Closed and open heating systems: features
If you do not need to connect a hot water supply, then you probably will not care what kind of heating system you have - open or closed (except for academic interest). However, the open view is the most simple and independent.
The circulation of coolant here can take place in a natural way, according to the laws of thermodynamics, due to increased pressure at the outlet of the boiler, but it can also be forced. Let's take a closer look at their differences, positive and negative sides, and in addition we will show you a themed video clip.
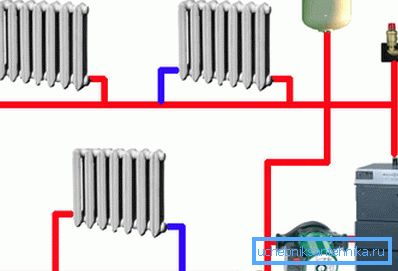
Distinctive features
Open system
Note. An open-type heating system implies an expansion tank that is not hermetically closed. Consequently, water evaporates and is added from outside sources (wells or centralized water supply systems) to the heating system.
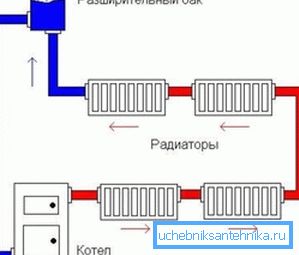
As a rule, in open-type systems, the circulating pump is not used, therefore, its operation will not depend on third-party energy sources - power lines or a diesel (carburetor) power generator. But nevertheless, the instruction does not prohibit in any way a plunging pump into the return pipe at the boiler, which will increase the efficiency of a solid fuel boiler, stove or fireplace with a water jacket by about half.
However, a very important difference of such a system is that it can function autonomously, without electricity or natural gas, and it can be installed in areas completely cut off from all communications.

Considering the fact that water in an open system will circulate rather slowly (the classic version - without an auxiliary pump), the heating pipes are selected with a large diameter, at least 40 mm, since it is necessary to ensure the possibility of their gradual heating in order to avoid damage.
In addition, the expansion tank made of steel or plastic should in any case be located above the heating circuit to ensure that the system is filled with water from this tank.
In such contours, the slope of the horizontal pipes is obligatory - this is done to allow normal circulation of the coolant. According to calculations, such a slope should be 0.01% of the coolant supply point at the boiler, but this option is rather difficult to calculate - it is much easier to observe a slope of about 8-10 mm per linear meter when installing and you will ensure proper circulation for this system.
The advantages and disadvantages of an open system

- The main advantage of an open heating system is its absolute independence from third-party energy sources, that is, it can function both with them (when connecting a circulating pump) and without them when the circulating pump is not activated. That is, when you want to start the forced circulation, then shut off the valve, which is located between the bypass pipe (see photo above), the flow of water, and it moves through the auxiliary pump. When there is no electricity, this valve opens, but is blocked at the stroke, in front of the pump, and the coolant continues to circulate naturally.
- It is easy to connect such a system to the boiler, since special knowledge is not needed here, for example, as when installing an electric or gas unit. Here, even a brick stove with a tank for heating water can be used as a boiler.
- Here, fuel can serve not only coal and firewood, but also various organic waste in a dry form, which can be in the household.
- The main drawback of the open system is the need to drain the water when the boiler has to be forced to stop, and also the heating of the circuit, which is rather slow, although even, heating the circuit.
- Antifreeze cannot be used for the coolant, moreover, it is constantly necessary to monitor the level of liquid in the expansion tank, low efficiency.
- A great danger is created when air traffic jams form - it is extremely difficult to expel air from the circuit in a natural way - for this you need to create artificial pressure. This is done by pumping water into the system.
Closed system
Note. The main difference of the closed type of the heating system is the tightness of all its components, and the evaporation of water is completely absent here. Circulation of the coolant in closed circuits is possible only as a forced (circulation pump). The whole system consists of a heater, pipes, radiators (floor heating) and an expansion tank.
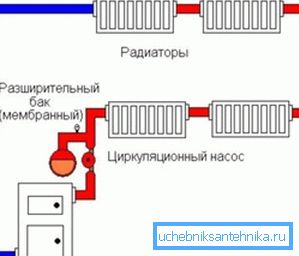
In cases where the pressure of the coolant in the circuit rises above the norm, the flow valve is activated in the expansion tank and the excess liquid flows there, thus stabilizing the total pressure.
When the water temperature drops, the pressure drops, but the circulating pump restores its shortage, automatically pumping the required amount of water to achieve the desired value. Generally speaking, the fuel equipment here performs the function of deaeration.
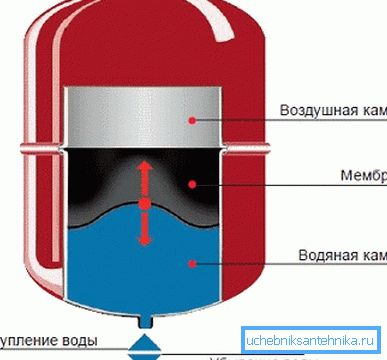
A very important and basic node for deaeration is the expansion tank, which consists of two halves (this can be seen in the upper image) rolled up with the edges of each other. Inside this tank is a membrane or diaphragm, which is made of heat-resistant rubber.
The tank contains a certain amount of gas, most often nitrogen (if it is pumped by the manufacturer), but it can also be ordinary air that will accumulate there if necessary.
Inside, the tank is divided into two compartments by the membrane - in one of them there is nitrogen or air, and in the other - the excess heat carrier, which is squeezed there under pressure through a safety valve, while the two media do not come into contact with each other. When the liquid cools, its pressure in the tank drops, and the gas from the other compartment through the rubber membrane pushes it back.
Advantages and disadvantages of a closed heating system

- The advantages of closed heating systems include a fairly convenient installation (the tank can be installed anywhere above and below the circuit), as well as the absence of the need to constantly monitor the water level.
- To protect such a system from defrosting, it is possible to use antifreeze. The room temperature can be regulated by increasing or decreasing the volume of fluid in the heating circuit, while the pressure can be adjusted independently.
- An additional source of heating can be connected to the system, that is, a backup boiler, as well as such boilers can operate simultaneously.
- Due to the absence of natural evaporation, there is no need to feed from an external source (well or centralized water supply).
- But there are a number of drawbacks, for example, the uninterrupted operation of the boiler, directly depends on the electricity for the operation of the circulation pump, besides, the heaters have a high price.
- In addition, there may be a problem with the placement of the expansion tank - it is filled with coolant by 30-60%, while the smallest percentage falls on large containers, the volume of which may be several thousand liters. But in autonomous circuits, this problem is not relevant.
Conclusion
Any of the above systems, you always, with certain skills, you can mount your own hands. But, both in one and in another case, it is very important to correctly determine the power of the boiler, which will be sufficient for a given area of the room.