Copper-aluminum heating radiators - uncompromising
Since 1857, the official date of birth for everyone familiar with the heating battery, a long time has passed. Instead of cast iron, other metals became widely used, for example, aluminum and steel, bimetallic radiators appeared, in which 2 types of metal were combined at once. Each of the competitors has its own strengths and weaknesses, bimetallic radiators, for example, deserve attention due to outstanding heat transfer.

Competitors of copper-aluminum radiators
Most often, the classification of radiators is given depending on the type of metal used for its production.
In general, there are:
- cast iron batteries - considered a classic. They are distinguished by outstanding durability, with their use heating systems are distinguished by high inertia. Manufacturers usually indicate a maximum lifespan of about 30-35 years, but this looks like a reinsurance.

Note! Some of the pioneering batteries (which were released at the Sangalli plant in the 19th century) still work as part of the palace heating system. So with longevity problems will not arise.
- steel - low price and excellent thermal conductivity are the main trump cards of steel radiators;
- aluminum - in comparison with pig-iron and steel analogs it is favorably allocated with small weight. But hydraulic shocks are poorly tolerated, and when using copper connecting elements form a galvanic pair, which results in a reduction in service life;

- bimetallic batteries - in the construction of such devices 2 metals are used. On the market are models using steel and aluminum, as well as copper-aluminum devices. The latter are characterized by maximum efficiency in comparison with all mentioned radiators.
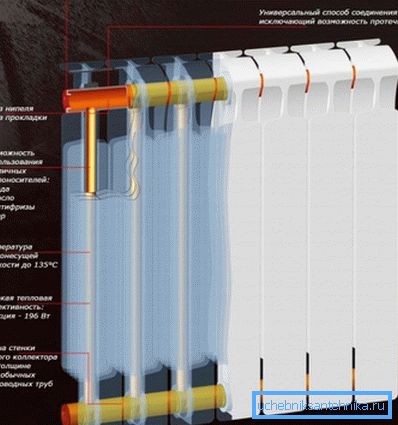
All you need to know about copper-aluminum radiators
In bimetallic radiators made of aluminum, fins are performed, and a steel or copper pipe can act as a heater. Its superior thermal conductivity speaks in favor of copper, if for steel this indicator is 47 W / m • K, then copper has about 400 W / m • K. Most thermal conductivity except silver (430 W / m • K).
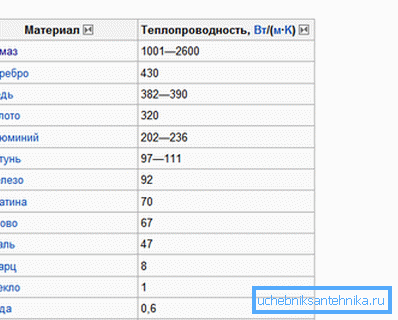
Devices completely made of copper cost a lot, and the use of aluminum can significantly reduce the cost, while maintaining a fairly high efficiency. Aluminum has a thermal conductivity of more than 200 W / m • K, which is quite enough for rapid heating of the room.
The advantages of a combination of copper and aluminum
Copper-aluminum heating radiators in almost all parameters bypass the steel and cast-iron counterparts.
The strengths of such radiators include:
- high thermal conductivity, and therefore greater efficiency with equal surface area;
- Such constructions are manufactured in one piece, that is, aluminum plates are simply put on and soldered to the copper tube (coil) at the factory. Compared to sectional devices, the risk of leakage is much lower;

