thermal energy. Where there are no gas mains, gas-holders or cylinders may be used instead.
However: in this case, the price of a kilowatt-hour of heat will increase markedly.
- Firewood and coal. Solid fuel boilers for these energy sources are usually unified. Their main drawback is the limited autonomy of work: the laying of the fuel and the cleaning of the ash pan are required several times a day.
However, gas generators and upper burning boilers can somewhat increase the gap between the pads.
- Pellets. Pellet boilers with bins and dispensers can achieve autonomy in a few days.

- Solarium. Here, autonomy is already calculated in weeks; The disadvantages include high noise level of the equipment and the need for bulky diesel fuel capacity.
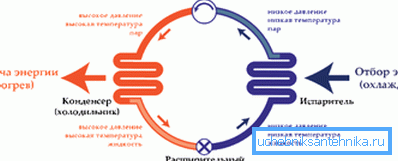
- Electricity. Along with direct heating devices, heat pumps use it, which use electricity to transfer heat from a relatively cold environment (air, water or soil) to a warmer room.
Here is a rough estimate of costs for different sources.
| Heat source | Price kilowatt-hour |
| Gas boiler (trunk) | 0.7 p. |
| Solid fuel boiler (firewood) | 1.1 p. |
| Heat pump | 1.2 p. |
| Solid fuel boiler (coal) | 1,3 r. |
| Gas boiler (gas tank) | 1.8 r. |
| Gas boiler (cylinders) | 2.8 p. |
| Diesel boiler | 3.2 p. |
| Electricity (direct heating) | 3.6 p. |
Central source and distributed heating
The most common scheme with one centralized heat source (boiler or stove), peripheral heating devices and pipelines for transporting heat. However, along with them, distributed heating systems are also used.
Examples?
- Electric underfloor heating with independent thermostats.
- Electric convectors placed in each room.
- Gas convector with gas distribution around the house.

- Independent power infrared emitters.
- Heating is air conditioned with private split system in each room.
Heat transfer method
The transfer of heat energy can be done in several ways.
Heat carrier
In this capacity, water or its mixtures with ethylene and propylene glycol are used, freezing at lower temperatures. The high heat capacity of the heat transfer fluids makes it possible to dispense with relatively small cross-section mains.
Air
Air heating means that the heat source directly heats the air entering the room. Air heating systems are often combined with ventilation. The main disadvantage of the decision that influences its popularity is the need to install air ducts of large cross-section: without prejudice to the finish, this can be done only at the construction stage.

Steam
Heating systems with superheated steam with a temperature of 200-400 degrees in our time are used exclusively at industrial facilities. They are convenient because, due to the high temperature of the heaters, they ensure their minimum dimensions with high values of heat output. The lack of steam is a serious danger to the inhabitants of heated premises in case of accidents.
Infrared radiation
The so-called infrared heaters transmit a substantial part of the heat not to the air around them, but directly to the surrounding objects and people through infrared radiation, which lies outside the visible part of the spectrum.
The use of IR emitters is economically justified, first of all, because it reduces the comfort minimum of the room temperature. Due to the direct heating of the skin in open areas of the body, the zone of subjective comfort begins already from + 15-16С.

Convection and underfloor heating
The usual for us since childhood, the scheme of heating a room with point sources of heat with a relatively high temperature (radiators, convectors, registers, etc.) is called convection. Each heater generates a convection flow; these streams stir the air in the room.
The main problem of convection heating is that the temperatures in a heated room are extremely unevenly distributed.
Not only that: they are also distributed inefficiently. Under the ceiling, the temperature is 5-8 degrees higher than at the level of human growth. Do you spend much time on the ceiling?
One of the side effects of overheating of air near the ceiling is a sharp increase in heat leakage through the ceiling. Heat losses are directly proportional to the temperature delta between the sides of the building envelope.
An alternative to convection heating is a warm floor. The floor surface is heated to a temperature of 25-35 degrees with a cable, film heater or a pipe with water.
As a result:
- The temperature is maximum precisely where there is a need - at the level of the floor.
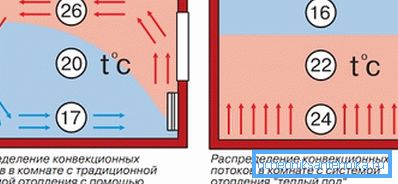
- A thermal curtain preventing freezing of walls forms around the entire perimeter of the room.
- By reducing the average temperature in the room provides significant energy savings.
Water heating
In the case of the use of a liquid coolant, the classification of the heating system is possible by several other parameters.
Central and autonomous
In DH systems, the heat source is CHP or boiler room. Heat carrier - technical water - is transported along heating lines; the circulation in separate circuits is ensured by the difference between the feed and reverse threads.
The function of the junction between the highway and the heating system of the building is performed by the elevator node.

