How to calculate heating radiators without the use of
Batteries, the price of which is low, are the most common heating device used everywhere: in residential, commercial, industrial and public buildings. They consist of metal hollow elements filled with coolant.
When heated, they give energy to the rooms.

Components of calculations
- Before purchasing devices, one should pay attention to their two technical characteristics: power and withstand pressure of the heat-transfer fluid.
- It is necessary to calculate not only the number of devices and elements in them, but also to choose the material of the radiators.
- The main thing that needs to be determined is the ability of one section to release the maximum amount of heat energy. That is, you need to know how to calculate the power of radiators.
- This value will be the basis of calculations for the entire heating system.
Power calculation

- The instruction says that at 1 m? rooms require 100 watts of heat. Knowing this, you can determine the number of radiators you need. Therefore, first of all you need to know the area of the room that will be heated.
- When calculating, one should also take into account the height of the room, the number of doors and windows and their material. These factors determine the heat loss in the room.
- Before calculating a heating radiator, you should determine the lowest temperature in your area and the temperature of the heat carrier in a given period of the year.
Note! All calculations must be made using the coefficients, they are contained in the SNiP. Given these numbers, you can accurately determine the performance of heating.
A preliminary calculation is carried out simply: it is necessary to multiply the area of the room by 100 watts. However, such calculations will not be accurate. To adjust them and need coefficients.
Performance Correction Factors
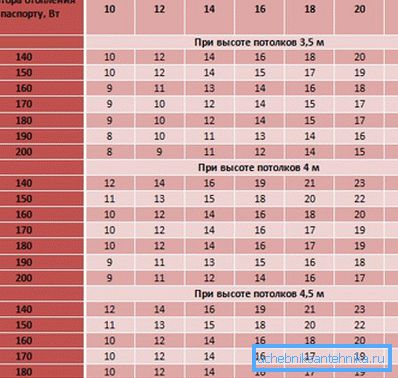
There are two types of factors: reducing and increasing power (see also the article Two-pipe or one-pipe heating system - the eternal question).
The first of them are applied in the following cases.
- If the window units are multi-chamber plastic windows, the preliminary figure is multiplied by 0.2.
- When the height of the room is less than the standard (3 meters), the reduction factor will be the ratio of the actual height to the standard equivalent. So, if the height of the room is 7 m, then the coefficient: 2.7: 3 = 0.9.
- When the heating boiler is operated at increased power, then every 10 ° of the heat energy generated by it reduces the capacity of the batteries by 15%.
Power factors are applied in the following circumstances.
- When the height of the room is higher than the standard, the coefficient is calculated in the same way as in the case of low ceilings.
- When the apartment is butt, then before calculating the capacity of the heating radiator, the coefficient 1.8 is used to increase this indicator.
- If the batteries are connected from below, then 8% are added to the base digit.
- When the heating boiler reduces the temperature of the heat carrier in the coldest time, for every 10 ° decrease it is necessary to increase the radiator capacity by 17%.
- In the case when negative street temperatures reach critical values, the power must be increased by 2 times.
How to determine the number of sections of one battery

In the professional design of heating systems, experts use the following indicators and data.
- Regime temperatures in the region in winter.
- Total heat loss of all surfaces of the building.
- Battery connection diagram.
- The number of doors and windows (the number of cameras), their dimensions.
- The frequency of air exchange rooms with adjacent rooms and the street.
- The design temperature of the supply and return flow of the coolant, as well as the speed of their circulation.
- The thermal power of the battery, its temperature mode.
- Operating pressure in the heating system.
Simplified Calculation Techniques
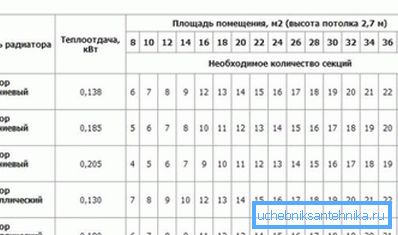
Professional calculations are very complex, so experts suggest doing their own hands more simple methods of calculation, which are suitable for small private houses and apartments.
- The first method is the simplest. In the passport of the goods sold, its technical characteristics must be indicated. Among them is the power of one section declared by the manufacturer.
How to calculate the number of radiators of this method.
Suppose the parameter is 200 watts. Next, we determine the power required for space heating, taking into account the coefficients.
Suppose it is 2.4 kW. Then it became a simple mathematical operation: 2400: 200 = 12. So many sections should be installed to effectively heat this room.
- The second way is to carry out the calculation, taking into account the ability of one section to warm the volume of the room specified by the manufacturer. For this purpose, the volume of the room is calculated, and then divided by the amount of volume heating of one section.
- Further practical advice from the masters, how to calculate bimetallic radiators of heating.
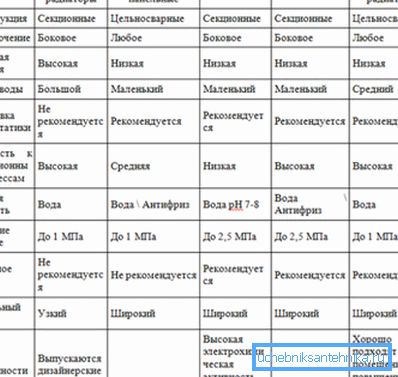
Note! All batteries from different materials have almost the same dimensions. Practitioners have noticed that with a room height of 2.7 m, one section of any device can heat an approximate area of 1.8 m ?.
Suppose a room has a size of 20 m. We carry out the calculation: 20: 1.8 = 11.1. That is, it will be necessary to assemble a battery of 11 sections.
Conclusion
As it was possible to understand from the article, for an apartment or a small house it is not difficult to calculate and the number of heating devices. If we are talking about a large building, then it is better to use the services of specialists (see also the article Whether the floor-mounted two-pipe heating system of a two-story private house is profitable).
Video in the article will help to learn about its topic even more.