How to calculate the heating in the house without help
In the modern world, heating systems are often arranged by the owners themselves with their own hands so as not to spend extra money. However, at the preliminary stage it is required to make the correct calculation of the heating of the house, then the winter frosts will not be so bad. If calculations are made with a large error, then it is not possible to achieve maximum efficiency while providing housing for heat.
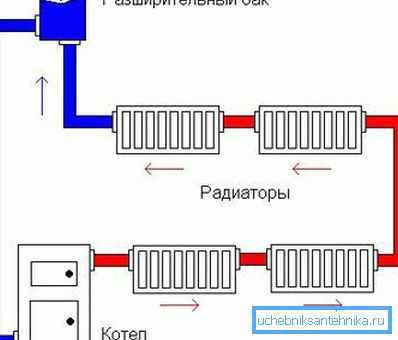
Determination of thermal power
To find out the required parameters of the heating system of a building, it is necessary to apply a special formula: Qt = V *? T * K / 860, where Qt is the required thermal power, V is the building volume,? T is the temperature difference, K is the heat loss indicator. The resulting product of the listed data is divided by 860, to translate the result in kW / h.
Volume of heated object
When the calculation of the heating system at home, the most important parameter is its cubic capacity, that is, the space to be heated. Further, it is proposed to make calculations for the building 68 with an attic.
The ceiling height is 3 m, and the distance from the base of the pediment to the ridge is 5 m.
- First of all, the volume of the first floor is determined, for which the width is multiplied by the length, and the result obtained is additionally multiplied by the height. It turns out such an example: 6 * 8 * 3 = 144 cu. m
- Further, the cubic capacity of the entire attic is calculated.. In this case, the division is added to the above operations, since the gables have a triangular shape. It comes out of this: 6 * 8 * 5/2 = 120 cu. m
- To get the final volume, it is necessary to simply add the results obtained in the previous paragraphs.. As a result, it will be possible to determine the space that will be heated: 144 + 120 = 264 cu. m
Note! In this situation, the calculations were considered for an object of a simple form. If the building is based on complex shapes, it is better to break them into simpler parts.
Temperature difference
Thermometer indicators inside and outside will be very different. The main task is to determine the difference between indoor and outdoor air temperatures in winter. You can determine this parameter if you subtract more from the smallest number.
When carrying out calculations it is necessary to focus on the level of comfort that you want to get from the thermal installation. Usually for residential buildings, the normal air temperature is 18-20 degrees. However, this figure may vary slightly depending on the preferences of the owners.
The temperature of the outside air can be determined independently, but in ordinary cases a special table is used, which reflects the average indicators for large cities.
| Title | Temperature |
| Moscow | -28 |
| Samara | -thirty |
| Kazan | -32 |
| Rostov | -22 |
| Yekaterinburg | -35 |
| Kaliningrad | -18 |
| St. Petersburg | -26 |
| Nizhny Novgorod | -thirty |
| Novorossiysk | -13 |
Addition! More detailed information on the climatic conditions of a specific region is reflected in the documentation of SNiP 23-01-99. All parameters are presented in the form of schematic maps and special tables.
The calculation of the difference between the temperature of the external environment and the internal space should be analyzed with a concrete example. If in a house located in the Moscow region, an indicator of 20 degrees is considered optimal, then it is necessary to do the following calculations: -28-20 = -48. Thus, managed to get the difference. This parameter will be substituted into the basic formula without a minus.
Heat loss coefficient
In our case, this indicator will be approximate, so as not to resort to complex calculations. The coefficient depends on the type of building, as well as its insulating features.
Below are the basic values that can be substituted into the formula.
- From 0.6 to 0.9 - an indicator for objects with a high level of thermal insulation from all sides. That is, the floors, roof, walls are additionally insulated, and the window openings are equipped with double glazed windows.
- From 1 to 1.9 - values in this range are suitable for buildings with an average level of thermal insulation. These include buildings with double brickwork and objects built from 150150 mm timber.
- From 2 to 2.9 - the coefficient is suitable for simplified structures with light insulation. The building can be attributed to this category if it has a single brickwork or is constructed from a bar of 100,100 mm.
- From 3 to 4 - the indicator is used only for light structures such as metal containers, single-skinned frame structures and other similar structures.

Example! Making the calculation of the heating of a country house, made of 150 x150 mm bar and having double glazing, you need to substitute a unit. If there are a lot of windows, then the value can be increased to 1.5.
Results substitution
After reviewing the basic parameters used in the formula, you can go directly to the calculations. Calculations will be made for the structure, the volume of which was indicated above.
His level of insulation is very high, and he is in the Moscow region. Thus, it turns out: 264 * 48 * 1/860? 15 kW / hour.
Suitable pipe diameter
In order for the heating system to function properly, it is necessary to correctly determine the diameters of the conductive elements, otherwise even with a high power of the domestic boiler for heating the house it will not be possible to achieve good results.
In the calculations, the following formula is used: D = v354 * (0.86 * Q /? T) / V, where Q is the heat load,? T is the temperature difference at the boiler inlet and outlet, V is the coolant velocity.

Heat load
At the initial stage, this parameter corresponds to the power indices, however, with branching of pipelines, the value may change. However, in most private houses, the elements are connected in series, therefore, the reduction of the cross section is usually not done. If the pipes of the system are separated, then the total result should be divided by the number of branches.
Temperature difference
In this case, indicators are measured at the inlet and outlet. After determining the two parameters, the smaller one is subtracted from the larger number. For example, if at the outlet of the boiler the temperature is 95 degrees, and at the reverse entrance - 65, then this difference is calculated as follows: 95-65 = 30 degrees.
Coolant speed
Circulation of hot water in the system can occur due to the temperature difference and with the help of a special pump, but the speed should be in the range of 0.8-1.5 m / s.
If the values are exceeded, there may be noise effects in the pipelines, which adversely affects the living conditions. Too low speed can cause air blockage.
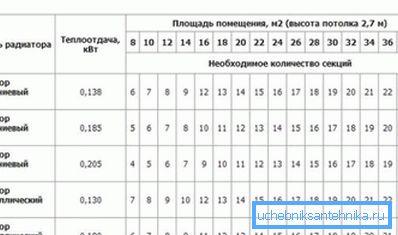
Number of radiator sections
Rather accurate calculations are obtained taking into account the volume of the heated room. First, the total heat demand is determined, after which the number of sections is calculated. The result can be divided into separate parts, if you plan to install several batteries in different parts of the room.
The following are specific calculations for a room measuring 35 meters and a ceiling height of 270 cm.
Such an instruction allows to obtain fairly accurate results.

- First you need to know the volume of the room, for which the main parameters are multiplied - length, width and height. As a result, there should be approximately the following example: 3 * 5 * 2.7 = 40.5 cu. m
- Now you should find out the necessary heat output for heating the room. SNiP recommends allocating about 41 watts per cube. In this regard, the following goes: 41 * 40.5 = 1660.5 watts.
- At the final stage, the result remains divided by the power of one section of the radiator. Let this parameter be equal to 170 watts. The result is: 1660.5 / 170? 10 sections.
Note! Correctly made calculations provide an opportunity not only to provide the room with heat, but also to save, because the price of some types of radiators for heating systems is quite high, especially for bimetallic counterparts.
As a conclusion
Having studied the presented materials from the beginning to the end, individual developers will be able to understand how to calculate the heating of the house independently immediately before the main works. At the stage of installation, it will only be necessary to install the system elements in the right places and connect to the main heat source. For acquaintance with other data special video is presented.