Heating system with natural circulation: 2 ways to install
Regardless of the type of boiler used, in order to effectively heat a house or an apartment, it is necessary to properly organize the circulation of coolant through pipes and radiators installed in the dwelling. The most effective and widely distributed gravitational system. The principles of its work, the existing varieties, as well as how to design heating with natural circulation with their own hands will be discussed below.

Principle of operation
There are two main schemes of arrangement of engineering networks of heating:
- Heating system with forced circulation. In this case, pumping equipment is used, thanks to which water is supplied in the right direction. The disadvantages of this solution are the noise produced by electrical devices, as well as the dependence of heating on the availability of electrical energy.
- House heating with natural circulation. In this case, the flow of water from the boiler to the radiators and back is provided by changing the thermodynamic characteristics of the fluid.
The essence of its operation is as follows: water expands when heated, as a result of which its density decreases, and the liquid is pushed into the upper part of the heating system. As it cools, the coolant gradually goes to the boiler along the pipes laid obliquely, after which the cycle resumes.
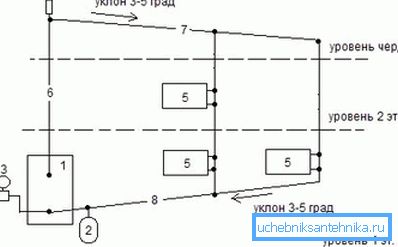
Note! Natural circulation of heating is possible only with properly mounted pipes and the presence of an expansion tank. The latter is necessary to remove air from radiators and create the necessary pressure in the engineering network.
The disadvantages of the described scheme include the fact that the water heating system with natural circulation has considerable inertia and is poorly suited for heating large areas (100 square meters and above) or houses with 5 or more rooms.
Circulation head
In order for the heat exchange organized by the coolant to be most effective, it is necessary to correctly calculate the heating system with natural circulation.
It is important to consider the following indicators:
- the difference in height between the location of the heat exchanger of the boiler and the drain hole of the lowermost radiator of heating - the greater this value, the better the liquid will circulate;
- the temperature to which water is heated in the chamber of a gas, electric or solid fuel boiler - the greater the difference, the more efficient the system will work;
- installation height of radiators and the angle of inclination of pipelines - the higher this indicator, the more effectively the cooled coolant will overcome the internal resistance at the reverse current to the boiler.
Note! The heating boiler must be located below the radiators, otherwise cold water will not be able to reach the heat exchanger. For this reason, individual heating by natural circulation is not used in urban apartments, as there is no space for the installation of the heater.
When designing any heating system, it is also necessary to correctly calculate the power of the central element - the boiler - which heats the coolant supplied to the radiators.
To do this, apply the following formula:
W = Wud * S / 10, where:
- W is the required equipment power, kW;
- Wud is the coefficient of correction for a geographical area (from 0.7 to 1.5 depending on the climatic zone);
- S - area of heated premises, sq.m.
Pipeline Ways
Heating of a private house with natural circulation can be installed in two fundamentally different schemes.
They differ in such features:
- by joining radiators of water heating with main pipes supplying water - there is a one-pipe and two-pipe scheme (the price of the latter is higher due to the increased consumption of materials, however, it is more efficient);
- the place of laying the main water pipelines - they can be at the top (above the radiators) or below (along the floor);
- water pipe arrangement scheme - dead-end (water is supplied to each radiator separately and is removed from it in the same way) or by-pass, when all the heating radiators pass through the heat transfer medium from the upper to the lower point;
- arrangement of risers - they can be fixed horizontally and vertically.

