Radiator fluid: features of aqueous and alcohol-containing
Of the entire range of coolants, water enjoys well-deserved popularity due to its physical properties, as well as the ratio of availability and price. The corresponding water heating systems are traditionally mounted without requiring exotic components. On the basis of the material of the system and the operating conditions, additives may be added to the coolant, changing its physical properties and limiting the corrosion processes.

H2O with variations
Traditionally, residential heating systems use water - an environmentally friendly substance that is cheaper than other heat-transfer fluids.
It is easily and safely added to the heating system, and the physical properties are used with maximum benefit:
- surface temperature of the heaters does not exceed the hygienic limit - 80 °, which eliminates the possibility of getting burned;

- due to good fluidity the room warms up evenly;
- high heat capacity of water allows the use of pipes with a smaller cross section, therefore reduces the cost of equipment;
- leakage is not life threatening.
At the same time, seemingly harmless fluid for radiators has insidious abilities:
- freezing below 0 ° C to increase in size and easy to break the pipe;

- permanent corrosion processes involving air in the system from which water was drained;
- carbonate salts are actively decomposed in hot water and scale is formed on the inner surfaces of pipes without a protective coating and it is necessary to add additives that are mostly toxic;
- mandatory annual flushing of the system and the prevention of the boiler.
Note! Boiling removes water from the salts that settle on the bottom, and the addition of soda, slaked lime, orthophosphate from magnesium and calcium compounds. This is followed by settling and filtering.
The ideal heat carrier for the heating system can be distilled water, which is usually sold in pharmacies. Given that the system will need more than a dozen liters and stock to refuel, the cost of your heating system will increase significantly. Priority cost - the integrity of the valve is only for you.

Alcohol-containing solutions
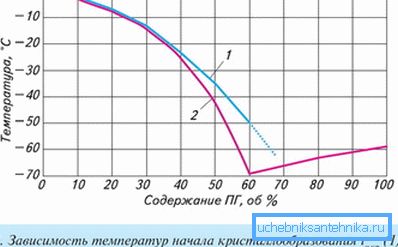
Aqueous solutions of glycol or the more popular name of the fluid in the radiator of heating - antifreeze, have become lifesavers for heating systems that are included from time to time. Nezamerzayki produced on the basis of ethylene and propylene glycol, which does not allow the system to freeze, but radically different in some other parameters.
The advantages of ethylene glycol include:
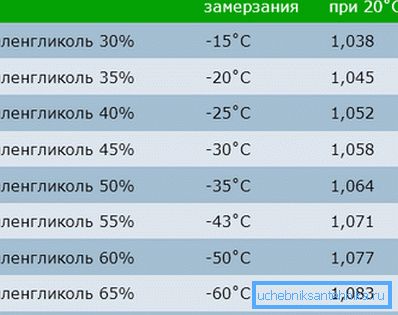
- low freezing point - -13 ° C,
- low sedimentation rate;
- at freezing the volume increases by only 1.5%;
- affordable price.
The negative aspects include:
- high toxicity - even inhalation of vapors is dangerous;
- not having an unpleasant smell, does not cause alertness for leaks;
- becomes viscous at low temperature;
- special disposal procedure;
- poured fragments should be replaced when spilled.
The properties of propylene glycol non-freeze can be called ideal:
- freezing point -60 ° C;
- freezing increases in volume by 0.1%;
- non-toxic;
- "Friends" with all materials of the heating system;
- do not form deposits and remove existing;
- good fluidity.
The disadvantage of propylene-based antifreeze is its cost, which is 2–2.5 times higher than ethylene glycol.
Moydodyr for radiators
The overgrowing of the inner walls of the pipes with scale leads to poor heat transfer and it is necessary to rinse them, which can be done with your own hands during the non-heating season at least once a year.
You will need:
- dense rags;
- fitting tool;
- a bottle of acetic 70% essence or, for example, "Mole".
Before work, turn off all necessary valves to avoid flooding:
- drain water from the radiator;
- dismantle it;
- insert a fine-mesh filter into the bathtub drain, cover the bottom with thick rags and put the battery in;
- fill the radiator with water, shake it and drain it;
- fill up the radiator repairing fluid and leave for an hour.
Note! Do not use acid / alkaline solutions for aluminum radiators, in order not to spoil it.
- shake and drain;
- rinse with water until it flows clear;
- Replace the battery.

Note! In a private house, the coolant may come from a well / reservoir and contain mechanical suspensions. It is advisable to wash not only the radiators, but the entire system with a conventional hose or a special gun.
Planned force majeure
Periodic 1 time in 3 years replacement of fluid in the radiator of heating due to:
- changes in the physicochemical properties of the coolant;
- deterioration of the heating system caused by chemical processes.
This procedure is best left to professionals who:
- will conduct a preliminary analysis of the fluid;
- determine the rate of corrosion;
- flush and flood the system;
- dispose of seized material.
As a result, you save your time and get a guarantee of safety and quality, especially when it comes to antifreeze.
Electric heat
An alternative to the traditional method of heating are liquidless electric radiators or convectors with a housing mainly made of aluminum. The coolant is presented in the form of a nichrome filament in a steel pipe, the presence of 2 rods allows for the economical use of half the power.

The electronic control panel provides the set temperature with a minimum error of up to 0.1 °, while the manual setting of the thermostat fails 0.5–2 ° C.
The big plus of convectors is:
- the absence of problems associated with corrosion, freezing and gusts of the system;
- mobility;
- elementary rules of use;
- esthetics and wide color range.
A huge disadvantage, often limiting the possibility of using dry batteries, is their absolute dependence on the voltage in the network.

Word Archimedes
Reconstruction or repair of the system may require the calculation of fluid for the radiator section of the heating or the entire system. Usually a section of aluminum radiator holds 0.45 liters of coolant, cast iron - 1 or 1.75 liters; The linear meter of a pipe with a diameter of 15 mm is 0.177, and 32 mm is 0.8 liters, plus the volume of the boiler is taken into account.
The calculation is made according to the formula: V = (VS x E) / d, where:
- V is the volume of the expansion tank (10% of the total volume of fluid in the system, if the tank is with a membrane, look for the data in the data sheet);
- E is the percentage expansion coefficient of the liquid, for example, for water it will be 4%, for ethylene glycol - 4.4%;
- VS is the total volume of the system (boiler, pipes, heat exchangers, radiators);
- d - indicator of the effectiveness of the expansion tank.
Another instruction for calculating the volume takes as a basis the system power indicator. If 1 kW is proportional to 15 liters of liquid, then with heating power, for example, 75 kW, the formula is: VS = 75 x 15 = 1125 liters.
Note! On our website or reference books it is easy to find the corresponding calculation tables.
Summarizing
The choice of a heat-transfer fluid is possible only for a private household, where the owner chooses a way of life and, accordingly, heating. Depending on the climatic conditions, it can be water or antifreeze, and with reliable energy supply, dry radiators. Liquid batteries require more attention and periodic prophylaxis, significantly extending the operational properties of the system as a whole.
The video in this article reveals the tricks of radiator repair without running water from the heating system.