Monotube heating system leningradka: simplicity and
In this article we have to get acquainted with one of the most simple and common heating schemes - Leningrad, or the barrack system. We will find out what advantages and disadvantages it has against the background of alternatives, how to properly connect heating devices to it and what diameters of pipes should be oriented. So go.
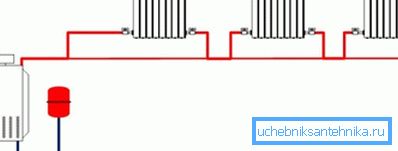
What it is
Leningradka is, quite simply, a bottling pipe encircling a house or a heated room around the perimeter. Heating devices are embedded directly into it with short liners. The differential required for circulation is usually created by a circulation pump or a tie-in into the heating main through the elevator unit.
To adjust the circulation rate of the coolant (and, accordingly, the temperature of the radiators furthest from the beginning of the ring) can be used:
- Smooth or step adjustment of the circulation pump.
- Throttling valves.
- Retaining washer.
In addition: Leningrad can be used in systems with natural circulation of the coolant (gravitational). In this case, the circulation rate is controlled by heating the heat exchanger in the furnace or boiler.
Areas of use
Limitations flow from the hut scheme.
- It can be used in rooms whose configuration allows you to make the ring unbreakable. A large number of partitions, panoramic windows and doorways do not just put a cross on Leningrad, but they will make its installation so laborious that you necessarily think about alternatives.
- This scheme is not suitable for high-rise buildings.. At least in its pure form: a single-tube ring is often used within individual apartments in new buildings; However, the heating system of each apartment is embedded in a pair of traditionally divorced risers.
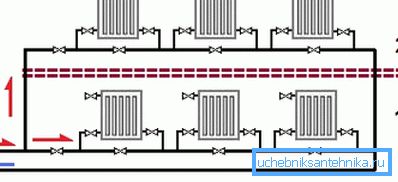
Advantages and disadvantages
What is useful to know about Leningrad?
Merits
- She is failsafe. Absolutely failsafe. The situation when the system stops due to airing is completely excluded.
- It allows independent adjustment of heaters and their dismantling. At the same time shutdown, throttling or absence of one radiator does not affect the operation of the others.
- As already mentioned, it can work with forced and natural circulation.
- Starting the circuit is extremely simple regardless of the presence of air in it. Since the pressure in the plumbing or heating main is much higher than atmospheric, when radiators are located above the bottling air will be forced out to their upper part.
- The circulation of the coolant will begin even when the system is airborne, and due to the thermal conductivity of the heaters, they will be fully heated before the air is vented.

Nuance: the circuit will work in the manner described only with the radiator wiring diagram from bottom to bottom.
disadvantages
These include, perhaps, only the inevitable temperature variation between the first and last heating devices in the circuit. To be precise, the spread will be noticeable at the radiator inlet: balancing the heating single-pipe system, if necessary, is able to equalize heat transfer.
Installation Features
Are there any rules that should be followed when installing Leningrad with your own hands?
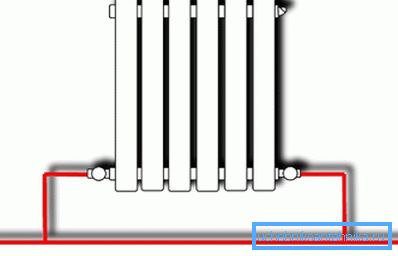
- Radiators do not break the filling, and crash parallel to it. With a consistent insertion of heating devices, the flow of coolant through them will slightly increase, but we will lose all the bunks of the hut scheme - simple start-up, fault tolerance and the possibility of independent temperature control on each battery.
- As already mentioned, it is better to use the inset from the bottom to the bottom: eyeliners are connected to the lower radiator threads on both sides. The instruction is connected with the fact that it is under such a scheme that the presence of air in the battery will not affect the circulation through its lower collector. For the same reasons, bottling should be located under the heating devices, and not above them.
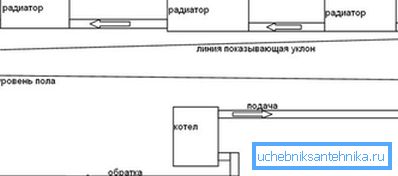
Nuance: these recommendations are not applicable to a system with natural circulation. To move the water by gravity, bottling will, willy-nilly, have to be laid with a slope; the first radiators will be below it. However, with an open expansion tank, air bleeding is definitely not a problem.
- As heating devices, you should not use convectors (coils with fins to increase heat transfer). Again, they will deprive us of one of the Leningrad's buns - the ability to work on heating, even in the impressed state.
- When designing a system, it is worth adhering to the following minimum sizes:
| Heating element | Minimum remote control |
| Radiator outlet | 15 |
| Filling in the system with forced circulation with a length of up to 50 meters | 20 |
| Filling in the system with forced circulation with a length of 50-100 meters | 25 |
| Gravity filling system | 32 |
Nuance: a reasonable maximum length of filling in a system with natural circulation is about 40 meters. With a larger area of the house is better to splurge on the circulation pump.
- Each heater is equipped with the following set of valves:
- Shut-off ball valve at the entrance. It will completely turn off the radiator for repair or replacement without dropping the entire circuit.
- Throttle outlet. With it, you can again completely cut off the heater or limit circulation through it, thereby reducing the temperature. Instead of a choke, a thermostatic head can be installed, which will regulate its own passability in automatic mode, depending on the temperature in the room.

Useful: for reasons of economy, another valve can be installed instead of a throttle or thermal head. Its price is much lower; However, it is rather inconvenient to regulate the flow of the eyeliner with a valve.
- Air vent on one of the upper radiator plugs. For air bleeding, a Mayevsky faucet, a valve, or a conventional faucet can be used.
- When mounted on steel liners on the cork side with a left-hand thread, a removable drift is installed, which allows, if necessary, to remove the radiator without welding. As a rule, steel connections with bimetallic radiators are used in homes connected to central heating with its not always predictable temperatures and pressures. Autonomous systems use pipes made of polypropylene and metal-plastic; to connect the batteries in this case it is easier to put a couple of American women.

Conclusion
We hope that the material proposed to the reader will help him in the design of the heating system and its installation. As always, you can find additional thematic information in the video attached to the article. Successes!