In him:
- Differential between threads is leveled. In the track it reaches 3-6 kgf / cm2; at the same time, for a stable circulation of a circuit of a reasonable size, a drop of 0.2 kgf / cm2 is sufficient.
- The involvement of part of the coolant volume from the return circuit to the re-circulation is ensured. Thus, the temperature variation between the closest to the elevator node and the farthest from it heating devices is reduced.
- The mode of operation of the hot water supply system (hot water supply) is regulated. Depending on the supply temperature, the DHW is fed from a direct or reverse thread.
In the case of an autonomous system, we are dealing with a closed loop filled with a constant-volume heat carrier and not connected with external objects. Hot water is not taken from the circuit.
Circulation stimulation
In the DH system, the coolant is driven by a differential between the threads. And what about autonomous circuits?
There are two possible options.
- In a system with forced circulation, it is provided by a circulation pump - a relatively low-power device, often with the ability to stepwise or smoothly adjust the capacity.
- Gravitational systems operate due to the difference in density between the heated and cold coolant. From the boiler it rises along the so-called accelerating collector and slowly returns through the radiators, releasing heat along the way.
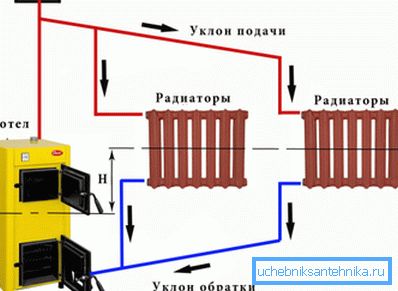
Useful: it is easy to upgrade the gravitational system to speed up circulation in it by installing a circulation pump in the circuit with your own hands. The instruction is quite simple: the filling is broken by a valve or non-return valve, on either side of which inserts are made to the pump. Sidebars are equipped with a sump in front of the pump and a pair of shut-off valves.
One and two pipe systems
The layout of the coolant to the heating devices can be one-pipe and two-pipe. In the first case, the radiator breaks the only filling or, more rationally, cuts parallel to it. In the second, each heater is a jumper between the supply and return pipes.
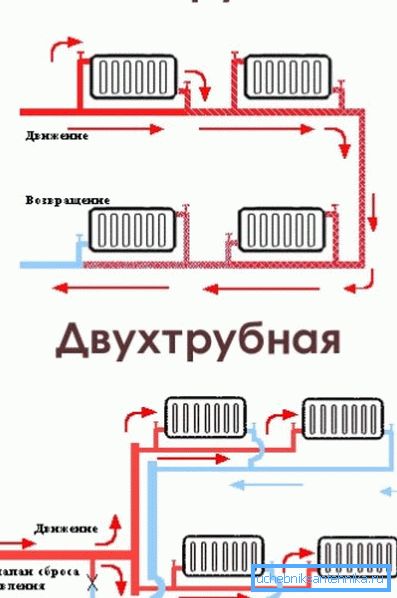
An important point: in the second case, the system requires mandatory balancing - setting the permeability of the batteries by throttling valves. Without it, radiators far from the boiler simply will not work.
Vertical and horizontal
Leningradka - a single-tube ring around the perimeter of a house with batteries embedded parallel to it, is a typical horizontal system. The heating stand in an apartment building is as typical vertical. As you might guess, they are often combined: for example, in the same apartment building with a vertical stand next to the horizontal bottling.
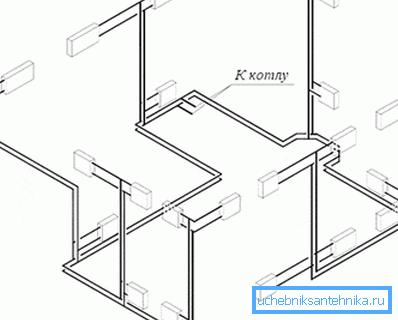
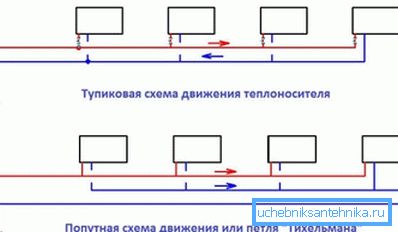
Passing and dead ends
If the coolant from the boiler outlet to the inlet does not change the direction of movement to the opposite - this is a passing system. If changes - deadlock.
Top and bottom bottling
In apartment buildings, you can find two types of wiring risers.
- The bottom filling means that the supply and return flow are in the basement. The risers are connected in pairs with a jumper in the attic or the upper floor. Each pair of risers short-circuits the supply and return pipelines.

- In the case of the upper filling, the feed is moved to the attic and is equipped with an air collection tank. Each riser has to be shut off at two points; but when you start the system, there are an order of magnitude less problems: you do not need to bleed air on every pair of risers, but only in a single tank.

Connecting radiators
Sectional heaters can be connected to the supply lines in several ways.
- Side connection is most advantageous in terms of aesthetics. However, with a large length of the device, the outer sections will be noticeably colder than the first ones from the liner.

- Diagonal connection will allow the battery to warm up along its entire length.
Advice: to connect to the left traffic jam, use not a sweep, but an American. It will significantly simplify the dismantling and installation of the radiator.
- Finally, the scheme from the bottom down will not only warm up the radiator evenly, but also relieve it of the need for flushing. Continuous circulation through the lower collector will not allow it to silt. The downside of such a connection is the need to supply the upper plug with a Mayevsky valve and to bleed air at each start.

Conclusion
We hope that our insight into the theory, albeit somewhat superficial, will prove useful to the reader. As usual, the attached video will offer him additional material.
Successes!