Domestic heating boilers: an overview and characteristics of
To heat the mansions at the moment they use stoves, fireplaces, air-blowers, as well as gas, electric, diesel and solid fuel domestic boilers, which can be different modifications and work according to different principles.
The installation of a particular heating device depends on the technical conditions of the building project, as well as on the possibility of using one or another type of energy resource, that is, whether you have natural gas or whether your house is electrified.

However, you will choose yourself, but we will tell you from which models you can make this choice in general, that is, we will explain how they work, and we will show a video clip in this article.
Solid fuel boilers
Traditional

Let's take a look at how household solid fuel boilers work on the example of DAKON DOR 12 - this model has complete autonomy (does not depend on electricity) and practically any solid fuel (wood and coal) is used here, but the optimal material for burning is coal. Power adjustment is performed using dampers (thermomechanical regulator), which increase or decrease the air flow into the fuel chamber and bleed.
The heat exchanger for DAKON DOR 12 is made of extra-strong heat-resistant steel, but there are also models where the heat exchangers are made of cast iron - due to the thick walls, the lifetime of the unit increases. In this case, the combustion of fuel ensures high combustion efficiency, this is due to the special design of the fuel chamber.
It uses primary and secondary air, which is regulated not only by valves, but also by a system of turning and tilting the grate, as well as a shaking lever located on the side of the boiler.
Heat-resistant segments and fireclay boards in the combustion chamber are combustion catalysts, and in addition, increase the service life of the unit (do not burn out so quickly). An adjusting choke is mounted on the door of the ash pan, which is also a combustion catalyst - it regulates the inflow of primary air. On the side panels, in their middle part, there are special openings for the supply and adjustment of secondary air.
Note. The shaking lever, which is available in almost all models, makes it possible to dispense with the opening of the firebox in order to separate the ash or slag from the burning fuel. Almost all boilers of this type have a thermomanometer on the front. Fuel can be loaded from above, from the side, or automatically, through a loading container with which some boilers are supplied.
Gas Generator

Pyrolysis or gas-generating household boilers for heating with solid fuels work quite differently, unlike traditional units, they produce a minimum emission of combustion products into the atmosphere, since the fuel burns almost completely.
The principle of operation is the release of pyrolysis gas at a temperature of 200? C and lack of oxygen, mixing it with hot secondary air and the final burning of this gas in the afterburner.
To put it simply, solid fuel is put in the primary fuel chamber and, after sufficient ignition, the access of primary air, which through the blower under the grate supports combustion, is greatly reduced - wood or coal simply smoke, which means intensive pyrolysis gas evolution. Adjustment is made using special valves.

Released pyrolysis gas (thermal decomposition product of fuel) enters the afterburner chamber, and during the transition of the boiler to the gas generation mode, secondary air also enters the afterburning chamber, which reaches the required temperature along the route (through the furnace) and enters into a thermochemical reaction with the pyrolysis gas.
This heated secondary air does not flow arbitrarily, but through specially calibrated openings in the afterburner, which allows you to adjust the speed of the process and, therefore, the power of the boiler.
Note. When burning solid fuel as described above, at least 90% of the solid material and thermal decomposition products burn, which indicates a high ecological purity of the gas-generating boilers. The efficiency of such boilers is up to 85%, and the power control module can operate in the range from 60% to 65%.
Diesel (fuel oil) boilers

