Heating pipe radiators: types and characteristics, the
The range of various devices for space heating in the modern market is striking in its diversity, now you can easily find products for almost every taste and budget. Nevertheless, heating radiators with their own hands are made of pipes, to this day. These structures can be welded or prefabricated, for this production different metals are used, and as for the forms, everything depends on the master's imagination. We will discuss all these subtleties further.

Which metal is better
To begin with, we note that structures of this kind can be intended both for heat transfer, performing the function of radiators, and for taking heat when the tubular register is mounted directly in the combustion chamber of a boiler or furnace.
Plus, in some models, instead of a liquid coolant, heated gas is used, for example, a radiator chimney.
- Steel pipes for radiators deservedly considered the leaders of this market sector. Of course, the heat output of steel is not as high as that of aluminum or copper, it is susceptible to corrosion and requires regular maintenance. But these shortcomings are more than offset by the affordable price, as well as a wide range of types and sizes. In addition, cooking ordinary ferrous metal is much easier than color.
- Stainless steel is rarely used for such constructions.. Apart from the fact that its cost, to put it mildly, is far from the budget, argon welding is used for soldering stainless steel, and not every professional welder can work with it.

Important: galvanized iron in this case simply does not make sense to use. A thin zinc coating during the welding process simply burns. As a result, the already weak weld is additionally affected by corrosion.
- The use of copper tubular registers is justified only in the case of copper wiring around the house. The heat output of copper is four times higher than that of ferrous metals, so here you can talk about heating with pipes without radiators, more precisely with a minimum number of radiators. But, firstly, the price of copper is fabulously high, and secondly, this metal is very demanding of operating conditions.

- Copper systems require a finely cleaned coolant that does not have solid abrasive impregnations.
- In such systems, fittings must be copper or from compatible metals, such as bronze, nickel, chrome or brass. Moreover, aluminum and copper is strictly forbidden to combine.
- Copper pipelines necessarily require high-quality grounding, as there is a danger of electrochemical corrosion.
- Copper is a soft material, so the system needs additional protection, naturally, covers and shields also cost money.
- The cast iron radiator heating pipes shown in the photo are still used in industrial buildings and technical rooms.. But the weight of this design is much higher than that of household cast-iron batteries. Given the non-aesthetic appearance and rather low efficiency, they are not popular.

Tip: cast iron tubular registers are perfectly suited for installation in the combustion chamber. Optimum heat capacity, low price and unpretentiousness in relation to the coolant make them leaders in this direction.
Types and characteristics of tubular radiators
From all the above, it becomes clear that there is practically no alternative to steel pipes. Although the appearance of constructions welded with their own hands is very mediocre, but for a garage, a greenhouse or a dacha, they are quite suitable, plus the instructions for self-assembly here are not complex.

Types of improvised tubular radiators
Self-made structures of this kind are often made serpentine or register. The configuration of the first laid in the title. The metal pipe is curved in the form of a snake, after which the connecting pipes and, in some cases, fastening strips are welded to it.

The whole-bent radiator naturally has significant advantages over welded structures. But to bend a steel pipe, you need a special pipe bender or at least a gas burner. Plus pipe diameter, as a rule, does not exceed 50 mm. Therefore, for more powerful systems it is customary to use register constructions.

There are no restrictions on the diameter of the tube for the radiator in the register system. The most commonly used are smooth round pipes from 32 to 150 mm in diameter.
Sections can be connected in two ways - in a string or in the form of a column. The connection thread, in fact, differs from the coil only by the presence of connecting pipes. Otherwise, it is all the same consistent snake.
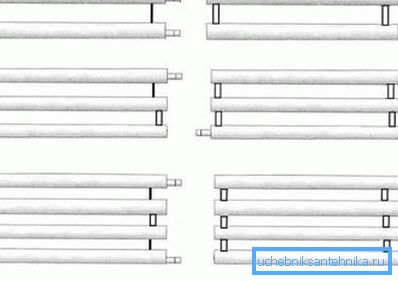
Column tubes are connected in parallel. That is, horizontally mounted sections of larger diameter, are interconnected by vertical lumps on both sides. It kind of resembles a standard factory radiator, just upside down.
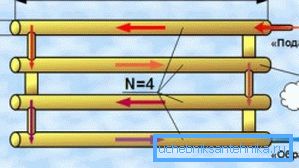
Such self-made registers can be connected to both one-pipe and two-pipe systems. The technical characteristics of the type of system is not reflected. Such registers, due to their large diameter and minimal hydraulic resistance, work best in heating systems with natural coolant current.
But do not forget that natural systems are mounted with a slope in the direction of the water flow, about 5 mm per 1 meter long.

Important: in the presence of a welding machine, a grinder and other auxiliary tools, it is also easy to assemble heating radiators from a shaped pipe with your own hands as well as from a round one. Of course, the hydraulic resistance here will be somewhat higher, but for pipes with a cross section of more than 50 mm, this error is not significant.
Both in self-made, and in factory designs products with fins or "plumage" are widely used. In this case, it is a question that metal strips or plates are welded on a smooth pipe. Due to increase in the area of metal, the thermolysis considerably increases. In particular, the pipe radiator for fireplaces, shown in the photo, works exactly according to this principle.

Calculate a homemade tubular radiator
Compared with the internal volume of the coolant, the area of contact of the radiator with air is small, so you should not expect high efficiency from such structures.
The problem can be partially solved by inserting a circulating pump into the system. But here it is necessary to be careful, the increase in pump power will inevitably entail the appearance of extraneous noise.

As already mentioned, the diameters of the pipes are in the range of 32–150 mm, this causes a large volume of coolant. On the one hand, the boiler will operate in a softer, sparing mode. But at the same time, energy for overclocking will be required many times more, and it is very difficult to control the temperature with a large volume.
Despite the simplicity of assembling self-made tubular radiators, there are still limitations. In particular, for effective system operation, pipes should not be too close. According to the rules, the distance between the sections should not be less than one and a half the radii of the main pipe.

In essence, such constructions are a very long pipe, bent in a certain way in order to make the system more compact. To calculate the number of improvised steel radiators, the same parameters are used as for conventional steel pipes. The table shows averaged data, focused on the middle lane of our country.
But if the right tables were not at hand, you can go the other way. For approximate calculations, specialists, as a rule, use a simple formula. The only thing that you will need to take from the tables is the heat transfer coefficient of the material. All other data can be obtained on site.

Pros and cons of self-made steel structures
- Perhaps the most important advantage is the low cost of such a battery. But this is true only if welding is not a problem for you and everything will really be done independently. If you pay for the work of the welder, the price of such a radiator can be equal to the cost of an inexpensive aluminum product from China.
- Such batteries, for the most part emit radiant heat energy, so that oxygen is not burned.
- It is much easier to care for volumetric smooth surfaces than for modern corrugated batteries.
- Steel easily withstands any working pressure and is not afraid of water hammer.
- Steel self-made batteries work equally well in a system with forced and natural circulation of the coolant.
We partially set out the disadvantages of such structures above. In particular, steel is susceptible to corrosion, such batteries need to be painted with heat-resistant paints, the design is very mediocre and, finally, the heat transfer leaves much to be desired.

The video in this article provides material on this topic.
Conclusion
Deciding what is best for heating pipes or radiators, should be depending on the specific conditions and type of room. After all, the expensive iron casting will also look ridiculous in the country greenhouse, like a steel home-made serpentine in a luxurious bathroom.
