How to determine the required power of radiators - a
Before buying any heating radiator you need to know the required thermal power of this device. Actually, on the basis of these data, the selection of the number of sections is performed. Skipping the calculation stage may eventually result in a violation of the microclimate in the room, so it will be useful to familiarize yourself with the calculation method.

About the calculation of the heating system
At this stage, it is necessary to ensure that the heating capacity of the heating radiator provides a constant temperature in the room during the coldest time of the heating season. Determining the power of the heating radiator is necessary in order to determine the required number of segments (see also the article How to connect radiators in a central or autonomous system).

Note! To be able to smoothly adjust the operation of the heating battery, installing a thermostat will not be redundant.
The whole process is carried out in several stages:
- heat losses through the enclosing structures are calculated;
- according to the technical documentation, the heat transfer of one segment of the selected radiator is found out;
- calculate the required number of battery segments.
Heat loss calculation
This is the first thing to start with when it comes to how to determine the power of a heating radiator.
Heat is consumed through:
- walls, both external and internal (if the room is bordered by an unheated room);
- floor;
- ceiling;
- windows and doors.
The calculation of losses is carried out taking into account the type and thickness of the material, the formula is used
in this formula
- Q - heat loss;
- S - area of the room, m2;
- ?t is the temperature difference inside and outside the room,? С;
- ? - reference value - thermal conductivity coefficient, W / m •? С;
- v - thickness of the building envelope, m.
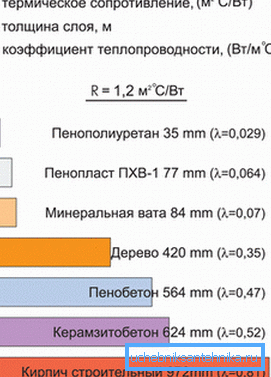
From the point of view of heat loss, the upper floors are in a disadvantageous position, because an unheated attic is located above them, and the outside wind is stronger. So for them, the resulting heat loss can be increased by about 10%.
Note! When calculating you need not forget about ventilation, because the air exchange in the winter does not stop. For this purpose, a multiplying factor 1.1 - 1.4 is introduced. Greater importance is taken for intensive ventilation of housing.
Calculation of the radiator
Having on hand data on heat loss, you can proceed to the selection of the battery. At the same time, it is necessary to take into account the efficiency of the device, for example, the power of steel radiators is inferior to bimetallic counterparts.
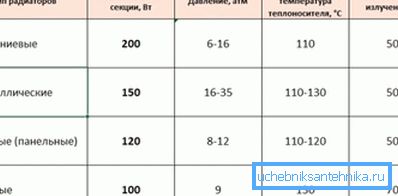
The required number of segments is defined as the ratio of heat loss to heat transfer of one segment. But the heat output section - the passport value, the manufacturer must indicate it for each model of the radiator. The formula used is:
in this formula:
- n is the total number of battery sections, pcs;
- Q - heat loss, W;
- N - power of one section, W.
It should be borne in mind that the passport data on the power of the 1st segment are given for a certain temperature difference (usually 90/70). But quite often the temperature of the coolant is different, in this case, and the heat transfer of the heating battery varies. For example, the power of cast-iron radiators when the temperature difference changes from 80-100 to 50-60 drops by about 15-20%.
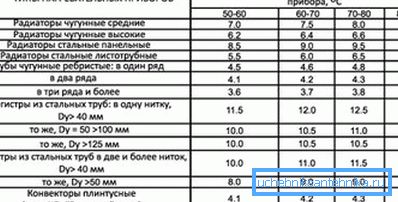
To calculate the power of the segment with an arbitrary temperature head use the formula
in this formula
- k - heat transfer, passport value, W / m2•?WITH;
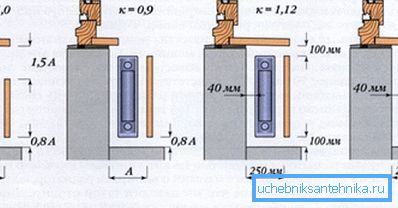
- A - section area, m2;
- ?T - temperature pressure,? С. Calculated by the formula
Tunder and tarr - the temperature of the coolant, respectively, at the entrance to the battery and out of it,? With;
Troom - room temperature,? C.
Simplified Method
If all the work in the house is done by hand, then quite often, instead of a detailed calculation, people are content with an approximate selection. It should be noted that the result in this case, though not very accurate, will come down for the selection of the radiator.
There are several ways to approximate the calculation:
- with standard parameters (ceiling height in the room up to 3m, temperature of the heat carrier 85-90? С, 1 window and 1 door in the room) you can use the dependence 100 W / 1 m2 square. For a room of, for example, 20 m2 need a battery that is able to provide heat output of 2 kW;
Note! For corner rooms, as well as apartments on the upper floors, a multiplying factor of 1.2 is introduced. The price of batteries is not so high, so it is better to err.
- calculation can be carried out taking into account the cubic capacity of the room. In this case, it is based on the proportion that 200 W of heat power is capable of heating 5 m.3 room space.
Note! Practice shows that the result in this case turns out to be overestimated by about 10%.
The results for both methods should be approximately the same. It is more convenient to compare them with a specific example. Suppose you need to pick up a radiator for a room with dimensions of 5x5x3 meters, it has 1 double-glazed window, 1 interior door, the apartment is located on the lower floor.
The first simplified method of calculation involves the following sequence of actions:
- determined by the area of the room, 5x5 = 25m2;
- considering the proportion of 100 W / 1 m2, determines the power of the device, in our case 2.5 kW;
- the power of one section of a specific radiator is written from the passport characteristics. For example, choose the aluminum model A350, 1 segment is able to give 138 watts of thermal energy;
- counted the number of segments, 2500/138 = 18,12? 19 pieces.
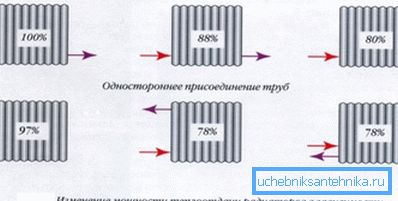
Note! The method of connection also plays a large role in the uniformity of its warming up, and therefore the heat transfer.
When working on the 2nd method, the instruction will look like this:
- considering the proportion of 200 W / 5 m3 Determine how much air will heat 1 section of the selected battery. In our case, 1 section will warm up 3.45 m3;
- determine the volume of the room 5 • 5 • 3 = 75 m3;
- counts the number of sections 75 / 3.45? 22 sections.
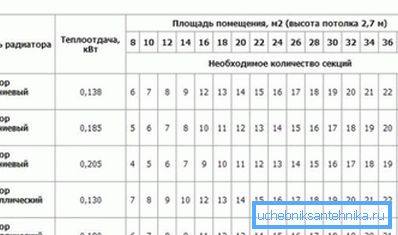
The error in the calculation by the 2nd simplified methods was 13.6%, which is not so bad for an approximate calculation. The results obtained are roughly consistent with the recommendations of the manufacturer (shown in the table).
Summarizing
To maintain a normal indoor microclimate, it is necessary to achieve a balance between the heat input and the heat loss. This condition can be met only with proper calculation of the heating system in general and heating radiators in particular. The calculation methods proposed in the article may well be used in selecting the number of sections of a heating battery in an apartment or a private house (find out here how to fix a heating radiator with improvised means).
The video is a brief instruction on the calculation of the heating battery.