How to calculate the heating of a residential apartment or
During the repair of an apartment or the construction of a private residential building, most tenants need to perform an accurate calculation of the heating system. Immediately, it should be noted that solving this issue requires a balanced approach, since the competent performance of this task determines the level of comfortable living in the house during the autumn-winter period, and the lack of knowledge of how to calculate the heating tariff can lead to a significant increase in the cost of payment and without more expensive utility services.
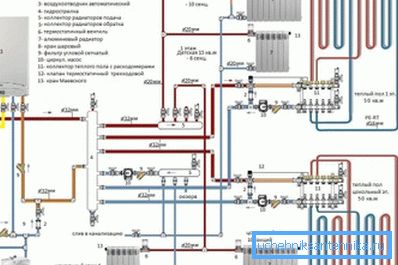
The method of calculating a household heating system
In order to perform all thermal engineering calculations, it is first necessary to have the exact design and actual dimensions of each room of a residential house, have data on the thickness of the external walls of the building and the nature of the heat-insulating materials used, as well as know the climatic features and the approximate minimum temperature in the cold season for a given region.
Next, the article will provide step-by-step instructions that, based on all these data, will help determine the optimal power of the boiler equipment and calculate the required number of radiators or batteries.
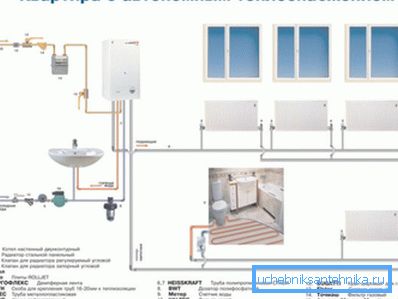
The method of calculating the power of the heating boiler
For heating the heat carrier in autonomous heating systems, solid fuel, liquid fuel, electric or gas heating boilers are most often used. The amount of thermal energy that must be used to heat any room per unit of time depends directly on its volume.
The average height of residential premises is 2.7 m, therefore, the calculation of the power of the boiler equipment for any room whose height is not more than 3 m is performed on the basis of its total area.
In order to know how the heating of the main area of a dwelling is calculated, it is necessary to follow the simple formula:
W cat = S x W beats / 10,
Where:
- W cat - the minimum recommended power of the heating boiler (kW).
- S is the total area of all heated premises (m?).
- W beats - the value of the specific power of the boiler, which is expressed in the amount of thermal energy, which is necessary for heating a room with an area of 10 m? (kW / 10m?).

The value of the specific power of the boiler equipment is determined based on the climatic features and weather conditions of a particular region.
- For regions of the extreme north and regions with a sharply continental climate should the specific power value be in the range from 1.5 kW to 2 kW for every 10 m? the area of the heated room.
- For middle latitudes, as well as regions with a temperate continental or temperate climate the value of the specific power can be from 1.2 kW to 1.5 kW per square 10 m ?.
- For southern latitudes and regions with a subtropical climate, the average daily air temperature in which rarely drops below 0 ° C, the specific power can be from 0.7 kW to 0.9 kW per 10m ?.

Note! The calculation of the power of the boiler according to the presented formula will be fair only if the building codes are complied with and high-quality thermal insulation of the exterior walls, floor and roof of the building is performed.
Calculation of the required volume of coolant
In order to achieve optimal operation of an autonomous heating system, an equally important parameter is the volume of the liquid coolant that will circulate in a closed heating circuit. Its value depends entirely on the power of the boiler, and is calculated by the following formula:
V syst = W cat x 15,
Where:
- V syst - the total volume of the closed circuit (l).
- W cat - the minimum recommended power of the boiler, calculated by the formula given above (kW).
Thus, it becomes clear that the optimal value of the coolant volume is 15 liters per kilowatt of boiler power.
As an example, we can consider the calculation of the boiler power and the required volume of heat carrier for heating a residential house, with a total area of 120 m? Located in the middle lane with a temperate climate.
- W cat = 120 x 1.5 / 10 = 18 kW.
- V syst = 18 x 15 = 170 l.
Based on the obtained calculations, it can be concluded that it is necessary to use boiler equipment with a capacity of at least 18 kW to heat the specified building, and the optimal volume of circulating coolant is 170 liters.

Tip! As a heat carrier, instead of water it is better to use a special non-freezing liquid based on ethylene glycol or propylene glycol. At first glance, its price may seem rather high, but it has much less corrosive activity than water, and its use will help avoid the destruction of pipelines and radiators in the event of stopping or failure of boiler equipment at negative air temperatures.
Calculate the number of installed radiators
The quality of heating of any room directly depends on the number of radiators installed in it, so before you install and connect water radiators with your own hands, you need to correctly calculate the necessary number of sections.
In order to know how to calculate the heating correctly and choose the optimal number of radiator sections, you need to use the formula:
W happy = S x h x 41,
Where:
- W glad - the total power of radiators necessary to ensure a comfortable temperature in the room (W).
- S - the total area of the room (m?).
- h is the height of the room from the finished floor to the ceiling.
- 41 - a standard indicator of the amount of thermal energy required for heating 1m? air in the living room.
The resulting calculation, the total power of radiators (W rad) must be divided by the value of specific heat transfer, which is indicated by the manufacturer in the technical data sheet of each radiator. The result of this calculation will be the required number of working sections of the radiator, which must be installed to heat this room.

Calculation of heating costs
When connected to the central heating system, the calculation of payment for the consumed thermal energy is performed according to one of two schemes, depending on the meter reading, or according to the consumption norms.
In the first case, in the presence of a common house heat meter, the payment is charged in accordance with the amount of heat actually consumed by all residents of the house, and is proportionally distributed according to the total area of the apartments. The following calculation formula is used:
P opl = V total x S lived / S unde x T,
Where:
- P opl - the amount of payment for the consumed heat (rub.).
- V total - the amount of heat consumed during the reporting period, according to the testimony of the general-purpose metering device (Gcal).
- S lived - the total area of a particular residential apartment in the house (m?).
- S nek - the total area of non-residential and technical obschedomovyh premises (m?).
- T - the established tariff, according to the current legislation (rub / Gcal).

In order to know how the heating tariff is calculated in the absence of a common house metering device, it is necessary to use the following formula:
P opl = S lived x T
Where:
- P opl - a fixed amount of payment for heat (rub.).
- S lived - the total area of a residential apartment (m?).
- T - the established general tariff, according to the current legislation (rub / Gcal).

Conclusion
By performing simple calculations using the formulas presented, it can be concluded that in the case of an installed metering device for heat energy, the amount of payment for consumed heat for each apartment owner will be significantly lower than the amount of monthly payment at a total rate, according to the size of the living space.
To learn more about the information provided, you can watch the video at the end of this article, or read similar materials on our website.