Gravitational heating system: principle of operation,
How and by what means does gravitational heating work? What influences the circulation of the coolant? What equipment is needed for full and trouble-free system operation? In this article we will try to find answers to these and many other questions.
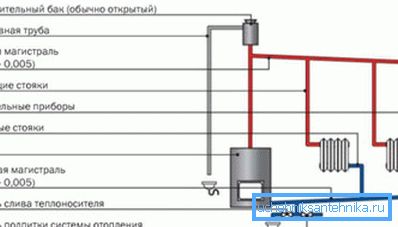
What it is
In any water heating system, the function of transfer and distribution of heat to the heating devices is performed by the coolant — a liquid substance with a significant specific heat capacity.
Most often, this role is played by ordinary water; however, in cases where the house may be left without heating during the winter chill, liquids with lower phase transition temperatures are often used.
Regardless of the type of coolant, it must be made to move, transfer heat.
There are not many ways to do this.
- In central heating systems, the function of encouraging circulation is the pressure drop between the supply and return pipes of the heating main.

- Autonomous systems with forced circulation for this purpose are completed with circulation pumps..
- Finally, the coolant in gravitational (gravity) systems moves only by changing its own density during heating..
How it works
Principle
Let's try to more visually imagine the mechanism of operation of such a system.
Simply put, it consists of two communicating vessels connected by pipes (heating circuit) into a single ring. The first vessel is the boiler, the second is the heating system itself, consisting of radiators, bottling and connections. The height of both vessels is the same.
Specify: as a rule, the heating circuit has a significant height. At least - much more than a boiler. To overcome this problem, the circuit immediately after the boiler is completed with an accelerating collector - a vertical section into which the heated coolant is forced.
After the heat exchanger is heated, its contents rush upwards, displaced by colder masses. Having reached the upper point of the accelerating collector, the hot coolant begins to descend, passing through the heaters along the way and gradually giving them thermal energy.
When cooling down, it increases its density and at the lower point of its route is already ready to push the heated liquid in the boiler heat exchanger into the accelerating collector, starting a new system operation cycle.
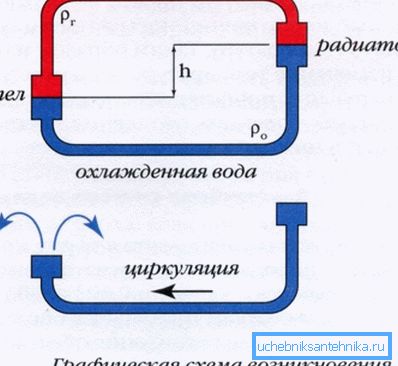
Factors
Obviously, the greater the rate of circulation - the more uniform the distribution of heat in the circuit will be, the less will be the temperature variation of the batteries. What determines this speed?
The balance of two opposing factors: created when the pressure system and the hydraulic resistance of the circuit.
What does each of the factors depend on?
Head pressure
- From the height of the upper section of the circuit (that is, the total height of the section of the boiler - upper stage collector). To increase it, the boiler, if possible, is mounted in the basement, and the upper part of the filling is carried to the attic.
- From the slope of bottling. As a rule, it is made permanent: from the top point the filling goes down to the boiler, losing at least a centimeter above the floor level per linear meter of length. Thanks to the slope, the cooled coolant makes its route, carried away by its own weight.
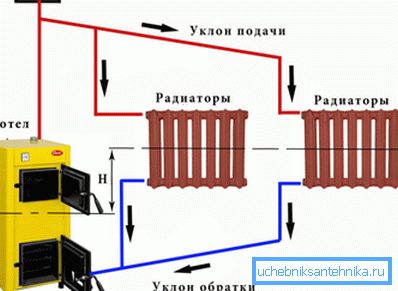
Hydraulic resistance
The lower it is, the easier it is for water or another coolant to make its way with a fixed head.
What influences the hydraulic resistance of the system?
- The diameter of the filling. The larger it is, the less resistance the pipe has to the flow of water. The absolute minimum diameter is 32 millimeters; more often, when building a gravity system with their own hands, a pipe of 40–50 mm in size is used as filling.
- The length of the filling. A contour with a length of more than a hundred meters with a reasonable diameter will simply be inoperable. Usually gravitational heating systems do not make longer than 40-50 meters.
- The number of bends and transitions of diameter. Each of them increases the resistance to the movement of water.
- The number and type of valves. The fewer twists on the choke devices, the better.
Practical consequence: it is better not to use a screw valve in the gravitational system. In addition to the fact that their design is obsolete long ago morally, their moves create a much greater hydraulic resistance than a smooth slotted ball valve.

- Finally, the pipe material and its age have a strong influence on the resistance to flow. To be precise, the determining factor is the so-called roughness coefficient. Compare its value for different pipes.
| Pipe description | Roughness coefficient |
| Polymer or metal polymer | 0.1 - 1 |
| New steel | 6 |
| Galvanized steel after 5 years of operation | 15 |
| Black steel after 5 years of operation | 20 |
| Black steel after 20 years of operation | 200 |
Practical consequence: when installing it is better to use plastic or metal-plastic. You can not be afraid of overheating: as long as there is water in the circuit, the temperature of the pipes will not exceed 100 degrees.
Equipment
Gravitational can be either a closed system that does not communicate with atmospheric air, or open to the atmosphere. The type of equipment that it needs depends on the type of system.
Open
Actually, the only mandatory element is an open expansion tank.

