Heaters for ventilation: types, installation, calculation
The topic of this article is devices for air heating in supply ventilation. We will find out what they are and how they are mounted. In addition, we have to find out how the calculation of the air heater is performed.

Purpose of use
And in fact, why do you need heated air supply?
There are several reasons:
- Its low temperature means inevitable condensation in the ventilation ducts.. Any measures for heat insulation of ventilation pipes will only reduce its number, but will not solve the problem completely. But heating the air at the inlet from the street will allow you to forget about moisture condensation.
- A jet of icy air in a bedroom or nursery will hardly make your stay comfortable and safe for your health.
By the way: often in these rooms only the hood is organized. Inflow is provided due to air circulation between the rooms.
- Finally, there is such a thing as an air heating system. Heated supply air, coupled with recovery systems, eliminates the need for radiators or underfloor heating, along with the complex and expensive wiring of the heat carrier.

Kinds
According to what signs can the heaters be classified?
Heat source
In its quality can be used:
- Electricity.
- Heat generated by an individual heating boiler, boiler room or CHP and delivered to the heater with coolant.
Let us examine both schemes in a little more detail.
The electric air heater for fresh air ventilation is, as a rule, several tubular electric heaters (heating elements) with fins pressed on them to increase the heat exchange area. The electrical power of such devices can reach hundreds of kilowatts.
With a power of 3.5 kW, they are not connected to the outlet, but directly to the panel with a separate cable; with power from 7 KW, power from 380 volts is strongly recommended.
Reference: conductor heating is directly proportional to the current flowing through it. Increasing the supply voltage allows you to reduce the operating current while maintaining electrical power.
What are the advantages of an electric heater for ventilation against the background of the water?
- Easy installation. Agree that it is much easier to connect the cable to the heating device than to circulate the coolant in it.
- No problems with liner insulation. The loss in the power cable due to its own electrical resistance is two orders of magnitude less than the heat loss in the pipeline with any coolant.
- Simple adjustment of air temperature. In order for the supply air temperature to be constant, it is sufficient to mount an uncomplicated control circuit with a thermal sensor in the power supply circuit of the heater. For comparison, the system of water heaters will force you to solve the problems of matching the air temperature, the heat carrier and the power of the boiler.
Does the power supply have flaws?
- The price of an electric device is somewhat higher than the water one. For example, a 45-kilowatt electric heater can be bought for 10-11 thousand rubles; water heater of the same capacity will cost only 6-7 thousand.
- What is more important, when using direct heating with electricity, are outrageous operating costs. To heat the coolant, which transfers heat to the water heating system of air, the heat of combustion of gas, coal or pellets is used; this heat in terms of kilowatts is much cheaper than electricity.
| Heat source | The cost of a kilowatt-hour of heat, rubles |
| Main gas | 0.7 |
| Coal | 1.4 |
| Pellets | 1.8 |
| Electricity | 3.6 |
Water heaters for inlet ventilation are, in general, conventional heat exchangers with developed fins.

The water or other coolant circulating through them gives off heat to the air passing through the fins.
The advantages and disadvantages of the scheme mirror the features of the competing solution:
- The cost of the heater is minimal.
- Costs during operation are determined by the type of fuel used and the quality of heat transfer wiring insulation.
- Adjusting the air temperature is relatively complex and involves a flexible system for controlling the circulation and / or the boiler.
Materials
For electric air heaters, aluminum or steel fins are usually used on standard heating elements; a less common heating scheme with an open tungsten coil.

For water heaters are characterized by three versions.
- Steel pipes with steel fins ensure maximum construction cheapness.
- Aluminum tubes with aluminum fins due to the higher thermal conductivity of aluminum guarantee a slightly higher heat transfer.
- Finally, bimetallic heat exchangers made of copper pipe with aluminum fins give the maximum heat transfer at the price of somewhat lower resistance to hydraulic pressure.
Custom execution
A pair of solutions deserves special mention.
- The air handling units are a heater with a pre-installed fan for air supply.
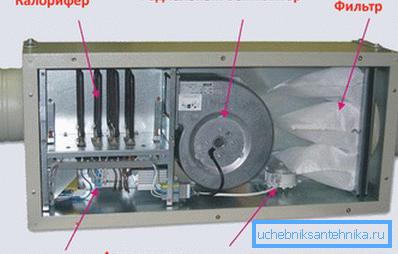
- In addition, the industry produces products with heat recuperators. Part of the heat energy is taken from the air flow in the exhaust ventilation.
Installation
If there are no special problems with installing electrical devices, then with water ones everything is somewhat more complicated. What is the binding of the ventilation heater? For a self-powered low-power air heating system, the simplest solution would be to install a pair of shut-off valves (in case of repair) and a thermostatic head at the outlet into the gap in front of the heater.
In addition, the tie-in to the general heating system is necessarily supplied with a bypass, which will allow switching off the device without stopping the circulation. If a high-capacity air heater is responsible for heating the air in the ventilation of the whole building, such instruction will obviously be unsuitable. Here is one of the possible strapping schemes.
Probably, the scheme requires a few comments.
- Shut-off valves at the inlet, as in the previous case, are needed in case of repair or replacement of the heater itself or of the shut-off valves without stopping the circulation in the main circuit.
- A coarse filter prevents seizure of the three-way valve or a pump of dross, sand or rust.
- The circulation pump allows the coolant to circulate through the small ring through the jumper.
- The check valve prevents the coolant from moving through the jumper in the opposite direction: the pressure on the flow pipe is always greater.
- Finally, the main element of the scheme - a three-way valve with an electric drive and a temperature sensor - allows mixing the heat transfer medium from the supply and return pipes, dispensing the mixture depending on the sensor readings.
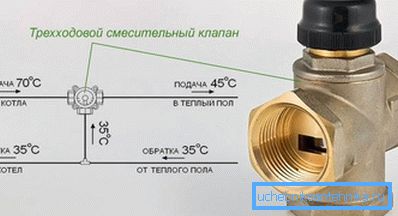
Important: The moment that is not indicated on the schematic image - it will be operational only if there is a retaining washer on the return pipeline (for example, on one of the flanges of the lower valve).
Payment
What is the calculation of the power of the ventilation heater?
Here a simple formula of the form Q (W) = L * 0.335 * (TV-Tn), where:
- Q - power of the device;
- L - air flow in cubic meters per hour;
- TV and Tn - temperature outgoing and injected flow.
So, for an outdoor temperature of -5C, the target temperature of inlet ventilation + 18C and air consumption of 500 m3 / hour, the calculation of the ventilation heater will be 500 * 0.335 * 23 = 3852.5 watts.
Conclusion
We hope that we were able to answer all the questions that have accumulated in the reader.
Additional case material, as usual, can be found in the attached video in this article. Successes!