Pipeline installation: how to design and build a system
Pipelines are the main element of most utilities. They are always subject to increased requirements for design, assembly and operation. The installation of process piping is especially complicated and responsible, since hazardous toxic, explosive or combustible substances can be delivered through them.

System Design

- Network Design - it is the choice of the type of pipes, fittings and fittings, the implementation of hydraulic calculation, the selection of the installation method and the optimal operating conditions of the system.
- Pipes are selected based on the service conditions of the pipeline.: temperature, pressure, desired life, degree of aggressiveness of the working environment.
Note! Especially important is the hydraulic calculation of pipelines. It determines the pressure loss in overcoming resistances that arise in the pipes at their joints, in the sections of turns and transitions of the network section.
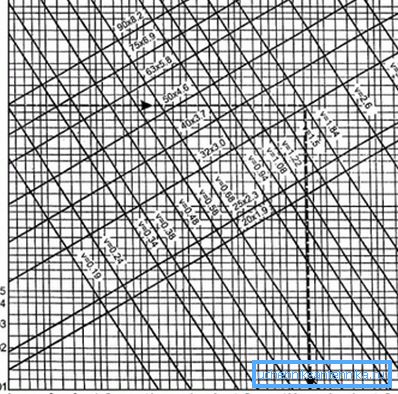
- In general, pipeline design is the creation of technical documents.: Feasibility Study (Feasibility Study), Estimates, Calculations, Layouts, Drawings, Explanatory Notes, etc.
- The design methodology of engineering networks strictly regulates the content and sequence of its stages in accordance with the Unified System for Design Documentation.
Installation of non-metallic networks

The assembly of non-metallic systems has some features arising from the characteristics of the materials used.
- Polyethylene, polypropylene, PVC and fluoroplastic networks are laid out of ready-made nodes and elements.
- When installing PE and vinyl pipes, it is necessary to ensure reliable fixation of the reinforcement to the base, observing the step between fasteners and maintaining the gaps from hot types of communications.
- In order for pipes transporting substances with a temperature of more than + 40 ° to not be damaged and not sag, they should be fixed horizontally along the entire length of the network. This is done with the help of gutters and trays of metal corners.
- For systems with a working environment of less than +40 degrees, steel or plastic hangers and mounting brackets, tight-fitting pipes can be used.
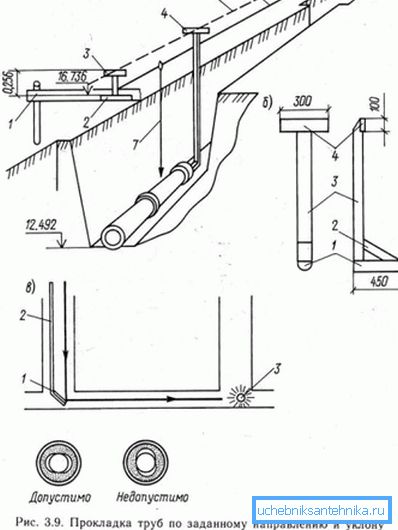
- When laying pipes horizontally, fasteners are installed in increments of: no more than 150 cm for a network having a conditional passage of up to 50 mm and no more than 300 cm for analogues more than 50 mm.
- For vertical assembly of elements having a length of more than 200 cm, in order to avoid shrinking them under their weight and medium weight, fasteners are mounted directly under the shaped socket.
- The instruction notes that if the network passes through ceilings, walls, foundations, and other structures, steel cartridges with rounded ends should be placed on these sections.

