Modern heating systems: water, solar, heated floor, infrared
What modern heating systems of a private house are used in our country? What makes them attractive against the background of traditional solutions? Do the circuits used have any serious disadvantages? How economical are they? Let's try to answer these questions.

Traditional and new ways
Let's immediately separate one from the other. Traditional schemes of water heating to this day remain the most popular.
There are several reasons for this:
- Cheap gas and firewood.
To clarify: the cheapest type of fuel has been and remains the main gas. Despite the abundance of advertising statements, any modern technology in heating will cost more than a gas boiler in terms of operating costs.
- Low cost of equipment.
- A large amount of information and practical skills of specialized experts in the field of conventional water heating. In order to massively offer something new in the domestic market, it is necessary to have comprehensive information about the advantages and disadvantages of the solution. It is with this that problems sometimes arise.
A little further we will find out how traditional heating systems of a private house from modern components can look. In contrast, we have to get acquainted with truly new technologies, literally turning over ideas about heating.

Water heating
So, how has the modern heating of a country house changed within the framework of the usual scheme with heat carrier and convection heating devices?
Heat sources
At the beginning - some general comments. Here is the approximate cost per kilowatt-hour of heat for different ways of producing it.
| Heat source | Price 1 kWh, rubles |
| Burning main gas | 0.7 |
| Firewood burning | 1.2 |
| Coal burning | 1,3 |
| Pellet burning (granulated sawdust) | 1.5 |
| Burning gas from a gasholder | 1.9 |
| Burning gas from cylinders | 2.9 |
| Diesel burning | 3.4 |
| Direct heating with electricity | 3.8 |
Along with efficiency, however, it is worth considering the ease of operation of a particular type of equipment.
And on this basis, our ranking table looks very different:
- Electrical equipment does not require maintenance, works without human intervention for an unlimited time and allows the use of elements such as thermostats, programmable heating mode, control via GSM, etc.

- Gas boilers with electric ignition are not inferior in functionality to electric ones, but require removal of combustion products, and when working from a gas-holder and cylinders - also their periodic refueling.
- Solar heating systems have the same functionality, but they make more noise and require a bulk fuel storage tank.
- Pellet boilers with automatic feeding systems should be serviced at least once a week: the hopper needs to be loaded and the ash pan to be cleaned.
- Finally, outsiders - solid fuel (coal and wood) boilers. They need to load fuel every few hours; an attempt to increase the frequency by limiting the thermal power (closed blower) leads to a catastrophic decrease in efficiency due to incomplete combustion with a limited influx of oxygen.
And now - a list of new products that have appeared in this area over the past decades.
Induction and electrode were added to electric boilers on heating elements:
- Induction The heating of a ferromagnetic core placed in a dielectric and diamagnetic tube by the eddy currents excited by the inductor is used. The core transmits heating to running water. The advantage of the solution is a practically unlimited resource: there are no elements that wear out or degrade over time.
- Electrode Boiler, on the contrary, it requires periodic replacement of the electrodes and control of the salt composition of the water. Its advantages are compactness and absolute safety when depressurizing the circuit: if the water leaves the case, current will simply cease to flow between the electrodes.

Curiously: sellers often position these types of boilers as economical. This is a first-class lie: the efficiency of any device of direct heating is 100%, which directly follows from the law of conservation of energy. Only the ratio of heat dissipated in air and transferred to the coolant may change, but all of it is used to heat the room in any case.
No less curious are the so-called condensing gas boilers. They provide more complete utilization of the heat of combustion of gas, condensing the products of combustion on a separate heat exchanger. The difference in efficiency with traditional solutions reaches 10 - 11%.
Modernization of solid fuel cats predictably aimed at increasing the duration of their battery life.
- Gas generators or pyrolysis boilers break the combustion of fuel into two separate stages. At first it smolders with limited access of air; then volatile hydrocarbons and carbon monoxide are burned in an additional chamber. This scheme allows you to put the fuel no more than twice a day and eliminates the drop in efficiency with limited power.
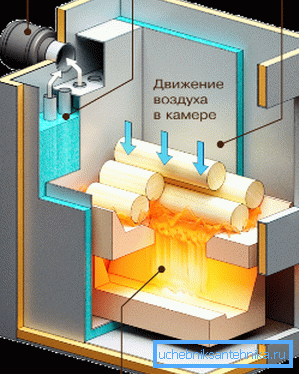
- Boilers top burning also use pyrolysis; but at the same time the process of smoldering fuel is transferred to the upper part of the furnace, which can significantly increase its volume. Ash is carried away by the upward flow of combustion products. The autonomy of the best samples of the upper combustion boilers of the Lithuanian company Stropuva reaches 31 hours.
Radiators
Some modern heaters are significantly different in their efficiency from conventional cast iron batteries.
The thermal conductivity of aluminum makes it possible to supply aluminum sectional radiators with developed fins, thereby providing a heat transfer of more than 200 watts per section with a small internal volume.
The heat transfer of copper-aluminum convectors is even higher: in them aluminum fins plates are pressed onto copper tubes with heat carrier.

