Radiator binding - schemes and docking
By and large, tying the heater is connecting a new player to the game. The radiator fits in with the pipes, it is equipped with new plugs and regulating cranes - that's all, it is already in the game.
But the voiced simplicity will work only when everything is done correctly, the coolants pass the radiator in the right direction, the radiators themselves are equipped with fittings with a full understanding of compatibility problems, the connections are sealed with knowledge.

A simple process, but knowledge is needed
To understand the correctness of the process we divide it into components.
The whole instruction is as follows:
- The available diagrams for connecting radiators - we choose;
- Compatibility of various types of batteries and fittings - check;
- Strapping radiators with pipes - dock.
For information! Separately, the general rules of spatial placement of the radiator will be considered, since neglecting them can significantly reduce the efficiency of the battery.
General concepts
Violation of simple rules for placing batteries can negate all subsequent stages of strapping, reducing the efficiency of one link to 25%.
So:
- The distance from the window sill should not be less than 10 cm;
- The distance from the floor to the lower edge of the radiator should not be less than 12 cm;
- The radiator is not placed close to the wall, the minimum gap between them should be 20 mm;
Note! The assembly kit with plugs includes holders for sectional batteries, and for panels, fasteners are included with radiator. They were originally designed for the required period.
But our man’s desire to save money and do everything in his own way makes him do it. Another trick that will remind you about the need for a gap - a heater with a foil reflector is glued to the wall under the battery, and a gap is needed between it and the radiator.

- Be careful with the niche under the battery. The desire to hide the heater can lead to loss of efficiency and heat transfer. For lovers of aesthetics, the price of a question can be 10% loss of heat transfer in semi-open niches and 20% in closed niches.
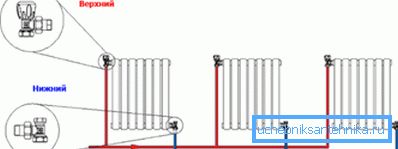
We will understand with the schemes
It is important to correctly enter the radiator in the scheme. In the cottages, in small apartment buildings there may be two heating schemes. In apartment buildings, as a rule, one option.
Here they are:
- Single pipe design;
- Two-pipe scheme.
With a one-pipe scheme, the water from the boiler goes through the whole cycle from the boiler, through the batteries, into the boiler through one pipe.
It is difficult to say what the initial idea of the development engineers of this scheme is, but it has many drawbacks:
- Water or heat carrier under pressure is fed to the upper point and self-draining goes down. The air temperature in the upper rooms or floors will be higher than in the lower ones;
- Virtually no process regulation. With simple equipment, you can set the calculated value for the coolant, but there will be no reason for the lower floors;
- Emergency work of both local and whole riser cause a lot of problems. It is necessary to disconnect the riser or the house.

Note! Saying that there is no regulation of the process, we have somewhat moved away from the truth; now there are complex systems that allow regulating this process. But they are very expensive and are designed only for homes with independent boiler.
The two-pipe design is both simpler and more reliable. The coolant is fed through one pipe, the cooled water goes through the other.
There are two connection options:
- The first - the pipes leading and taking away, settle down on the one hand;
- The second - leading pipe comes in one direction, and the discharge goes to the other side. This scheme is applicable for long and low batteries, as a rule, of floor type, for high-quality heat distribution.
Attention! Whatever type of connections are used, a pipe with warm water should be on top, and a pipe with cold water, also called “return”, should be on the bottom. In the sources you will find the option of bringing hot water from below as possible or alternative.
It was acceptable about 40 years ago, when polypropylene heating radiator piping was from the category of science fiction, and the pipes were only metal, but then they also came out of the situation. We speak at once - the lower eyeliner of hot water will disappoint you.
Radiators are ready
Collection of radiators will not be a problem, everything is done by hand with the standards:
- We will determine the connection scheme (hot supply from the top, you remember), give the lower part under the return flow;
- At the upper inlet, opposite to the inlet of the coolant, a stopper is placed with a Mayevsky valve to lower the air;
- At the lower exit, opposite to the return outlet, we install a blind radiator plug.

Tip! All threaded connections for which rubber seals are not provided are sealed with tow and special paste, or with special FUM tape that resembles insulating tape.
A few words about compatibility
| Material | Properties |
| Cast iron | Takes everything that fits him on the thread |
| Steel | Feels great with brass, stainless steel, copper. |
| Aluminum | Poor tolerates copper, brass. Galvanizing perceives as a necessity |
Docking - the final process
At present, three types of pipes can take part in the strapping process:
- Binding of cast iron radiators with metal pipes. To be honest, metal + cast iron is a variation of yesterday. We chose cast iron batteries because of their reliability, prolonged temperature retention, please use, but pipes can be exchanged for polypropylene;
- Binding of radiators of heating with metal-plastic pipes. Enough reliable option. It has a metal sheath, allows you to go to any hard-to-reach places without changing the connection scheme. Perfectly repeats any curvature of the wall.
- The piping scheme of heating radiators with polypropylene is the most interesting. With all the advantages similar to metal-plastic pipes, polypropylene compounds are much more reliable. So, in this case soldering is used with the help of special soldering irons for such pipes.

Tip! Polypropylene constructions are set more slowly than metal-plastic, but you get a guarantee on the pipe, connections, soldering. In the case of metal-plastic, the temperature differences give different extensions to the metal and plastic, which can lead to leaks, and at the most inopportune moment.
Finally
The rules of binding the radiator are simple: the main thing is to know where to connect, and the video in this article will tell you which fittings you need and which key.