Heating scheme: how to lay pipes for an autonomous heating
Before installing any heating system, it is necessary to determine the method of distributing pipelines. There are both well-known and frequently used single-pipe and two-pipe methods for arranging a climate network, as well as more exotic ones. These include the heating scheme for two wings, radial, multi-circuit and so on.
Read more about the most popular of them in the material below.
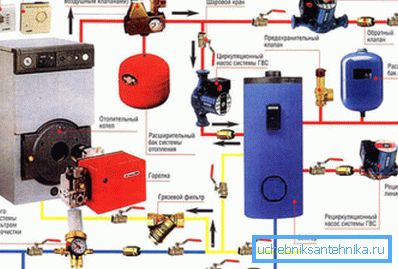
Varieties of heating systems
Before developing these or other schemes - heating with your own hands, hot water supply and the like - it is necessary to determine the type of climate system by the method of organizing the coolant current. From this directly depends on which method of laying pipes is suitable in your particular case.
The simplest version is the gravitational heating system, in which the coolant current occurs due to the difference in temperature and density of water flowing through the pipes. With such schemes, residents of cities living in the Khrushchev or another apartment building with a centralized supply of heat carrier are familiar firsthand.
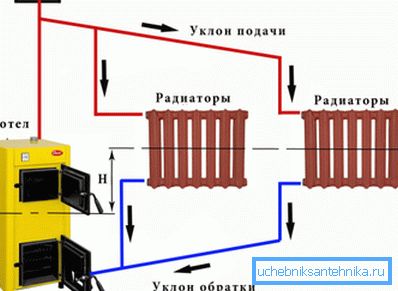
The principle of operation of the heating system with natural circulation is as follows:
- The water heated in the boiler becomes less dense and, accordingly, lighter, as a result of which it is forced out by heavy water masses to the upper point of the system.
- From there, the liquid flows through the installed pipes through the radiators installed in all the rooms, giving off heat energy to the air in the rooms.
- The cycle ends with the entry of cooled water into the boiler, where a new turn begins.
Note! To ensure the normal flow rate and air removal of their system, heating pipes should be placed at a gradient of 3-5 degrees towards the boiler. This is an obligatory requirement fixed by the SNiP.
The gravitational heating system has many advantages, however, its use is associated with some difficulties. All the pros and cons of operating the engineering network with natural coolant current are shown in the table.
| Benefits | disadvantages |
| Full autonomy. Heating, operating on the principle of gravity continues to function when a power outage. The main thing that the heating unit continued to properly heat the water in the pipes. | The complexity of installation. During installation, you must strictly observe the slope of the pipes, otherwise the cooled water will not fall to the boiler, and the released air will form a plug, which will cause the entire system to stop working. |
| Reliability. At installation of a network of heating the difficult electric equipment which can break or demands thin adjustment is not used. Everything is based on the laws of nature, which work independently of the engineering networks and units created by people. | With the help of a gravitational heating system, you can heat a house of no more than 200 square meters. meters In addition, the installation of a circulation pump is also necessary if the total length of the heating pipes exceeds 30 meters. |
| Easy operation. Just run the boiler and set the modes you need. After this, no intervention in the operation of heating is required. | The difference between the temperature of the water at the outlet from the boiler and in the return pipe is quite large. This adversely affects the operation of the heater and increases the fuel consumption required for heating. |
| Noiselessness Considering that no pumps are needed for heating, it works completely silently. | In gravitational heating systems, an open expansion tank is often used, from which the coolant evaporates. It is necessary to constantly monitor the water level and top up if necessary. |
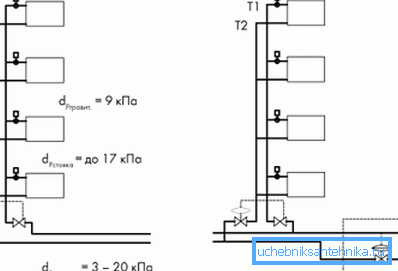
Gravitational schemes for heating buildings can also be used in individual construction. The only difference is that you can install an expansion tank and install from vertical risers not in the attic, but under the ceiling of the upper floor (of course, at the highest point of the climate system).
Therefore, you can safely take available in the building directories or the following typical heating schemes, upgrade them to your own needs and implement.
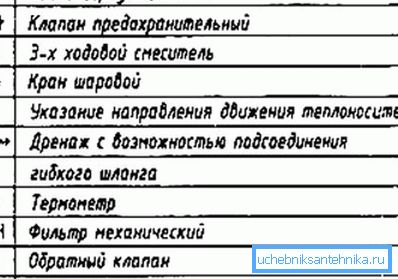
Tip! To understand the sketches and projects prepared by engineers, it is necessary to know the symbols in the heating schemes. There are few signs and they are intuitive, so memorizing them will not take you much time, but will provide an opportunity to easily navigate the construction documentation.
If you are not ready to put up with the drawbacks of the gravity system, you can use heating installation schemes with forced fluid flow. In this case, a mandatory element is a circulation pump installed on the return pipe.
Only having decided on the question considered above, it is possible to choose the scheme of laying of pipes.
There are several of them:
- single pipe;
- two-pipe;
- ray.
Let us dwell on this in more detail.
Ways of laying
Single pipe heating network
We will begin the analysis of the heating scheme with a single pipe, which serves both to supply water to the batteries and to transport the cooled liquid to the heating boiler.
If it is necessary to heat two wings or several floors of a house, it is necessary to divide the water flow into two or more parts using a tee. It is desirable to equip each circuit with shut-off valves, which, if necessary, cut it off without interrupting the operation of the entire system.
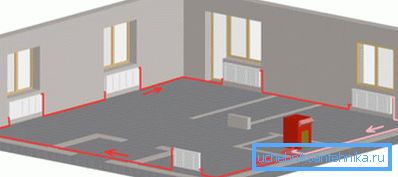
After passing through all the radiators, the flows must be again combined into one pipe, which is connected to the inlet of the heating boiler.
Radiators in one-pipe heating system can be connected in two ways:
- Consistent. In this case, the pipe supplying the coolant is connected to the inlet of the battery and to the outlet. No additional items are mounted. Coolant can not flow past the heating radiator.
- Parallel. Here, the water line is simply laid around the perimeter of the entire house, and the radiators are joined with the help of tees and tap-off sections. Plus the fact that the failure of a single battery does not disrupt the work of the rest of the heating system.
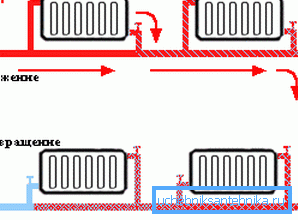
When arranging a one-pipe heating system, it is desirable to provide for the presence of the following elements:
- Valves at the inlet and outlet of the battery. With it, you will not only be able to regulate the volume of water entering the radiator and, accordingly, the temperature in the room, but also to repair or replace the heating element without draining the coolant.
- When connecting the inlet and the outlet of the battery in series before the shut-off valves, it is advisable to connect them with bypasses — sections of pipes of smaller diameter that will provide water flow in case of cutting off the radiator.