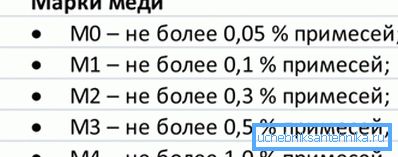
- only copper will come into contact with water, and this one is resistant to corrosion. In addition, for the manufacture of the coil is used only the purified metal, the proportion of impurities in it does not exceed 0.01%;
- compared to a cast-iron radiator, a copper-aluminum analogue of a comparable size will weigh about 4-5 times less, this makes installation easier, and fixings can be made not as powerful as for cast-iron batteries;
- the inner surface of the copper tube is never covered with a layer of scale and after 10 years of operation will remain as smooth as it was at the time of purchase;
- Considering that the device is manufactured in one piece, it can withstand the working pressure in the heating system without problems (about 8-12 atmospheres). The copper tube will withstand without problems and short-term increase in pressure up to 20 and above atmospheres. This allows the use of copper-aluminum radiators in unstable heating systems.
About compatibility of copper and other metals
When copper-aluminum heating radiators are used in the heating system, certain restrictions apply to the pipeline material (supply and discharge). The fact is that with some metals, copper, when in direct contact, forms a galvanic pair, which leads to the rapid destruction of the junction.
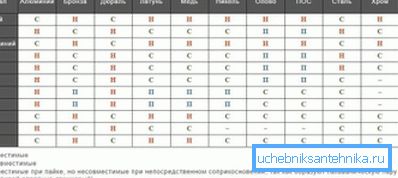
Note! Destruction will not occur if there is a layer of neutral material between the metals, and the system itself has a reliable ground (that is, there are no microcurrents).

Therefore, if the copper-aluminum radiator is still installed in the apartment, then it is desirable to abandon the steel pipes. As an option, you can consider the use of copper pipes, but it will cost a lot, and the reliability of the connection of copper pipes is not up to par. Optimal can be considered a variant of the use of PP reinforced pipeline.
Types of Copper-Aluminum Radiators
The division into types is rather arbitrary, because the construction still remains the same - the same copper pipe on which the aluminum plates are located.
You can highlight:
- radiators - most often they look like cute panel heaters. The unattractive design of a copper tube with fins is hidden behind a beautiful metal casing. In the upper part of the casing there are holes that direct the warm air into the room;

- convectors - the same design, and the price is comparable.

The main difference between a convector and a radiator consists in the principle of operation. So, for a radiator, infrared radiation (that is, thermal) is more characteristic, and in the case of a convector, air constantly passes through it, that is, air flow is observed.
The classification takes into account what percentage of heat transfer occurs in infrared radiation and convection. If the share of convection accounts for less than 75%, then the device can be safely attributed to the class of radiators.
The practice of operating copper-aluminum radiators
Such devices cannot be recommended for widespread use. For example, with centralized heating, the composition of the coolant is far from ideal, with time the place of solder will necessarily flow.
Note! Currently, most manufacturers of copper-aluminum radiators in advertising emphasize that it is their radiators that have been developed taking into account the particularities of centralized heating in Russia and give them a considerable guarantee. This is nothing more than a marketer's trick, and when a battery fails, you will still have to prove that it was operated according to all the rules, so it’s best to refrain from experimenting and limit yourself to regular batteries.
If an autonomous heating system is installed in a private house, and all the work is done by hand, then such devices may well be used.
At the same time you need:
- install shut-off valves made exclusively of brass, bronze. Copper is fully compatible with these metals - that is, there will be no potential difference during operation;

- pipes should be copper, polypropylene or metal-plastic. It is better to forget about steel rolling;
- It is desirable to control the composition of the coolant and not to use various additives, they are unlikely to add durability to the heating system.
Installation of copper-aluminum radiator
Before installation, it is necessary to compare the parameters of the heating system and the technical characteristics of the radiator in order to assess whether it can work for a long time in such conditions.
Pay attention to the following parameters:
- system pressure - must not exceed 20 atmospheres;
- the heat carrier should not be heated above 130? С;
- Ph coolant should not exceed 7-9;
- the oxygen content is also normalized - the maximum level is 0.02 µg / l.
As for the installation of the radiator itself, the instruction does not differ from the installation of a conventional battery.
It is necessary:
- dismantle the old battery;
- install fasteners in the wall (when using a wall-mounted radiator);
- hang a new battery;
- connect the inlet and outlet pipes to the inlet and outlet, install shut-off and control valves;
- check the system for tightness.
Note! Some manufacturers do not care much about the ease of installation of radiators. The entrances can be located close to each other, so it will not work to put 2 corners. You need to pay attention to this when buying.
Summarizing
The use of copper-aluminum heating radiators can significantly improve the efficiency of heating. This effect is achieved due to the high thermal conductivity of copper and aluminum fins. The relatively low distribution of such a device can be explained by the high price and a number of limitations associated with the use of copper pipes in the structure.
The video in general shows the principle of operation and the device of the copper-aluminum radiator.