Reference: the thermal conductivity of copper is almost twice as high as that of aluminum and four times more than steel.
Finally, another simple modification of heating devices helps to increase heat transfer: they are supplied with low-speed fans, blowing air through the fins. If desired, such an upgrade is easy to do with your own hands, by providing a conventional fan with a dimmer that reduces speed.
Layout
And in this area in recent years, a couple of interesting new products.
- Polypropylene pipes with a high enough for an autonomous system of strength and exceptional durability are very cheap and are easily mounted by low-temperature soldering using a simple soldering iron. As a rule, an aluminum-reinforced pipe is used for heating. Reinforcement does not so much increase the tensile strength as reduces the rather high thermal expansion of the polymer.
- No less curious pipes made of cross-linked polyethylene - durable, perfectly tolerate high temperatures and very elastic. It is used for collector wiring heating devices with laying liner in the screed.

Heat accumulator
A modern heating system is often equipped with a heat accumulator - a massive heat-insulated container that allows you to accumulate a large amount of thermal energy and spend it on maintaining the temperature of radiators.
Why do you need it?
Let's give a couple of examples:
- Heat accumulator allows reducing the amount of kindling of a solid fuel boiler during the day. For example, with an average power consumption of 3 KW by radiators, the 24-kilowatt boiler is melted once a day and operates for three hours at rated power (which, by the way, will allow to avoid a drop in efficiency). The rest of the time, the heated water circulates between the tank and the heating devices.
- When using electric boilers of any type, the presence in the heat accumulator circuit will allow using the night tariff for electricity, which is 2-3 times lower than the daily one.

New schemes
As already mentioned, all of the above solutions represent a particular degree of modernization of the long-known water heating. And what are the truly modern technologies of home heating?
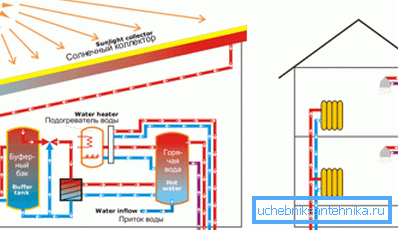
Solar collectors
The simplest collector is a black painted hermetic tank. The purpose of its installation is quite obvious: having heated up in the sun, water can be used for household needs. However, a simple scheme remains operable only in summer — in the cold season, the amount of heat loss due to convection will be quite comparable with what the tank receives from the sun.
In modern collectors, this problem is solved simply and elegantly:
- Shaded tubes with coolant are placed in vacuum flasks, preventing direct contact with atmospheric air.
- The efficiency of the device is additionally increased by a special coating capable of utilizing up to 94% of infrared radiation.
As a rule, the collector battery is mounted in a common circuit with a heat accumulator that can accumulate the heat obtained during the day and use it for heating at night or in cloudy weather. Alas, solar heat is not able to provide a house with free heating even in warm and sunny regions of the country; However, it is quite possible to reduce heating costs by 25–30% due to its utilization.
Warm floor
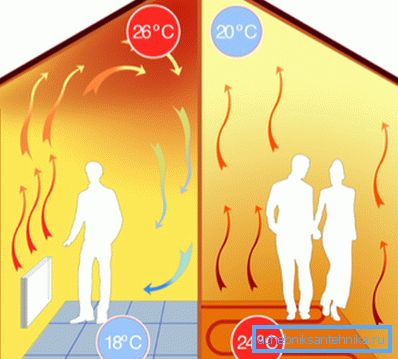
The main drawback of any convection heating system with wall or floor heating devices is the uneven temperature distribution in the heated room. The upward flow that forms above the device effectively heats the air under the ceiling, but the floor remains relatively cold.
As a result, the homeowner faces obvious negative consequences:
- With an average air temperature in the room, say, 25C under the ceiling may well be 35, and at the floor level 15. Meanwhile, the person, sorry for the involuntary pun, it is to the floor. It seems that the reader will not remember among his acquaintances a single original who spends his free time on the ceiling.
- The more delta temperatures on either side of the building envelope, the more heat is dissipated through it. Heating the air under the ceiling also means a sharp increase in heat leakage through the upper ceiling.
Modern heating schemes with a warm floor are different from convection in that the entire floor surface is transformed into a heating element.
Heating can be provided by:
- Laying in the screed floor pipe with a circulating coolant.
- Laying in the same heating electric cable.
- Installation under the finish coating film heaters.
Working temperature of warm floors ranges from 20 to 35-40 degrees. The average power density is 30-60 watts per square meter. Savings are achieved precisely due to a more rational distribution of heat: the warmest in the room will be the area above the floor.
Infrared heating
Remember your feelings at the winter fire? Despite the coldness around you, subjectively, you feel warm and comfortable. The reason is the transfer of heat between the flame and your skin and clothing due to infrared (thermal) radiation.
IR heaters use this effect: due to the small area, they give up relatively little heat to the air through direct contact. Its main amount is transmitted by radiation.
What is the result?
- The entire surface irradiated by the device turns into an analogue of a warm floor: it begins to heat the air in contact with it. This, again, provides significant heat savings (primarily with ceiling emitters) due to the rational distribution of temperatures.
By the way: in the area of the device is not recommended to put furniture made of natural wood. The instruction is related to its instability to heat: the wood cracks and cracks.
- Due to the fact that the skin of a person in the zone of the emitter is also heated, the comfortable temperature in the room is shifted a few degrees down. Already at +15 in the room is subjectively warm. Meanwhile, the lower the temperature in the house, the lower the cost of heating.

