Plate radiator: device design, principle of operation, main
An alternative to the usual sectional, panel and tubular models is the so-called plate radiator. Its design provides efficient heat transfer with a significant length of pipelines, which allows to effectively use such products not only in residential buildings, but also in public buildings and industrial facilities.
In our article we will talk about the features of the lamellar models, and also describe their main advantages and disadvantages.

Product Description
Device design
Old lamellar heating radiators in the USSR were used almost on a par with the usual cast-iron batteries. They were installed in schools, clinics, public institutions - i.e. where it was necessary to heat a large enough volume of air.

To date, the design of such devices has been slightly improved (mainly due to the use of modern materials), but the general scheme has remained unchanged:
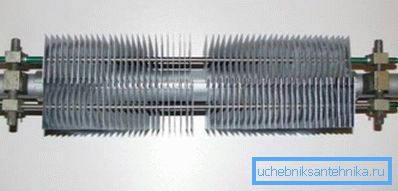
- The system is based on a U-shaped curved tube through which the coolant moves.. Taps are installed at the inlet and at the outlet, allowing the radiator to be cut off from the system.
Note! Simple ball valves are most often used, since adjustment of the coolant flow is not required, but reliability is needed as much as possible.
- Heat exchanger plates are put on the tube.. They can be made from the same material as the pipe itself, or they can be made from another metal.

- Most often, this entire system is assembled in a thin-walled metal case, the main function of which is to protect the heat exchangers from dust, scratches and burns when in contact with a heater a person is saved. To release hot air in the upper part of the body holes are made.

Operating principle
Such a system functions quite simply:

- The heat carrier (hot water or steam with a high temperature) moves under pipes up to 20 atmospheres. In this case, the high speed of movement leads to the fact that when moving along the contour, the temperature of the coolant decreases slightly.
- When passing through the area with heat exchangers, water gives off some of the energy to the plates. Those, in turn, quickly heat up to a high temperature.

- Cold air enters the radiator housing through the holes in the bottom.
- A large area of the plates facilitates heat transfer, since they are in almost all the surface in contact with air.
- After the air temperature rises, it rises and exits the case through the holes in the cover.
Note! There are also unpackaged models, but their efficiency is lower due to a certain percentage of heat loss.
The process of vertical movement of air during heat exchange occurs continuously and is called convection. Heating devices themselves are often called convectors.
It should be noted that not always the natural rise of air is enough. In this case, a fan is mounted in the lower part of the case, which provides movement of air masses. On the one hand, the cost of heating increases due to the use of additional electricity, but on the other hand, efficiency also increases significantly.
Main varieties
To date, the market offers several types of lamellar type batteries.
They can be divided into several signs:
| Characteristic by classification | Species |
| Material | It is the material that determines how efficiently the device will transfer heat:
|
| The number of pipes in the casing |
|
| Connection type |
|
| Mounting method |
|

Advantages and disadvantages
The demand for plate radiators on the market heaters for commercial and public real estate is due to their objective advantages:
- First, the high speed of the coolant allows you to lay long contours with minimal energy loss.
- Secondly, the absence of internal joints makes the system exceptionally reliable: a correctly mounted circuit without leakages and gaps must withstand an oppression pressure of up to 40 atmospheres.

- Thirdly, the undoubted advantage is the low cost of products and components for them, due to the simplicity of the design. This concerns, first of all, thermostats, which operate on the principle of dosing the flow of coolant.
Of course, there are disadvantages:
- On the one hand, the appearance of the radiators leaves much to be desired, since the box-shaped body is not distinguished by the original design.
- On the other hand, if you remove the case, the heat exchanger fins will become clogged with dust, which will significantly reduce the heating efficiency.
Tip! Even a closed battery should be periodically cleaned with a vacuum cleaner, removing dirt from the outlet openings in the upper part of the case.
Conclusion
The lamellar steel radiator is rather simple, but at the same time effective design. It should not be used everywhere, but where it is necessary to heat a large area quickly and efficiently, it will definitely be appropriate. You can learn more about the features of such batteries if you take the time to watch the video in this article.