The most demanded type of fuel for such boilers is solar and the instruction insists on separate storage of fuel, that is, not in the boiler room itself, but in another room or in some kind of container in order to avoid fire.
The units themselves can be made:
- either from steel;
- either from cast iron.
But for country houses, preference, as a rule, is given to the second option - its position during operation is most reliable. But the steel models are made for floor and for mounted (wall) installation, although the mounted version is by no means the best seller in spite of the fact that it has a thick layer of thermal insulation.
The current professional maintenance of this type of unit usually comes down to the technical control of a fuel nozzle and burner, as well as regular cleaning of the chimney. According to the method of heat energy production, liquid fuel boilers are divided into traditional and condensing, where the second option is more productive, since it allows using the maximum amount of energy of the installation itself.
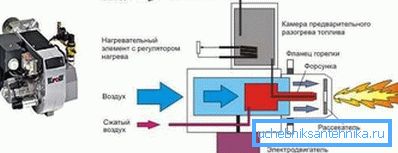
The principle of operation of a diesel unit is to heat the heat exchanger, which is usually made of cast iron less often from heat-resistant steel, which occurs with a burner and here the main difference is that they can be:
- single stage,
- two-stage,
- modulation.
The difference in degrees is the vastness of the adjustment range. So, single-stage burners are not regulated at all, that is, they have a constant heating power, two-stage burners, respectively, have two levels, but the modulation can be set to any suitable mode for a given case.
Diesel boilers for heating modern-type homes are equipped with an electronic control unit that automatically controls the system and turns it off in case of equipment problems, maintains the temperature you set, and has several levels of protection. Units can be single-circuit - designed only for heating the building, double-circuit - with the additional function of flow-through hot water and double-circuit with a boiler, where the hot water function is in constant mode.
Attention! Do not try to search for the sale of an atmospheric burner for liquid fuel - they do not exist! The process of burning fuel occurs only after it is sprayed by the nozzle.
Electric boilers
Heating element
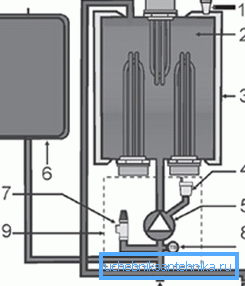
Explanation of the photo:
- Heaters are located at the top and bottom;
- Liquid heat exchanger;
- Insulating liquid layer;
- Expansion tank;
- Safety valve OB;
- Pressure meter;
- Hydro group (pipes, taps and valves);
- Heat exchanger air vent: A - return from the system, B - supply to the system
Most often, boilers working on heating elements, produce mounted type for mounting on the wall and it is quite justified. The depth of the device usually does not exceed 25-30 cm, not to mention the excellent design of the units, which fits very well into any room interior.
You can choose a suitable microclimate of the room for you by setting the desired temperature, and this function is provided by trigger thermostatic valves, equipped with sensors that monitor the temperature in the room and in the heating circuit.
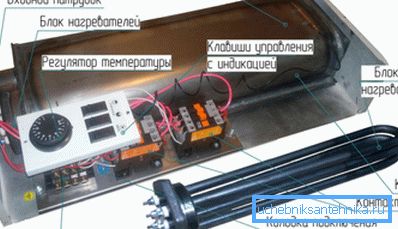
The tubular electric heater itself is made of steel, copper or titanium and in this tube there is a spiral, which is made of nichrome and the contact rods are sealed at the ends. The spiral in the metal tube is pressed by quartz sand, and the contact rods are fixed with porcelain plugs, so that the nichrome does not have contact with the external environment.

The power of the boilers operating from the 220 / 380V network can differ greatly from each other, but for household use, as a rule, single-phase (220V) units are used, where the output can be from 2 to 30 kW.
For example, in the top photo you see the German model WAILLANT eloBLOCK, which ranks second in the world in popularity in the market. The power of such a device can be about 6-28 kW, so you can always choose the right model for a mansion with any area of heated space.
The WAILLANT eloBLOCK model has a maximum water heating mode up to 85? C, which is typical for the vast majority of all similar boilers operating on heating elements. In this modification, the expansion tank has a capacity of 7 liters, and the working pressure can be varied within 0.8-3.0 bar, although the recommended optimal range is 1-2 bar. Such a device weighs only 34 kg, and its dimensions (height / width / depth) are 740x410x330 mm.
Electrodes