- The space between the sleeve and the pipe should be clogged with a soft seal.
- The gap between the polymer and hot pipelines should not be less than 10 cm.
- When the network can be damaged during operation, it should be protected with a wooden or metal (solid or mesh) fence.
- If the system transports a medium having a temperature of + 60 / + 90 degrees, it should be laid in a casing of metal pipes.
- Underground laying of plastic pipelines should be done in trays, channels and trenches.
Arrangement of technological communications

Technological networks are divided into:
- working under high, medium and low vacuum;
- non-pressure analogues;
- under low pressure (up to 10 MPa);
- pressure systems - under pressure over 10 MPa.
Based on the operating temperature, distinguish pipelines:
- cold, working with negative temperatures of substances;
- normal analogues - temperature of transported media 0/100 °;
- hot nets - substances heated to 100/300 °;
- overheated - the medium has more than 300 °.
The design of technological pipelines and their installation should be carried out in accordance with SNiP W-D No. 9/62. The document defines the implementation and acceptance of the assembly of technological networks operated at a pressure (absolute) of 30 mm Hg. st. up to 700 kgf per cm2.
It is important to comply with the provisions of SNiP № 3.05.05 / 84 "Technological equipment and pipelines."
Prerequisites for work
Material systems can serve:
- alloyed and carbon steels;
- non-ferrous alloys and metals;
- cast iron;
- different types of plastics;
- special glass.
Note! Most of the technical pipelines fit into cramped areas, at different heights, in high-rise buildings, on ramps, open spaces, in tunnels, and trays. Therefore, intrashop networks have a large number of used sizes, elements, fixings, stop and control valves.
Below is a table of the number of fittings and additional elements needed for such networks.
| Product | % to the mass of pipes | Number in pieces per 100 meters of pipes |
| Flanges | 5.47 | 25 |
| Taps | 3.72 | 23 |
| Tees | 1.84 | eight |
| Transitions | 0.34 | 0.6 |
| Stubs | 0.15 | 0.3 |
| Suspension and support | 2.41 | 12 |
| Fittings | 27 | ten |
In order to equip the intrashop system with your own hands, you should add up to 42% of the mass of pipes of various fittings, fixings and fittings. The complex design of technical networks leads to the fact that it is necessary to carry out a large number of connections of network elements: 60/80 weld seams per 100 m.
If you use ready-made sections, elements and assemblies produced in a pipe stocking workshop during assembly, this will greatly simplify the work and reduce the number of welding operations by 5/6 times. Reduced and the cost of mounting the network.
Preparatory work
Prior to the assembly of the pipeline such preparation is made.
- Master, foreman, brigadier studied the CPD and the project.
- Accepted components, parts and elements of the system. Their compliance with the project itself and its technical conditions is carefully checked.
- Determines the level of readiness of buildings, structures, structures for assembly, the associated acts are created. Particularly scrutinized is the observance of design tags for attaching the network.
- The equipment and devices for work are accepted, the correctness of their statement and compliance with the working drawings are checked.
- The areas for the pre-assembly, stage and other devices for work at height are prepared and arranged. Power supply for welded posts, tools, winches, lighting of the place of work.
- Crews are issued work orders and conditions are created for installation, according to safety and labor standards.
Assembly technology

