Heating system of a private house: how to choose the best
You can heat the building in different ways and using different energy sources, but the heating system in a private house, which is thought out to the smallest detail, will always be the best option.

If we are talking about the system, then, as a rule, there are three main types of it, it is:
- radiator circuit;
- warm floor;
- infrared film.
Although the fourth method is possible, it is a combination of two or even three types. We will tell you the main nuances of such devices, consider heating boilers and show a video clip on this topic.
Boilers
Gas
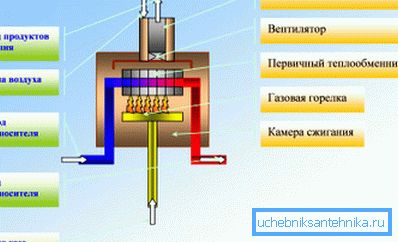
- Most often, heating systems for a private house operate with the help of traditional (convection) gas boilers, with the help of which they usually supply the radiator circuit or a combined variant - radiators plus a heated floor. The boilers work according to the scheme that you see in the upper image - the gas is supplied through a pipeline to the burner located in the fuel chamber and that, in turn, heats the heat exchanger, from which the coolant spreads around the entire circuit. Hot air, along with the products of combustion is discharged to the street through the chimney.
- The optimal temperature for such a device, the instruction recommends maintaining in the range of 60-80? C - so you can save the greatest life for the heat exchanger. The thing is that there is a point of formation of condensate - 55-57? C, but the condensate here turns out to be acidic, from the products of gas combustion, therefore the walls of the heat exchanger begin to collapse. This is the most common system of water supply and heating in a private house.
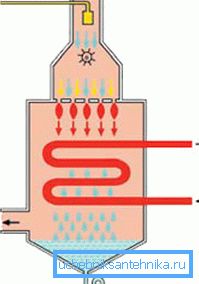
- In cases where the house has a floor heating system, it is best to use condensing gas boilers, also called low-temperature, to heat it.. The optimal mode of operation of such devices is in the range of 30-50? or 30-60 ?, although the working format reaches 100-110 ?, that is, they can be used not only for low, but also for high temperatures. It is noteworthy that the efficiency of different models reaches 109-111% and, although their price is higher than that of convection ones, such units pay off with interest over time.
- The principle of operation here is fundamentally different from traditional boilers, although the gas burner still heats the heat exchanger, but the secondary heat is not diverted outside, but is also used for heating.! Here, acid condensate is discharged through a special pipeline through the filters, which falls down in the process of formation. It is this moment of preservation of secondary heat that makes it possible to achieve such a high, even, at first glance, impossible coefficient.
Liquid fuel
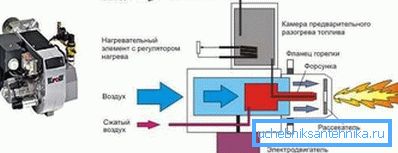
- In cases where there is no gas pipeline in the village, heating systems for private houses can operate from liquid fuel boilers, where solarium is most often used as an energy source.. The body of such a unit is usually made of cast iron and this is a floor option, although there are steel ones that can be made to be mounted on the wall, but, despite the powerful heat-insulating layer, the mounted models do not enjoy success.
- In diesel engines, as well as in gas units, the flame from the burner also heats the heat exchanger, which is made of heat-resistant steel, but more often of cast iron - due to the thick walls, the service life of the device increases significantly. Diesel heater burners can be single-stage, two-stage, and modulated - this is the main difference between boilers. If on a single-stage equipment only one combustion mode is possible, and on a two-stage one, two modes are possible, then the modulated device allows you to set the heating power at your discretion.
Solid fuel

- Also, heating systems of private houses can be powered by traditional solid fuel boilers, the principle of operation of which is very similar to the usual cooking stove, and wood and coal and firewood (briquettes, pellets, etc.) are used as energy carriers.. Heat exchangers for such units are made either from heat-resistant steel or cast iron, although the second option is most preferable - due to the thick walls, the service life increases. The efficiency of the boiler is significantly increased due to the various valves that regulate the air supply to the furnace and thrust channels.

