Heating and ventilation: norms, rules, features
Heating systems and building ventilation systems are an interconnected structure that should provide normalized meteorological conditions and quality (cleanliness) of air in the service area of residential, administrative, residential and industrial buildings. We will tell you what requirements the ventilation-heating system should meet.

Heating, ventilation and air conditioning systems (HVAC)
General provisions

Calculation, design and installation of heating and ventilation are carried out in a comprehensive manner, taking into account the mutual influence of systems on each other, as well as taking into account the possibility of combining their functions and saving energy. Why it happens this way, we show below.
Ventilation, air conditioning and heating activities, one way or another, are aimed at solving one problem - providing the necessary indoor climate. This means that each of these systems has an impact on the general climatic characteristics.

Modern climate systems, especially ventilation and air-conditioning systems, are controlled by automatic feedback, that is, climate changes in the service area affect not only the installation that led to these changes, but also the one that works in the same area, but with slightly different tasks.
For example, consider the situation in which heating devices heat the air at a time when ventilation removes the hottest air and delivers chilled streams from the street. If both systems do not take into account the effects that they have on each other, we may face a regime where excessive ventilation will result in inefficient heating or energy waste.

Unlike previous eras, our country has adopted the capitalist path of economic development, and now the consumer is paying for everything. In this regard, the issues of energy saving, which goes to heating, air conditioning and ventilation, become topical.
First of all, it should be remembered about the need for thermal insulation of the enclosing structures of buildings and industrial premises, pipelines and heat mains.
It is also important to equip the air conditioners with a flexible control system and high-quality automation, which will allow you to adjust the operation modes of all systems as efficiently, economically and adequately as possible to the operating conditions. Of course, without taking into account all the factors of influence, including the mutual influence of systems on each other, such a configuration is problematic.

Note! As you can see, ventilation, heating and air conditioning are considered as a single climate system, all nodes of which are interconnected and influence each other.
Structure and composition
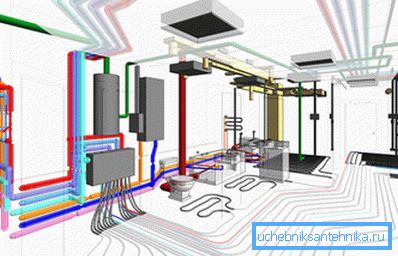
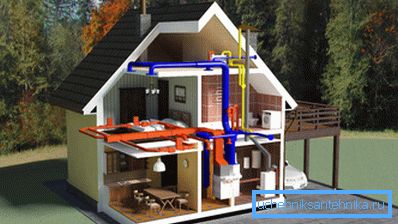
To understand the operation of the UWC as a whole, it is necessary to know which components and assemblies are included in their composition. It is also important to imagine the structure of the system and the relative position of the elements.
The most complex and extensive is ventilation.
If we consider a mechanical forced intake-exhaust ventilation system, then we can distinguish its components:
- Air ducts, ducts and mines. It is a system of paths through which the inflow and exhaust of air masses. They are made of various building materials, most often - from metal;
- Power plants - fans and pumps. Provide the movement of the specified volumes of air with a certain speed and pressure;
- Control system, automation and protection. It is a complex of sensors, controllers and executing mechanisms that monitor and configure the system in real time according to specified programs and modes of operation. They can control the rotation of the fans, the opening and closing of valves, the operation of heaters, emergency switches and other equipment;
- Air preparation unit. Here filtering, recovery, heating / cooling and dehumidification / humidification of the air are carried out with the help of various units: filters, heaters, recuperators and dehumidifiers;
- Remote Control with the possibility of manual and automatic adjustment of the most important parameters and modes.
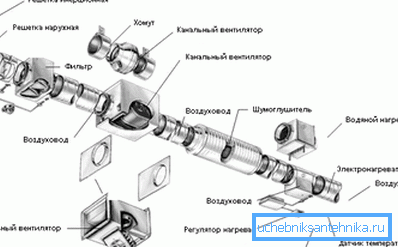
The heating system may consist of different units depending on its type:
- The centralized coolant supply system allows us to reduce its composition to the pipeline and radiators;
- The autonomous system, in addition to pipes and radiators, will be equipped with a heating medium heating boiler and circulation pumps to maintain the desired pressure and water flow rate;
- Wood heating is limited to the stove and chimney channels, which heat the house structure and air;
- Electric heating will consist of power systems, conductors and heaters. The latter can be with a liquid coolant (oil and water), with an incandescent spiral, with a tubular electric heater (heater) or an infrared reflector;
- A separate kind of central or autonomous heating system can be considered the “warm floor” system, since the floor screed plays the role of a radiator.
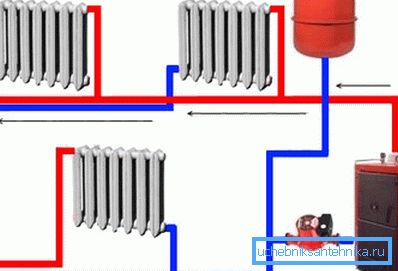
Depending on the design and logic of the HVAC operation, it can be used to heat the supply air, for which the heat transfer medium from the heating system can be used. Also, ventilation flows are often used for space heating, for example, in sports complexes one can see a heat curtain in the vestibule at the entrance, which is carried by masses of warm air and steam removed from the pool.
Finally, heat recovery uses the heat of the exhaust air to heat the supply mass, which also affects the air temperature in the room and saves energy for heating.
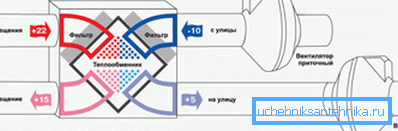
Air conditioning, of course, is included in the climate system completely. And partly it is ventilation, and partly - heating / cooling, therefore, when the air conditioner is on, the mode of operation of the general ventilation changes.
Note! In modern HVAC schemes, some nodes may be common, and the functions of others may be duplicated and interchanged. In general, they represent a unified climate system.
Considering that the price of equipment for a modern climate system is very high, it is desirable to carry out the design and installation by professionals and qualified specialists. It should be understood that in order to achieve the same results by the forces of independent units, the costs would have to be increased.
Regulatory requirements

