Heating elevator: first acquaintance
In this article we have to find out what the elevator in the heating system is and how it works. In addition to the functions, we will study the modes of operation of the elevator unit and how to adjust it. So go.

What it is
Functions
In simple terms, elevator heating nodes are peculiar buffers between the heating main and house engineering systems.
They combine several functions:
- They convert the pressure difference between the lines of the route (3-4 atmospheres) into the 0.2 necessary for the operation of the heating circuit.
- They are used to start or stop heating and hot water systems.
- Allow you to switch between different operating modes of the DHW system.
Specify: the temperature of the water in the taps should not exceed 90-95 degrees. In summer, when the temperature of the water in the supply line does not exceed 50-55 ° C, the DHW is powered from this thread. At the peak of cold weather, hot water supply has to be switched to the return pipeline.
Items
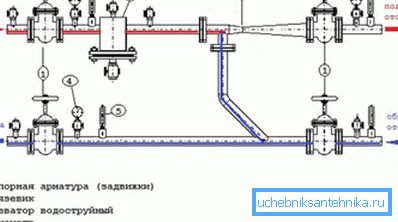
The simplest scheme of the elevator heating unit includes:
- A couple of input valves on the feed and return threads. Flow is always located above the return.
- A pair of house valves, cutting the elevator assembly from the heating system.
- Gryazeviki on the pitch and, rarely, on the return line.

- Dumps in the heating circuit, allowing to completely drain it or to reset the system to a discharge, expelling a substantial part of air from it at start-up. Discharges are considered to be good for drains.
- Control valves that measure the temperature and pressure of the supply, return and mixture.
- Finally, the actual water-jet elevator is a flanged tee for pipes with a nozzle inside.

How does the elevator heating system work? The principle of its work is based on the Bernoulli law, which states that static pressure in a flow is inversely proportional to its speed.
The hotter and higher pressure water from the supply pipe is injected through the nozzle into the elevator socket and creates, however paradoxically it sounds, a vacuum zone that draws a part of the water from the return pipeline into the repeated circulation cycle.
This ensures:
- Large coolant flow through the circuit with a minimum of its flow from the highway.
- Alignment of temperatures near to the elevator and distant heaters from it.
How are pressures measured during the heating season distributed? We give typical parameters.
| Measuring point | Pressure, kgf / cm2 |
| Feed after inlet valve | 6.0 |
| Return post | 3.2 |
| Mix after elevator | 3.4 |

Temperatures in the route and after the elevator are subject to the so-called temperature schedule, the determining factor in which is the outdoor temperature. The maximum value for the supply line of the route is 150 degrees: with further heating, the water will boil, despite the overpressure. The maximum temperature of the mixture is 95 C for two-pipe and 105 for one-pipe systems.
In addition to these elements, the heating system elevator may include hot water tapping.
Two basic configurations are possible.
- In houses built before the end of the 70s, the DHW is powered through one insert in the supply and one in the return line.
- In newer homes, there are two tie-ins on each line. A retaining washer with a diameter 1-2 mm larger than the diameter of the nozzle is placed on the flange for connecting the pipes between the inserts. It provides a drop sufficient to ensure that when turning on the DHW according to the schemes from the supply to the supply and from the return to the return, water is continuously circulated through the coupled risers and towel warmers.
Areas of responsibility
What is the elevator heating node - we somehow understood.
And who is responsible for it?
- The section of the route inside the house to the flanges of the inlet valves is the area of responsibility of the heat transporting organization (heat networks).
- Everything after the inlet valves, and the valves themselves are the responsibility area of the housing organization.
However: the selection of the heating elevator by number (standard size), the calculation of the diameter of the nozzle and retaining washers are carried out by heating networks. Homeowners only provide installation and dismantling.

Control
The controlling organization is again the heating network.
What exactly do they control?
- Several times during the winter, control measurements of temperatures and pressures of flow, return and mixture are carried out.. In case of deviations from the temperature schedule, the heating elevator is re-calculated with a bore or a decrease in the diameter of the nozzle. Of course, this should not be done at the peak of cold weather: at -40, access heating on the street can be grabbed with ice within an hour after the circulation stops.
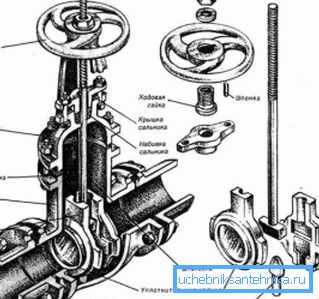
- In preparation for the heating season, the condition of the shut-off valves is checked. The check is extremely simple: all valves in the assembly overlap, after which any control valve opens. If water comes from it - you need to look for a fault; in addition, in any position of the valves, they should not have leaks over the glands.
- Finally, at the end of the heating season, the elevators in the heating system along with the system itself are tested for temperature.. The heating medium is heated to maximum values with the DHW supply turned off.
Control
We give the order of execution of some operations associated with the work of the elevator.
Start heating
If the system is full, all you need to do is open the house valves - and the circulation will begin.
Somewhat more complicated is the instruction for launching a dropped system.
- The discharge in the return pipe opens and the discharge in the flow closes.
- Slowly (in order to avoid water hammer), the upper house valve opens.
- After the water goes to the dump, it is clean, without air, it closes, after which the lower house valve opens.
It is useful: if modern ball valves are installed on the risers, the direction of the circuit to reset does not matter. But with a screw, a quick backflow can tear off the valve, after which the locksmith will have a long and painful search for the causes of the circulation stop in the risers.

Work without nozzle
At a catastrophically low return temperature at the peak of cold weather, an elevator without a nozzle is practiced. The system receives coolant from the highway, not the mixture. The choke is jammed with steel pancake.

Differential adjustment
When the return is too high and it is impossible to promptly replace the nozzle, it is practiced to adjust the differential valve.
How to do it yourself?
- The feed pressure is measured, after which the pressure gauge is placed on the return flow.
- The inlet valve on the return pipe completely closes and gradually opens with pressure control on the pressure gauge. If you just cover the latch - her cheeks may not fully fall on the rod and slide down later. The price of the wrong course of action is guaranteed unfrozen access heating.
At a time, no more than 0.2 atmospheres of differential should be removed. Repeated measurement of the return temperature is carried out in a day, when all values are stabilized.
Conclusion
We hope that our material will help the reader to understand the scheme of work and the order of adjustment of the elevator assembly. As usual, additional information will be offered to his attention by the attached video. Successes!