Heat pumps
If the last two schemes imply savings due to more efficient heat distribution, then modern heating of a private house with a heat pump is an approach to the problem from the other side.
In this case, energy is spent not on heat generation, but on its transportation from low-potential sources. Simply put, the heat pump takes heat energy from the cold environment and gives it to the warm air in the house.
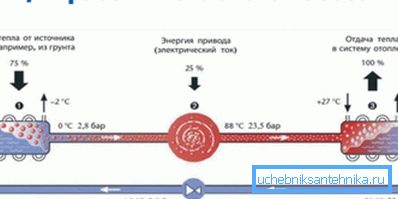
The scheme of the pump in general repeats the device of a conventional refrigerator:
- The gaseous refrigerant is compressed by the compressor, going into the liquid phase and heating up.
- Then it passes through a heat exchanger, where it gives off excess heat.
- After passing the expansion valve, in which the diameter of the route increases dramatically, the refrigerant returns to the gaseous state. At the same time its temperature drops sharply. The heat deficit is compensated through the second heat exchanger due to its environment.
What could be the source of low-grade heat?
- Priming. Soil heat exchangers can be immersed in wells or laid below the level of freezing horizontally. Heat pumps operating under the soil-water or ground-air schemes are the most productive, but require complicated and expensive installation of heat exchangers.

- Water. This may be an ice-free reservoir or a pair of wells, one of which is used to extract groundwater, and the second - for drainage.
- Air. Modern air-water and air-air heating systems are the cheapest and are relatively easy to install. However, their effectiveness decreases as the ambient temperature decreases; The lower threshold for performance is -25 - - 30C.

How economical are heat pumps? Their main parameter is C.O.P. (coefficient of performance, the ratio of heat produced and electrical power consumed) reaches 3-5, which brings them closer to the main gas in terms of costs and makes all other heat sources uncompetitive.
Perhaps the reader will benefit from the author’s own experience. As a source of heat, he uses a household air-to-air heat pump (also known as an inverter air conditioner). Place actions - Crimea, Sevastopol.
Here is a brief report of the results of heating one floor of the house over the past winter.
| Parameter | Value |
| Heated area | 75 m2 |
| Thermal power of air conditioners | 2x9000BTU (2x3.2 KW) |
| Average monthly temperature | +2 |
| Room temperature | +22 |
| Monthly electricity consumption | 800 KWh |

Conclusion
We hope that our acquaintance with modern heating systems will be informative and will help the reader in choosing a solution for their own home. Additional information will be offered by the video attached to the article. Successes!