Heating scheme with natural circulation of a private house:
In the 80s of the last century, experts said that the gravitational heating system became obsolete. However, this was not the case.
Pump devices of forced heating significantly raise its cost, besides that they depend on electricity. Therefore, in our time, part of homeowners from such heating refuses.
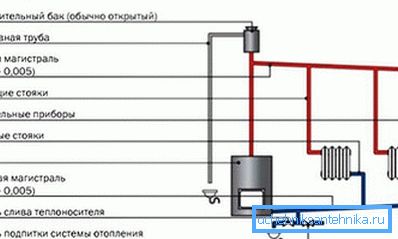
Note! The gravitational design of the heating system is the most simple and cheap. It has its drawbacks, the main one of which is the overall limit. Due to the small inertia, such a network is only suitable for buildings up to 100 m 2.
In this article we will talk about what is a scheme of a heating system with natural circulation, which has advantages and disadvantages.
What is such a heating
There are two types of heating schemes:
- system with a natural coolant flow (gravity, gravity);
- analogue with forced (pumping) circulation.
Both those and other networks can be one- or two-pipe.
The coolant in both cases are:
- ordinary water;
- antifreeze (i.e. non-freezing liquid)
- technical oil.
Note! If you plan to use antifreeze, check its compatibility with the material of the seals of the heating batteries. In such networks, the instruction does not recommend the use of aluminum radiators.
Natural circulation pattern
Self-flowing heating has several disadvantages:
- it is morally obsolete;
- has low productivity;
- the network is bulky;

- she has a relatively high cost of installation;
- it is not possible to separately regulate the temperature in each of the batteries.
However, it is indispensable in buildings where there is no electricity, because, equipped with a solid fuel heating boiler, it is able to work autonomously.
- The principle of operation of such a system is the formation of the temperature difference of the coolant on its flow from the boiler and the entrance.
- Due to differences in the density of the heat carrier during temperature variation, it moves through the system by gravity, without using a pump. In other words, the warm substance goes up, its already cooled stream takes its place from the return line.
- Flowing through the batteries in series, the heat carrier loses its temperature, radiating heat energy to the premises. Returning to the boiler, he again heats up and everything repeats.
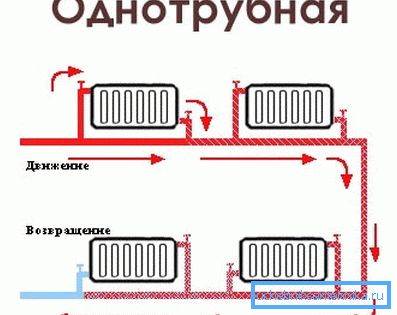
Consistent monotube heating
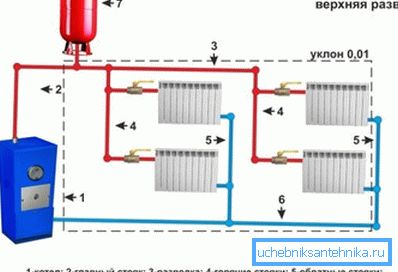
- For such a network to work, a prerequisite is a sufficient section of pipes.. It must be at least one inch. This primarily concerns the main riser. In addition, the slope of the system pipes must be at least 1 cm per 1 running meter.
- Another condition - the area of heat carrier intake from the riser pipe must be located above the top battery. At the same time, the heating boiler should be placed below the lowest radiator.
- The volume of heat carrier in such systems, with equal serviced area, is relatively large (3 times more, on average, than in compulsory analogues) and depends on the cross-section of pipes and the length of the network.
A large amount of water in the pipes increases the inertia of the system.
- This is an advantage of the system - when the boiler stops working, the heat in the network still lasts a certain period.
- The heating circuit with natural circulation implies that the successive flow of heat carrier through the battery leads to its cooling.
- So, those heaters, which are located at the beginning of the system, are heated more than their counterparts, installed at the end of the network.
- It should be noted that it is not possible to regulate the level of heating of the batteries in such a scheme.

Note! An important feature of such a system is its sensitivity to the material used pipes and fittings. Mounting the network with your own hands, please note that they must be metal. Pipes made of plastic will not be able to withstand the temperature resulting from overheating of water in the boiler.
- The result of such restrictions is a low level of heating efficiency, expensive installation (if the system is employed by hired workers), aesthetics of the network, due to the large cross-section of pipes.
- Heating circuits with natural circulation necessarily include an open expansion tank. It should be placed at the very top of the network. This tank should contain at least one tenth of all water in the system.
- The openness of the tank implies that the system must necessarily have constant contact with the pressure of the atmosphere.
Parallel battery connection
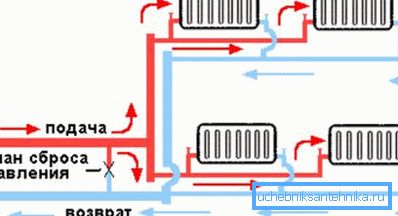
- The scheme of water heating with natural circulation can be one-pipe series-parallel. Then it becomes possible to regulate the flow of coolant in some radiators. (See also the article Single-pipe heating system: features.)
- It should be noted that in this case it will be possible to install thermostats only for every second parallel battery.
- A closed flow of water in the network is completely strictly forbidden to block, because of its overheating.
There is also a two-pipe version of parallel (horizontal) connection of batteries during the natural circulation of the coolant. In it, the temperature of the radiators is not so much dependent on their location. It is possible to adjust individual batteries.
Conclusion
The gravitational heating system has both its disadvantages and advantages. However, in some cases described above, it is the optimal choice of the heating scheme of a private house. The video posted in the article will continue its theme.