It combines several functions:
- Holds excess water when overheated.
- It vents air and steam generated by boiling water in the circuit.
- It is used to top up the water to compensate for its leakage and evaporation.
In cases where radiators are located above it in certain areas of bottling, their upper plugs are completed with air vent. In this role, both Mayevsky taps and ordinary water taps can be used.
To reset the system, it is usually supplemented by a branch pipe leading to the sewage system or simply outside the house.
Closed
In a closed gravitational system, the functions of an open tank are distributed to several independent devices.
- Diaphragm expansion tank of the heating system provides the ability to expand the coolant during heating. As a rule, its volume is taken equal to 10% of the total volume of the system.
- The safety valve relieves excess pressure when the tank is full.
- Manual air vent (for example, the same Mayevsky's crane) or automatic air vent is responsible for air exhaust.
- Pressure gauge shows pressure.

Important: in the gravitational system at least one air vent must be present at its highest point. In contrast to the scheme with forced circulation, here the airlock simply will not allow the coolant to move.
In addition to the above, a closed system is usually provided with a jumper with a cold-water system, allowing it to be filled after discharge or to compensate for water leakage.
Layout
The instructions for distributing radiators are determined primarily by the number of floors in the house.
One floor
When distributing to one floor, the author strongly recommends not reinventing the wheel and using the time-tested Leningrad. In the correct implementation, it is a ring laid along the perimeter of the house, with heating devices embedded parallel to this ring.
Each radiator is connected from the bottom to the bottom or diagonally. Leads are supplied with two valves or a valve in the feed and a choke on the return pipe. Shut-off valves will allow you to disconnect the batteries for repair, without stopping the entire circuit, or to throttle a part of the heating devices for temperature equalization.
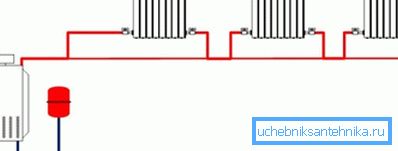
Two floors
But in the case of two floors the two-pipe scheme is optimal with again increased diameters of bottling and stand-by connection of radiators. In fact, we create a typical top filling scheme: after the accelerating collector, the heat transfer fluid is pushed into the supply pipe and from there by gravity returns to the filling of the return flow through radiators.
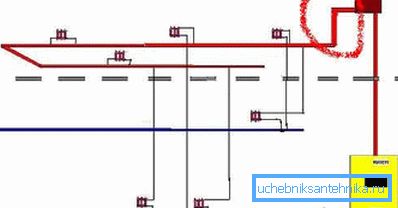
The most important point: the risers are necessarily throttled for balancing. Without it, we will get an extremely uneven temperature distribution: the entire coolant will go through the risers closest to the boiler.
If your boiler is mounted in the basement, it will be logical to bring the lower bottling into it.
Of course, subject to one of two conditions:
- The basement is insulated and has a year-round positive temperature.
- Your heating system - with antifreeze or any other antifreeze.

Advantages and disadvantages
What is gravity heating on the background of a system with forced circulation? Is it worth stopping at his choice when designing your own cottage?
Merits
- The system is absolutely failsafe. There are no moving or wearing parts; it does not depend on external factors, including unstable power supply outside the city.
- The gravitational scheme is self-regulating. The colder the return in it, the faster the circulation of the coolant: after all, it has a higher density than the masses heated in the boiler.
- Finally, when designing this system, it is not necessary to engage in complex calculations, special skills are not required: such schemes were also designed by our grandfathers. In rural areas, it is still possible to find contours attached to a steel tube heat exchanger placed in a Russian furnace.

disadvantages
Not without them.
- The system warms up quite slowly. From ignition of the boiler to the output of the batteries to the working temperature, one and a half to two hours can pass.
By the way: they will also cool down due to the large volume of coolant. Especially if cast iron heating radiators or massive steel registers are installed as heating devices.

- The simplicity of the system does not mean that its price will be significantly lower compared to alternatives. The solid diameter of the filling will take a significant cost. Here is an excerpt from the current price list for a reinforced polypropylene pipe from one of the Russian companies:
| Diameter, mm | Cost per meter, rubles |
| 20 | 52.28 |
| 25 | 67.61 |
| 32 | 111.76 |
| 40 | 162.16 |
| 50 | 271.55 |
- Without balancing, temperature variation between radiators can be noticeable.
- Finally, with a slight heat transfer from the boiler, the bottling areas carried out in the attic or in the basement can be grasped with ice in extreme cold.
Two in one
To solve all the listed problems of the gravitational scheme, it can be upgraded with a pump insert. In this case, the system will retain the ability to work with the natural circulation.
In carrying out this work, it is worth adhering to a few simple rules.
- Between the tapping points, a valve is placed on the pump or, much better, a ball check valve. When the pump is in operation, it will not allow the impeller to drive water in a small circle.
- Before the pump is required mud tank. It will protect the rotor and pump bearings from scale and sand.
- The tie-in to the pump is limited to a pair of valves that allow you to clean the filter or remove the pump for repair without loss of coolant.

Conclusion
We hope that we were able to answer all the questions that have accumulated in the reader. As always, additional information about the principle of operation of gravity systems and their device can be found in the attached video. Successes!