How to calculate the heating in the apartment and house in
It does not matter what you buy a boiler or lay a pipeline from it, if you can not properly distribute the heat energy in the room. The radiators are responsible for this and our task today is to explain how to correctly calculate the number of battery sections, based on the area of the room. Thanks to this approach, you will not need to spend extra money on equipment.
Principle of calculation
Manufacturers today offer a sufficient range of different heating devices, so the choice will not be difficult. The main thing is to understand the principle of how heating is calculated in an apartment or a private house.
Since the batteries can be of different types of performance and power, you will only have to follow our recommendations in order to get high-quality heating with minimal costs.
Heating radiators - what industry offers
This heater is designed to remove heat into the atmosphere of the room, which comes from the boiler, and consists of sections. You can install it yourself or invite experts to do this. There are several types of such equipment for the manufacture of which uses a different material.

Before dwelling on a particular one, it is necessary to understand that each variety has its own peculiarities, which will be discussed below:
| Cast iron | Modern radiators are compact and they have high thermal power. From the pros can be noted:
Not without drawbacks:
|
| Aluminum | Experts consider it the optimal choice because of the high thermal conductivity in combination with a large surface area of the device due to the projections and edges. From the pros, we note:
Minuses:
The second problem is solved by applying on the inside of the radiator a polymer layer that protects the material from contact with water. If the battery does not have it, we do not recommend closing the taps in the pipes in order not to cause structural failure. A good option is the bimetal battery for the heating system, which consists of an alloy of aluminum and steel. The model carries all the advantages of aluminum, however, the dangers and disadvantages of the gap are eliminated. It should be noted that their price is higher. |
| Steel | Different form factors are offered, which makes it possible to choose a device of any capacity. Because of disadvantages:
Equipment is characterized by a large heating surface that stimulates the movement of heated air. Therefore, such radiators are more appropriately attributed by type to heating convectors. |

How to calculate the number of sections
At the first stage, we consider the main factors used in determining the required power of the heater.
- K1 - glazing:
- energy-saving 3rd glazing = 0.85;
- energy saving 2 = 1.0;
- ordinary glass = 1.3.
- K2 - heat insulation:
- standard concrete slab = 1.3;
- a wall in 2 bricks = 1.0;
- concrete slab insulated with polystyrene foam 100 mm thick = 0.85.
- К3 - the ratio of the area of walls to the area of windows: if the 10% coefficient is taken 0.8, then for every 10% 0.1 units are added.

- K4 - the minimum temperature outside the building:
- if up to - 10 ° С = 0.7;
- if up to - 15 ° С = 0.9;
- if to - 20 ° C = 1.1;
- if up to - 25 ° C = 1.3.
- K5 - ceiling height: with standard 2.5 = coefficient 1.0; then for every 0.5 m you should add 0.5 units. For example, for 3 m it will be 1.05.
- K6 - the total heating coefficient for all premises is 0.8 units.
- K7 - the number of walls in the room:
- one = 1.1;
- two in the corner apartment = 1.2;
- three = 1.3;
- four in a separate house = 1.4.
To determine the total power of radiators should use the formula:
100 W / m2 x Spom x K1xK2xK3xK4xK5xK6xK7
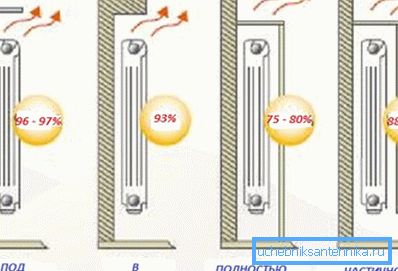
Calculation methods
There are several ways to calculate the heating of an apartment.
They are based on averaging the capacity of one section and accounting for 20% of the reserve:
- Standard - depends on the area. For example, building codes require that 1 m2 of 100 watts of power be spent on heating. With a floor space of 30 m2, and the average power of one section is 150 watts, the total will be as follows: 30x100 / 160 = 18.75.
Tip: all values are rounded up.
In our case, the room will need 19 sections.

- The approximate method of calculation is based on the height of the ceiling of the room and its area. Is it assumed that the section can heat 1.8 m? with a ceiling height of 2.5 m, so the result will be as follows: 30 / 1.8 = 16.67 or 17 sections. In this case, there is a large error, so we do not recommend using the method.
- Another method is based on the volume of the room.. Take a room with a length of 6 m and a width of 5 m, and a ceiling height of up to 2.5 m. At 5m3, 200 watts of heat are needed. Calculation instruction: 6 mx 5 mx 2.5 m / 5 m3 = 15 sections of 200 watts each.
Tip: each proposed calculation method has an error, so we recommend installing sections on the battery for 1 more. If you need to create a hot microclimate in the room, you need to add at least 5.
Conclusion
The article gave methods that allowed to understand how heating is calculated in the apartment. Therefore, before you buy a radiator, you must first determine the number of sections of this type for each room. Then you will not spend money in vain and make a microclimate in the room that is necessary.
The above formulas have some error, so you need to add to them at least one section. The video in the article will help you find additional information on this topic.