- And here is another type of unit operating on solid fuel - these are gas-generating or pyrolysis boilers, where the fuel burns almost without residue, but there are two chambers - the main combustion and afterburner. The principle of their work is as follows: coal or firewood inflame in the main firebox, after which oxygen is partially blocked there, which contributes to the process of pyrolysis (thermal decomposition) - this is accompanied by abundant smoke. Smoke enters the afterburner chamber, where hot air from the first chamber is also supplied and these unburned products of thermal decomposition burn to the end.
- Gas-generating boilers are very convenient for home use - their installation allows you to bookmark after 4, 6, 8 or 12 hours, and in some models this process is allowed after two or even three days! The range of laying fuel depends not only on the design of the boiler, but also on the fuel itself, for example, models working on coal have the rarest range (up to three days). The efficiency of such devices reaches 85%, and the smoke exhaust is minimal - you can safely hang clothes on the street without fear for its cleanliness.
Electricity

- The main advantage of any electric boiler over alternative types of the above-mentioned units is the absence of a chimney that needs to be brought outside - it is simply not necessary here, since there are no thermal decomposition products. Such devices can function (depending on power) from the AC 220 / 380V 50Hz network, although single-phase heaters are usually used for domestic purposes.
- The optimal mode of operation offered by the manufacturer is mainly in the range of 60-80? C, although the maximum is allowed 85? C, and at 90? C the automatic disconnection of electric heaters is activated. The highest efficiency of such heaters is 93% (higher only for condensing boilers), and from 220V you can choose models with a capacity of up to 9 kW - this is enough for heating 90m2 living space.