Two-pipe scheme of the heating network
The heating system with two pipes (supply and discharge) is more efficient, but requires more materials, because of which the cost of installation increases slightly. But the advantages are obvious. Its use, especially when paired with a circulating pump, allows you to more efficiently and evenly distribute thermal energy throughout the rooms of the house.
Instructions for constructing such a system will not cause difficulties for understanding even a novice master:
- Two pipes are laid from the boiler, one of which is connected to the outlet, the other to the inlet of the boiler. According to the first, hot water is supplied to the radiators, in the second, respectively, the already cooled coolant is delivered to the boiler.
- Insert radiators produced by branch pipes. The inlet is connected to the supply line, the output is connected to the return pipe.
- In order to avoid destruction of heating devices from overpressure, it is recommended not to install valves in the radiator outlet channel.
- Each battery must be equipped with an air valve — a Mayevsky valve, which is necessary to remove air plugs formed after pouring fluid into the system.
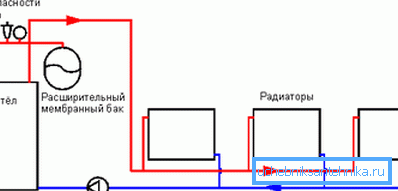
The advantages of the system are obvious, and as a drawback only greater material consumption can be noted - for a two-pipe system, two times more materials are needed than for a single-pipe one.
Collector diagram of the heating network
This is the most flexible and easily customizable heating system. Here you can accurately regulate the flow of coolant to each battery at home from one place - the collector cabinet. In the event of an accident, any battery is cut off using shut-off valves, making repairs easy and quick.
The scheme of the collector (ray) system is as follows:
- The main elements are two collectors: for the supply and discharge of the coolant.
- Each battery in the house is connected by a pair of pipes with the above-mentioned collectors. Thus, a separate circuit is organized for each radiator.

Radial heating scheme can be safely recommended for installation, if you are not afraid of the following nuances:
- for installation requires a huge number of pipes that need to be laid under the screed floor;
- the system must necessarily have a circulation pump, as it is not possible to observe the slope of the pipelines;
- during installation it is necessary to ensure that no fitting is installed under the screed, which can leak during the operation.

Conclusion
In addition to the methods of distributing main pipes considered above, which supply coolant to the batteries and deliver the cooled water back to the boiler, the connection diagram of the radiators (bottom, side, diagonal) is no less important. The correct connection not only increases the rate of circulation of the coolant and increases the efficiency of the batteries, but also prevents the occurrence of air plugs.
For more on this, see the video in this article.