How to calculate the diameter of the pipe for heating: a
How to calculate the diameter of the heating pipe, what should be the inlet to the radiator, and what - filling? It is clear that hydraulic and heat engineering calculations are extremely complex; However, perhaps there is some kind of simplified algorithm, even if it gives an approximate result?
Let's figure it out.

Description
Indeed, we can offer the reader the simplest scheme of approximate calculation. It comes down to using the table of heat flow dependencies at a constant delta of temperatures on the diameter of the pipeline and the speed of the heat carrier (see also the article What is the best pipe for heating: an analysis of the 4 most common options).
Given the fact that the diameter pitch of the pipelines used in heating systems is quite large, the error will have little effect on the result.
However, we must understand that we deliberately neglect a number of factors.
- Pipe material affects its hydraulic resistance. Steel with its roughness will inhibit the flow more than smooth polypropylene.
Note: over time, the difference in hydraulic resistance will increase. The steel surface will gradually become overgrown with rust and lime deposits, and the plastic will remain the same smooth and after 30 years of operation.
- Each turn or diameter transition further increases flow resistance.
- The same effect on it has valves. The pressure will inevitably fall on each valve and throttle.

There is some good news. Since the value of the heat flow is given for fixed values of the coolant velocity, it will remain unchanged for any changes in the configuration of the heating system.
Our task is only to ensure the appropriate values of speed; This will allow the use of a multi-stage circulation pump, the price of which is not much higher than that of a single-speed pump.
Initial parameters
So, how to choose the diameter of pipes for heating?
First you need to decide on the boundary conditions.
- For calculations, we use a temperature delta of 20 ° C typical for an autonomous radiator heating system.. As a rule, the flow temperature is maintained at about 75 ° C, the return flow - 55 ° C. Thus, we provide the maximum resource of the polymer elements of the pipeline, high heat exchange efficiency and avoid the formation of condensate on the heat exchanger in the boiler.
To clarify: of course, we are talking about solid fuel and gas heating equipment. For obvious reasons, the electric boiler of condensate on the heat exchanger is not afraid.

- The speed of the coolant should normally be about 0.6 - 1 meter per second. At smaller values of delta temperature in the circuit, any longer extent will inevitably exceed 20 degrees. At higher (1.5 m / s and more) - hydraulic noise will become noticeable.
Payment
Actually, the calculation of which diameter of the pipe is needed for heating consists of two operations.
- First, we calculate the need for thermal power for the house as a whole or a separate room.
- Then we check the table according to which we select the diameter for the required heat flow and coolant velocity.
Thermal power
The instruction for calculating the heat demand of a private house is as follows:
- The base value is taken as 60 watts per cubic meter of internal volume of the room.
Note: when calculating the heat demand of an apartment, this value is reduced to 40 W / m3. The building envelope is in contact with the cold street; the apartment is surrounded by warm rooms.
- Each window adds 100 watts to heat demand; door leading to the street - 200.
- Finally, in a warm and cold climate, real heat loss will vary. To compensate for this factor, a regional coefficient is introduced: 0.7–0.9 for the southern regions (Krasnodar Territory, Crimea), 1.2–1.3 for the central regions (Moscow and Leningrad Oblasts), 1.5 for the Far East and 2 , 0 for Yakutia and Chukotka.

Let us, as an example, calculate the need for heat of one floor of a house measuring 6 x 12 x 3.2 meters with four windows and two doors.
Location - Crimea.
- The volume of the room is 6 x 12 x 3.2 = 230.4 m3. Multiply by 60 W / m3: 230.4 x 60 = 13824 W.
- Four windows and two doors to the street will increase the need for heat to 13,824 + (100 x 4) + (200 x 2) = 14,624 watts.
- Crimea with its warm winters will make its own adjustments: 14,624 x 0.7 = 10,236.8 W, or 10 KW.

Diameter
Now it remains a mere trifle - on the basis of the need for heat to decide what diameter pipe to choose for heating. For this purpose, we will need reference data.
| Internal diameter, mm | Heat flux for temperature delta 20 ° C at the speed of the coolant, m / s | ||||
| 0.6 | 0.7 | 0.8 | 0.9 | 1.0 | |
| 12 | 5518 | 6438 | 7358 | 8277 | 9197 |
| 15 | 8622 | 10059 | 11496 | 12933 | 14370 |
| 20 | 15328 | 17883 | 20438 | 22992 | 25547 |
| 25 | 23950 | 27942 | 31934 | 35926 | 39917 |
| 32 | 39240 | 45780 | 52320 | 58860 | 65401 |
| 40 | 61313 | 71532 | 81751 | 91969 | 102188 |
| 50 | 95802 | 111768 | 127735 | 143702 | 159669 |
Obviously, for our purposes, a gasket for filling with a pipe with an inner diameter of 15 millimeters is sufficient at a flow rate of coolant of 0.7 m / s.
Nuances
- As it is easy to see, it’s not possible to do free-hand calculations for individual 1-3 KW heaters using this table. However, it is not required: pipes with an internal diameter of less than 12 mm you simply do not buy in the store.
- For polymer and metal-plastic pipes, sellers usually indicate not internal, but external diameter. Do not forget to take into account the thickness of their walls.
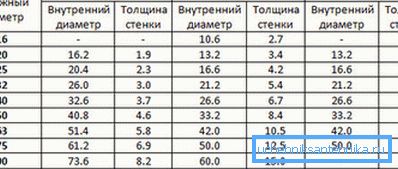
- If the filling of a single-pipe system should have a constant diameter, then in the case of a two-pipe scheme, the cross-section can be reduced as the distance from the boiler increases. The calculation is performed separately for each section, taking into account its heat demand.
Conclusion
We hope that this calculation will help the reader to avoid unnecessary problems and costs when building a heating system in their own home.
As usual, the video in this article will offer additional information. Successes!