Method 1. Monotube gravity heating system
Natural heating, made under the scheme with a single pipe, can have only the upper wiring of main canals. In this case, as the name implies, a supply line is installed, where the fluid returns after flowing through radiators.
In this case, the natural flow of the fluid is organized due to the difference in its temperature and, as a consequence, its density.
If the gravitational heating system is mounted in a two- or three-storey house, as the number of floors increases, the area of heating radiators must be reduced. In this case, despite the decrease in the temperature of the coolant, the heating will be uniform.
Pipes in a single pipe heating system can be installed in two ways:
- parallel - part of the water enters the radiator, and the rest of the coolant through the main channel passes further (the advantage of this solution is that using manual or automatic valves, you can limit the amount of hot water supplied to the heating panel, and thereby reduce the temperature in room);
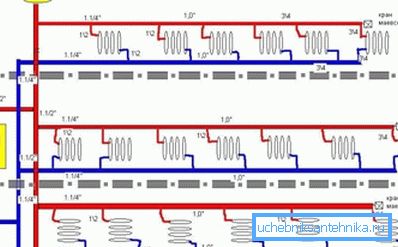
- flow through - in this case, the entire volume of heated water flows through each heating panel in the house (you will not be able to regulate the volume of water supplied to the radiator, as well as to completely shut off its supply, as this will lead to a malfunction of the entire system).
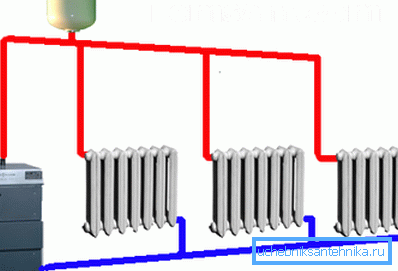
Tip! A more optimal scheme can be considered parallel. It makes it possible to regulate the temperature regime separately in each room. This saves energy (gas, diesel fuel, and so on) and creates a more comfortable indoor microclimate.
Considering that water supply in a single pipe system can be carried out only through one channel, the arrangement of this type of heating is possible only in buildings that have an attic floor where pipes with water heated in the boiler are placed.
The disadvantages of the one-pipe scheme include the inability to partially start the system, the advantages are lower cost due to the smaller amount of materials and installation work, as well as aesthetics.
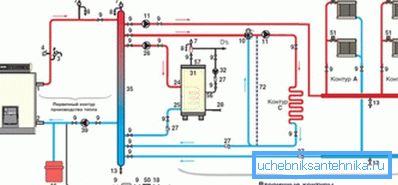
Method 2. Two-pipe gravity heating network
In this case, the installation of two pipelines is necessary:
- Inbound. It delivers a preheated heat carrier to the batteries. A pipe is drawn from the boiler, which enters the expansion tank, which is necessary to create pressure in the line. From it water mains go to the radiators. The volume of the expansion tank used depends on the size of the heating system. In some cases, this device must be equipped with an overflow pipe that removes residual liquid.
- Coming out. Through this pipeline, the cooled water is transported to the heat exchanger of the boiler for heating. The cold line should be laid in the same premises where the supply channel was mounted. This is a more efficient scheme, as it allows better control of the temperature regime in the rooms. Its disadvantages - the high cost of installation and bulkiness.

Choice of construction riser
There are two main options:
- Vertical riser. In this case, all the pipes from the radiators are joined to the central element passing through each floor of the house. The advantages of its use include the absence of the risk of air traffic jams, the disadvantages are the high cost (more pipes connecting the central pipe with radiators are needed).
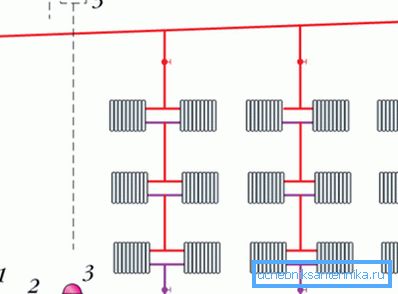
- Horizontal riser. All heating panels on each floor are connected to one supply line. More economical option. However, in this case, it is necessary to additionally install special air valves, which prevent the “airing” of the heating network, which affects its efficiency.
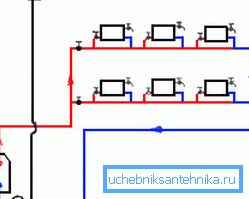
Advantages and disadvantages
The use of a heating system with natural circulation of the coolant has many advantages, the main ones of which include:
- easy installation, commissioning and maintenance;
- maximum efficiency - the gravitational heating network has a high efficiency and makes it possible to regulate the temperature regime of each room separately;
- profitability - gravity heating network is one of the least expensive among the existing home heating systems (if you take measures to reduce the thermal conductivity of the walls, floor and roof);
- noiselessness - the absence of working electrical equipment minimizes the noise that accompanies the operation of the climate system;
- non-volatility - a gravitational heating network put into operation will also work in the event of a temporary cessation of electricity supply, which otherwise would be needed to power the pumps;
- Long service life - with proper installation and proper maintenance, heating equipment will last more than 35 years without the need for major renovation.

The main disadvantage of heating with natural circulation is the impossibility of its use for large buildings. Due to the low pressure of the liquid, the length of the horizontal sections of pipelines should not exceed 30-35 meters, otherwise the efficiency of the system will significantly decrease.
In addition, you must have a technical floor in the upper part of the building where the expansion tank is mounted.
Also, due to low inertia, it is recommended to avoid laying pipes in unheated rooms, as there is a risk of freezing of the coolant and, as a result, violation of the integrity of pipelines.
Conclusion
A system with natural circulation is perhaps the best solution for arranging the heating of a small country house. However, it is absolutely not suitable for a city apartment, a summer house, where people and a cottage with an area of more than 100 square meters are not expected to live year-round. meters In this case, it is better to dwell on other heating methods, which are described in the video below.