The Gosstroy of the Russian Federation in 2004 adopted the SNiP on heating and ventilation under the number 41-01-2003, it regulates and determines the rules and regulations that the climatic equipment must comply with.
General provisions of the document require compliance with a number of technical parameters:
- Norms of meteorological conditions and air purity in the serviced zone inside the premises of residential and administrative buildings. GOST for this type of structures has the number 30494, and there is also a document SanPin 2.1.2.1002 on air quality;
- Norms of meteorological conditions and air purity in the serviced area inside the production, laboratory and storage facilities in accordance with GOST 12.1.005 or SanPin 2.2.4.548;
- Norms of noise and vibration load from the operation of equipment for HVAC systems and external sources in accordance with SNiP 23-03. For emergency and smoke-free systems in accordance with GOST 12.1.003, the noise level in rooms with equipment should not exceed 110 dBA, with a pulsed nature of noise - no more than 125 dBA;
- Norms of protection and protection of the atmosphere from harmful ventilation emissions;
- Norms maintainability of heating, ventilation and air conditioning;
- Norms for fire and explosive safety of climate equipment.

Note! All used pipelines, air ducts, thermal insulation structures and heating and ventilation equipment should be made of materials approved for construction. All materials subject to mandatory certification must have supporting documents for their use.
Special attention is paid to safety. All UWCs should be designed taking into account the safety requirements contained in the regulatory documents of the supervisory authorities, as well as the requirements of the manufacturer of equipment, materials and fittings, if these requirements do not contradict these rules and regulations.

In addition, the coolant in the internal heating systems must have a temperature 20 ° C lower than the self-ignition temperature of gases, aerosols and other substances in the room.
At the same time, the temperature should not exceed the maximum values specified in the technical documentation for valves, materials and equipment, as well as the values specified as the maximum in these rules and regulations.
If the temperature of the water inside the pipeline or radiator exceeds 105 ° C, then measures are needed to prevent boiling up. If the temperature of the accessible surfaces exceeds 75 degrees, the surfaces should be protected with fences or thermal insulation, especially when it comes to daycare facilities.

The temperature of the surface of thermal insulation should not exceed 40 ° C, while it should provide:
- Burn protection;
- Heat loss not exceeding the allowable;
- Protection against condensation;
- Protection of the coolant from freezing, if the pipeline is laid in unheated or cooled rooms.
You should also isolate hot surfaces of ventilation and heating equipment, chimneys, pipelines and ducts located inside the premises. On the surface of thermal insulation, the temperature should be 20 ° C lower than the ignition temperature of gases, aerosols and dust in the room.
For insulation adopted SNiP 41-03.

The intersection of air ducts with flammable and explosive substances by a pipeline is possible only if the difference of 20 ° C between the ignition temperature of the substance and the temperature of the pipe surface is observed. If the flash point is below 170 ° C, then such an intersection is unacceptable.
Air heating systems should not produce a flow that is hotter than 70 ° C when leaving the distributor. Air-thermal curtains at the outer doors are limited to 50 ° C, and at the external openings and gates - 70 ° C.
Note! When heating and ventilating premises, microclimate parameters are accepted according to GOST 12.1.005, GOST 30494, SanPin 2.2.4.548 and SanPin 2.1.2.1002. Standards for cold and warm periods of the year, as well as for different rooms are indicated in this document.
Maintenance of heating and ventilation systems is carried out by professional teams with their own emergency dispatch service.
Conclusion
Ventilation and heating are a single climate system, which is designed taking into account the interdependence of these functions. The parameters of HVAC systems are standardized and regulated by a number of official documents, where special attention is paid to safety. The video in this article complements what has been said with visual information.