In electrode boilers, the principle of heating the heat carrier is fundamentally different from all other methods, be it gas, diesel or solid fuel units - here the source of heating the heating circuit is the liquid itself. The principle of operation is very simple here - there are two polar electrodes in the tank, which are constantly in contact with the coolant.
Whether it is a 220V or 380V boiler, it still remains at a frequency of 50 Hz, therefore, the polarity of the electrodes changes 50 times per second, which with the same frequency causes the ions to move in opposite directions. From this speed of movement of the ions, the liquid heats up and enters the heating circuit in a hot state, something like a flow-through boiler is obtained, only there is no heat exchanger and a burner.
It turns out that the coolant closes the electrodes and if a leak occurs, the circuit opens, and the system shuts down due to the absence of a short circuit in the voltage circuit.
| Options | Optimal use of boilers | |||||||
| Hearth 2 | Hearth 3 | Hearth 5 | Hearth 6 | Geyser 9 | Geyser 15 | Volcano 25 | ||
| Dimensions of the room (m3) | 80 | 120 | 200 | 250 | 340 | 550 | 850 | |
| Rated power consumption (kW) | 2 | 3 | five | 6 | 9 | 15 | 25 | |
| Rated voltage (V) | 220 | 220 | 220 | 220 | 380 | 380 | 380 | |
| The average power consumption with sufficient insulation of the room (kW / h) | 0.5 | 0.75 | 1.25 | 1.5 | 2.5 | four | 6,6 | |
| Maximum current strength of each phase (A) | 9.1 | 13.7 | 22.7 | 27.3 | 13.7 | 22.7 | 37.5 | |
| Nominal current for automation in electromechanical version (A) | ten | sixteen | 25 | 32 | 3 to 16 | 3 to 25 | 3 to 40 | |
| Copper wire section (mm2) | 220V | four | four | four | 6 | - | - | - |
| 380V | - | - | - | - | four | four | 6 | |
| The recommended amount of coolant in the heating system (l) | 20 - 40 | 25-50 | 30 - 60 | 35 - 70 | 50 - 100 | 100 - 200 | 150 - 300 | |
| Internal diameter (DN) of nozzles at the inlet and outlet in the boiler (mm) | 25 | 25 | 25 | 25 | 32 | 32 | 32 | |
| Unit Length (mm) | 250 | 275 | 320 | 335 | 360 | 410 | 460 | |
| Unit weight (kg) | 0.85 | 0.9 | 1.05 | 1.1 | 5.0 | 5.3 | 5.7 |
Using this table, you can choose the desired modification of the boiler.
Gas
Convection (traditional) boilers
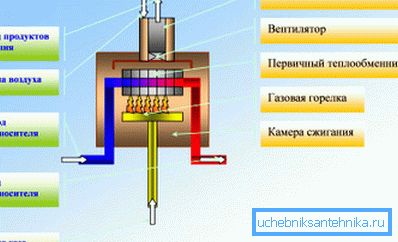
In the Russian Federation, traditional gas-fired boilers are most often used. They operate on the principle of convection - a gas burner that is located in the heating chamber, heats the heat exchanger and, in a closed circle, gives hot water to the system.
The scheme of work is quite simple, but at the same time the heat that is in the chamber is not consumed for heating, but is discharged into the exhaust vent tube as waste - products of combustion. As a result, their efficiency does not exceed 90%, although the output power may be different - from 16 kW to 36 kW and even more, but this significantly increases the gas consumption.
Traditional gas units can be mounted or floor mounted, as well as single-circuit, which are used only for the heating system or dual-circuit, where the second circuit is designed for hot water supply (HWS). All these installations are equipped with electronic sensors that make up the control valve, an integrated circulating pump and electronic ignition.
Heat exchangers

- The most significant drawback of such equipment is its heat exchangers, which can be made of steel, cast iron and aluminum, and the weak point here is the poisonous condensate that occurs as a result of the combustion of gas and fumes. The point of formation of condensate is at 55-57? C, and that is why the optimal temperature for condensing boilers is 60-80? C.
- If we talk about materials, then the most reliable, probably, can be called cast iron because of its thick walls, but in actual fact, devices made of heat-resistant steel have a longer operating life, although if you follow the rules of operation, you can call any of them good.

- Heat exchangers by appointment can be divided into two types - these are single-circuit, which are used exclusively for heating and double-circuit - where the function of hot water is added. But all double-circuit heat exchangers are again different from each other - they can be of a bithermic type (pipe in a pipe) or separate, where heating and hot water supply are separate circuits.
- At first glance, it seems that the bithermic version is better, since it is much more compact and lighter, but in fact it does not quite correspond to the real state of affairs, although in capacity and power they can exactly match each other. The thing is that even in autonomous systems, rarely anyone will use distilled water, and any other water contains salts and alkalis and cannot be cleaned with household filters.
- As a result of heating, scale builds up on the walls, which in a bithermic device is almost impossible to clean, although there are many different means for this - pieces of scale. If they lag behind the wall, they still do not dissolve and create a blockage in the thin tube. Experience suggests that it is still better to buy gas heating household boilers with separate heat exchangers, which can be cleaned in the event of the formation of scale on them.
Condensing boilers

For gas condensing boilers the condensate becomes not the enemy, but the surest way to increase the efficiency of the unit - just think about it, this factor for most models is about 109-11%! All this is possible thanks to the principle of operation of the unit.
In the combustion chamber, during operation, there is air with acidic vapor, the temperature of which reaches 150-180 ° C, but in traditional units it is immediately drained through the ventilation pipe to the street, and here this secondary heat is used to heat the heat exchanger.
When the temperature of the gas reaches the critical point (55-57? C), it turns into acid condensate and falls to the bottom of the chamber, where through a special channel, through filters, is diverted outside the equipment.
Due to this principle, condensing gas boilers are also called low-temperature, as their optimal mode is 30-55? C, although they can also operate at 110? C and supply a high-temperature heating circuit. They are very convenient to use for a floor heating system, where the temperature of the heat carrier is rarely even up to 50? C plus high efficiency.
Of course, the price of such boilers is much higher than the traditional ones, but this ratio of qualities very quickly pays for the initial cost of the unit.
Conclusion
I would like to remind you that when installing any domestic boiler with your own hands, you should invite a specialist with a license to inspect the launch. In this case, the warranty period will be calculated not from the date of sale, but from the moment the unit starts up.