The installation of a pipeline of steel pipes for technical substances consists of such steps.
- The layout of the network route.
- Installation of suspensions and supports.
- Pre-assembly of blocks, sections and nodes.
- Laying, assembly, welding pipes.
- Installation of valves, compensators, automation and control devices.
- Test the system.
- Letting her customer.
Installation of hot and cold steel pipes for water
Arrangement of such systems is carried out on the basis of project documentation, flow diagrams of pipe laying and provisions:
- SNiP №305.03 / 85 "Thermal communications";
- SNiP No. 2.04.07 “Rules for arrangement and safe operation of pipelines for hot water and steam”;
- SNiP III "Trunk types of pipelines"
- Organizational preparation and design of thermal systems is carried out on the basis of SNiP No. 3.01.01 / 85.
Stages of work
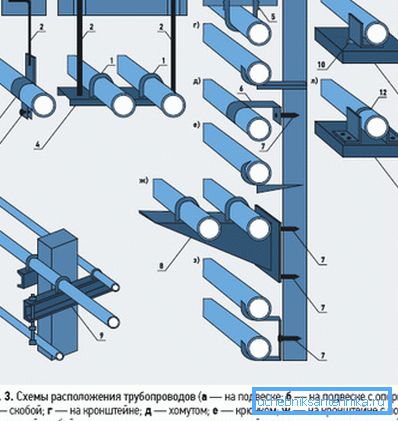
The sequence of stages depends on how the system is laid.
Typical steps are as follows.
- A breakdown of the route (in plan), based on the drawing of the geological base and the wiring diagram. Inspection of the markup by the admissions office.
- Preparation of trench channels and their digging in depth and width (including sand cushion). As needed, the strengthening of their walls, the reconciliation of the depth of geo-marks. Drawing up a relevant act.
- Laying pipes, fittings and other components.
- Check cable integrity for control systems.
- Installation of supports.
- Assembly of the pipeline and welding of its joints.
- Hydraulic or radiographic inspection of welds. Preparation of test acts.
- The connection of control cables at the joints.
- Hydro and thermal insulation of pipes.
- Drawing up an act of hidden works.
- Sanding the system with a sand layer, backfilling ditches (in addition to the installation sites for starting compensators), tamping the soil.
- Delivery of the object to the customer.
Preparation for installation
- Before installation, already insulated pipes, parts and connecting elements should be carefully examined to identify chips, cracks, cavities, punctures and other mechanical damage.
- If these defects are detected, they should be sealed with welding or by applying ring patches of heat-shrinkable tape type.
- Pipes and fittings and system components should be laid out on the bottom or side of the trench using a truck crane or a stacker so that the cables of the APC system are placed horizontally.
Note! It is necessary to lower heat insulated products into the ditch without jerking, smoothly, without hitting them against the bottom and walls of the trench. Before installing the elements, it is necessary to check the integrity of the indicator-conductors of the UEC device, and also measure the resistance between the steel pipe and them.
- Pipes mounted on sand bases should not rest against bricks, stones and other hard objects. They need to be removed, and the resulting potholes to be smoothed with sand.
Assembling the water supply network

- The installation of steel pipelines is usually carried out at the bottom of the pit. However, it is allowed to weld straight sections of elements in a section on trench edges.
- Arrangement of systems with thermal and waterproofing of polyurethane foam in a polyethylene sheath should be carried out at an ambient air temperature of at least -15 °.
- Steel pipes are cut, if necessary, with gas burners. Before this, heat insulation should be removed with a manual or mechanized tool on a product area 40 centimeters wide (20 cm on each side). End sites of isolation during the operation are covered with a damp cloth or shielded with rigid materials.
- It is necessary to weld the seams of the system and control the quality of the pipe joints, based on the norms set forth by SNiP No. 3.05.03 / 85.
- When all welding works are carried out, polyurethane foam and waterproofing layer should be reliably protected, in addition - the ends of cables without insulation should be protected from sparks flying off.
The table below shows the distance between the supports of the pipeline, depending on the water temperature in the system.
| Nominal outer diameter of the pipe, in millimeters | Distance, in millimeters, at a certain ambient temperature | ||||||
| +20 | +thirty | +40 ° | +50 | +60 ° | +70 ° | +80 ° | |
| sixteen | 500 | 500 | 500 | 500 | 500 | 500 | 500 |
| 20 | 600 | 600 | 600 | 600 | 550 | 500 | 500 |
| 25 | 750 | 750 | 700 | 700 | 650 | 600 | 550 |
| 32 | 900 | 900 | 800 | 800 | 750 | 700 | 650 |
| 40 | 1050 | 1000 | 900 | 900 | 850 | 800 | 750 |
| 50 | 1200 | 1200 | 1100 | 1100 | 1000 | 950 | 900 |
| 63 | 1400 | 1400 | 1300 | 1300 | 1150 | 1150 | 1000 |
| 75 | 1500 | 1500 | 1400 | 1400 | 1250 | 1150 | 1100 |
| 90 | 1600 | 1600 | 1500 | 1500 | 1400 | 1250 | 1200 |
Conclusion
Pipeline installation is a crucial set of operations. Reliability and efficiency of the system transporting certain substances depends on its proper implementation.
Check out the video in this article for more information.