- Everyone knows that the frequency of the current in our networks is 50 Hz and the operation of the electrode boiler directly depends on this. The coolant passes through its body and the electrodes themselves are immersed in a liquid. And in this case, when power is applied, the ionization process occurs. Considering that the electrodes change their polarity 50 times per second, the ions also change the direction of motion with the same frequency, which causes the liquid to heat up.
- These boilers can operate on AC 220 / 380V 50Hz on distilled or low-temperature water that does not freeze at -40? C, as well as on liquids whose boiling point is not lower than 100? C and they are certified by the manufacturer.
Note. There are also universal boilers that combine two or three types of fuel, for example, electricity and gas, gas and diesel, solar, gas and electricity. But such units are not particularly popular, since they do not provide complete returns in any of the modes.
Heating systems
Bandwidth
For proper installation of the heating system of a private house with your own hands, you need to accurately calculate the capacity of the pipes, relative to their diameter, in order to ensure sufficient heating of the room. For such calculations, you can use the formula D = v354 * (0.86 * Q /? T) / V, where D is the diameter, Q is the load in kW per test area,? T is the temperature difference on the supply and return tubing, V is the speed liquids in m / s.
But you can also use the table below.
| Consumption | Pipe capacity (kg / h) | ||||||||||
| Du pipe | 15 mm | 20 mm | 25 mm | 32 mm | 40 mm | 50 mm | 65 mm | 80 mm | 100 mm | ||
| Pa / m | mbar / m | ?0.15 m / s | ?0.15 m / s | 0.3m / s | |||||||
| 90.0 | 0,900 | 173 | 403 | 745 | 1627 | 2488 | 4716 | 9612 | 14940 | 30240 | |
| 92.5 | 0.925 | 176 | 407 | 756 | 1652 | 2524 | 4788 | 9756 | 15156 | 30672 | |
| 95.0 | 0,950 | 176 | 414 | 767 | 1678 | 2560 | 4860 | 9900 | 15372 | 31104 | |
| 97.5 | 0.975 | 180 | 421 | 778 | 1699 | 2596 | 4932 | 10044 | 15552 | 31500 | |
| 100.0 | 1,000 | 184 | 425 | 788 | 1724 | 2632 | 5004 | 10152 | 15768 | 31932 | |
| 120.0 | 1,200 | 202 | 472 | 871 | 1897 | 2898 | 5508 | 11196 | 17352 | 35100 | |
| 140.0 | 1,400 | 220 | 511 | 943 | 2059 | 3143 | 5976 | 12132 | 18792 | 38160 | |
| 160.0 | 1,600 | 234 | 547 | 1015 | 2210 | 3373 | 6408 | 12996 | 20160 | 40680 | |
| 180.0 | 1,800 | 252 | 583 | 1080 | 2354 | 3589 | 6804 | 13824 | 21420 | 43200 | |
| 200.0 | 2,000 | 266 | 619 | 1154 | 2488 | 3780 | 7200 | 14580 | 22644 | 45720 | |
| 220.0 | 2,200 | 281 | 652 | 1202 | 2617 | 3996 | 7560 | 15336 | 23760 | 47880 | |
| 240.0 | 2,400 | 288 | 680 | 1256 | 2740 | 4176 | 7920 | 16056 | 24876 | 50400 | |
| 260.0 | 2,600 | 306 | 713 | 1310 | 2855 | 4356 | 8244 | 16740 | 25920 | 52200 | |
| 280.0 | 2,800 | 317 | 742 | 1364 | 2970 | 4456 | 8568 | 17338 | 26928 | 54360 | |
| 300.0 | 3,000 | 331 | 767 | 1415 | 3078 | 4680 | 8802 | 18,000 | 27900 | 56160 | |
Proportional relationship between throughput and pipe diameter
Note. The boiler power for your system can be determined if you know the size of your house. With ceilings up to 260 cm, the quadrature is taken into account, and at higher rooms, the cubature of the house is already needed. Such indicators are usually found in the accompanying documentation of the boiler.
Heating circuits
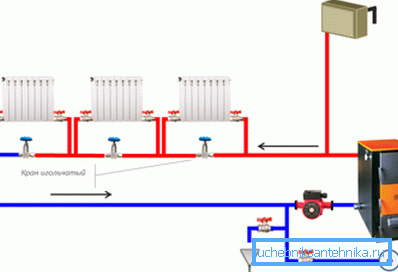
For a start, let's see how the radiator heating system is made in a private house with your own hands, because it can have either one or two circuits (one-pipe, two-pipe). If only one main pipe is laid from the heating unit, which is looped back to supply and return liquid, then in a building with a large area such a scheme would not be entirely effective.
The problem here is that each battery, getting coolant from the main pipe, returns it there too, therefore, with each successive radiator, the water in the system will cool more and more.
Even if you install shut-off valves (taps) between the supply and return connections, as shown in the upper image, this will only be beneficial for this battery, and in the next one the water will be even colder. Such systems are effective when no more than 3-5 devices are connected in the circuit, therefore, in large houses it is better to refuse it altogether.
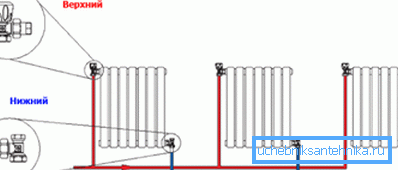
The most profitable and convenient two-pipe heating system in a private house, that is, for the supply and return of coolant from the boiler to the boiler are different heating pipes, as can be seen from the upper schematic drawing. Connecting batteries to the highway here can be done in different ways - from below, above and diagonally.
The temperature of the water in the supply pipe in a two-circuit system is practically unchanged throughout its length, since there is no inflow of cooled liquid, therefore, the heating of all radiators from the beginning to the end of the system will be the same.
Here it is very important to correctly calculate the diameter of the pipes, since as it increases, the volume of the liquid increases, and with it the energy costs for the boiler increase.
In the private sector, pipes with a cross section of 25-40 mm are usually used for risers, and 20 mm for radiators.
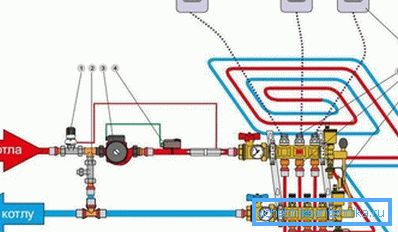
- Control valve with temperature sensor;
- Balancing valve;
- Circulation pump;
- Safety thermostat (invoice);
- Electric manifold valves;
- Collector;
- Bypass (needed in high-temperature boilers);
- Room thermostat.
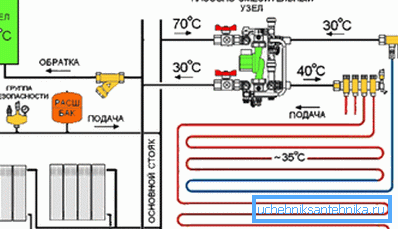
In the case of combining radiators with a warm floor, you will need to supply coolant with different temperatures - to batteries in the range of 60-80? C, and to the floor contour - 30-50? C.
To accomplish this separation, you will need a pump-mixing unit, which usually consists of a bypass. A three-way valve cuts in to adjust the hot flow. When the fluid in the pipe of a warm floor reaches the desired temperature, the valve from the supply pipe directs it not to the heated floor, but simply drops it into the return pipe until the thermostat gives a command to heat the circuit.
Conclusion
Some users are interested in how to flush the heating system in a private house, but this is quite an extensive topic, which should be highlighted in a separate article. We say only that this is done first with cold and then hot water with the addition of bleach and a compressor. The circuit is disconnected from the boiler by means of stop valves (taps).