Heat dissipation of radiators: approximate calculation and
The task of any radiator is to effectively heat the room. Therefore, one of the most important parameters of these devices is heat transfer, which determines how well the radiator will cope with the task. Below we will consider what factors influence this parameter, what heat transfer from different types of radiators and how to calculate it.
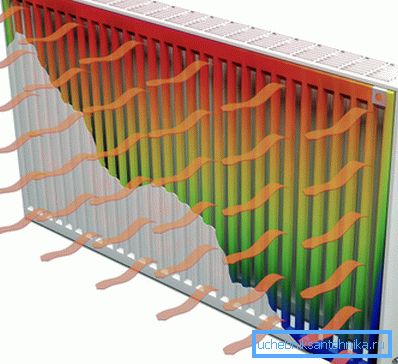
What is heat transfer
So, heat transfer is called an indicator denoting the amount of heat that the device transmits over a certain period of time. Often this parameter is also called thermal power, radiator power or heat flux. It is measured in watts, abbreviated - watts.
However, in some sources this parameter is measured in calories per hour - 1 W corresponds to 859.8 cal / h. However, such a measurement is rare.
It should be noted that the heat transfer from the battery is carried out by three processes:
- Heat exchange;
- Convection;
- By radiation.
Each battery carries heat in all three ways, but different heating devices have a different ratio. In fact, radiators are called only those devices in which at least 25 percent of heat is transmitted by direct radiation. However, this term has received a wider meaning, as a result of which it is also used for convection appliances.

Calculation of heat transfer
When arranging a heating system with your own hands, the calculation of the required power of the devices deserves attention. The choice and their quantity depends on it. On the one hand, each owner is trying to save money, so it does not make sense to buy extra batteries, but on the other hand, if they are not enough, you will not be able to maintain a comfortable temperature in your home.
There are two methods for calculating the heat output of a radiator needed to heat a room:
- Approximate calculation, which is based on the fact that per 10 square meters of a room that has one window and one outer wall, one kilowatt of power is required. If the room has two external walls, then it needs 1.3 kW to heat it.
- Calculation by the formula is a more complicated method, but at the same time allowing to obtain a more accurate value.
Below is a detailed look at each of these methods.

Approximate calculation
To calculate the heat transfer radiator radiators necessary to heat the room, you need to know the following parameters:
- Battery Type;
- Its size;
- Parameters of the room.
Below is a table of heat transfer radiators made of different materials:
| Type of | The effectiveness of one section at a temperature of 80 degrees |
| Cast iron | 125-160 W |
| Aluminum | 200 watts |
| Bimetallic | 204 W |
Note! The efficiency of radiators affects the way they are connected. The most effective is considered to be a one-way connection, in which the coolant is supplied from above and the return flows out from below. For devices with a large number of sections, a diagonal connection is more effective.

For example, the room has an area of 18 square meters, and it is planned to install cast iron batteries in it. Since the heat output of the radiator is 160 W per section, in our case we need - (18: 150) x100 = 11.25 ~ 12 sections.
Note! On sale you can find solid steel panels. To calculate their required power, you need a table of heat transfer from steel heating radiators, which are usually provided by their manufacturers.
Calculation by the formula
To get the desired value, you must use the following formula - P = Sxhx41, where:
- P is the desired value.
- h - Room height.
- S is its area.
- 41 - is a standard indicator of the minimum power per cubic meter of volume.
The obtained value should be divided by the rated power of the section to find out the required number.
Tip! If, as a result of the calculations, a fractional number is obtained, it should be rounded upwards, since the lack of power will have a much greater effect on the comfort of the room than its excess.

Features of devices of different types
As we found out, the heat transfer characteristics of heating radiators largely depend on the materials from which they are made.
Below we take a closer look at the heat transfer characteristics of different types of batteries:
- Cast iron - differ in the lowest efficiency. Moreover, this parameter depends on the interaxial space. This is due to his big run - from 120 to 160 watts. The exchange of heat mainly occurs due to direct radiation and only 20 percent comes from convection.

- Panel - heat transfer of steel radiators is not much higher than that of cast iron, however, to improve heat transfer, the design is made of several panels, between which the fins are located. Thus, the proportion of convective heat transfer increases significantly.
- Aluminum - efficiency is significantly higher than that of the two previous types of devices, however, the scope of such batteries is limited. The fact is that they are not designed for high pressure, which is available in centralized systems, and are also designed to work exclusively on a purified coolant.

- Bimetallic - in terms of efficiency, they even slightly exceed aluminum devices, and at the same time are more durable, which allows their use in centralized systems. Of course, the price of these devices is the highest, but due to the high power, it is possible to install radiators with fewer sections than to save a little.
Note! In order for the radiator to work at full power, it must be properly installed — without tilting and at a certain distance from the wall, as required by the instructions. The use of reflective penofol fixed to the wall will also help increase efficiency.
Here, perhaps, are all the most important points that you should know about the heat flux of radiators in order to correctly calculate the heating system and not be mistaken with their choice.
Conclusion
Thermal power of radiators is one of their most important characteristics. Therefore, on its basis, the calculation of the heating system of a dwelling is performed, without which it is impossible to ensure its comfortable heating in winter.
You can read more useful information on the voiced topic from the video in this article.