Radiators in the apartment: the characteristic of modern
Recently, the choice of heating radiator has become a very difficult task. It is necessary to take into account not only its technical characteristics, but also its appearance. A variety of heaters only complicates the choice. In order not to overshoot with the purchase, it is worthwhile to take a closer look at the advantages and disadvantages of the existing types of batteries, but to stop at the subtleties of choice.

Short characteristic of modern radiators
Types of heating radiators for an apartment for a long time are not limited to only iron or steel models.
In addition, models with the use of non-ferrous metals are popular on the market, such types of radiators can be identified as:
- cast iron Radiators have been known for more than 150 years; in fact, the progenitor of modern batteries was made of cast iron. Such heating devices are characterized by high inertia, democratic cost (with the exception of artistic models) and react poorly to the composition of the coolant. So it is not necessary to monitor the pH level;

Note! Cast iron almost does not tolerate water hammer, and indeed any mechanical effects. Given the heavy weight of the battery assembly, it is better not to carry out installation work alone.
- steel - panel radiators can be considered a typical representative of this group. Unlike other heating devices, steel is produced not sectional, but solid. Steel is quite sensitive to the quality of the coolant, for example, it is undesirable for the acidity of the water to be too high (the pH limit of 9.5 can be considered the upper permissible limit). The service life of radiators in the apartment is not very long just because of the quality of the coolant, the steel rusts relatively quickly;
- bimetallic - in cheaper models steel and aluminum are combined (pipes from steel, and ribs - from aluminum), in expensive models - copper + aluminum. Non-ferrous metals are used to increase the heating rate of the heater, and the heat transfer increases. The only disadvantage is the cost, the price of a copper-aluminum battery can be several times higher than the cost of an ordinary cast-iron;

- aluminum - differ from bimetallic in that the collector tubes are made of aluminum alloy (on the inside, the metal is covered with a protective layer);
- completely copper heating radiators are quite rare, the reason lies in the high cost;
- vacuum Batteries are still not widespread. This is due to their high cost and lack of experience in their application. Although the very idea of using boiling liquid looks curious, it is possible that with a decrease in cost, their popularity will increase.

It is rather difficult to compare the listed types of radiators, it all depends on which criterion is considered the main one:
- for example, bimetallic in terms of heat output. The heat output of the section can reach 200 W, for iron, this figure is about 1.5-2.0 times lower;
- in terms of durability cast iron is in the lead. The service life of cast iron heating radiators in an apartment reaches 50 years, but after half a century they can work more than one decade, because the cast iron does not rust;
- As for the appearance, all modern batteries look great (except for the old cast iron models, but if finances allow, you can buy art cast iron radiators).

Subtleties of choice
When choosing the main attention should be paid to the technical characteristics of the radiator, the appearance, of course, is important, but it is worth paying attention to it later. We will be interested in the dimensions of the battery and its heat output, as well as the operating pressure in the system and the temperature of the coolant.

Dimensions of the radiator
Heating devices are rarely placed just near the walls, usually people try to hide them in the niches by the windows. This decision is justified, but it is important that the distance to the walls from the battery is sufficient for air exchange. Otherwise, a significant part of the thermal energy will go to the heating of the walls.
Note! It is forbidden to close the batteries with curtains, this makes it impossible for the warm air to enter the room.
It is important to understand how the heating radiator in the apartment works, for example, bimetallic batteries combine direct heat transfer with convection, so that the distance to the window sill from the top of the device is especially important.
There are a number of general rules for placing a battery under the window:
- the gap between the floor and the bottom of the radiator should be 8-12 cm (it is not recommended to increase it as this will lead to a much colder level at the floor level);
- radiator width should be approximately 75% of the width of the niche;
- distance to the window sill - 6-12 cm;
- there should be a gap between the rear wall of the heater and the wall (about 5 cm).

Another important parameter is the center distance (also referred to as the distance between the centers of the nipple holes). This parameter is important when installing, if all the installation work will be done by hand, then you need to consider in advance that the distance between the supply pipe and the return should be equal to the center distance of the battery.
Note! In principle, pipes can be reduced / diluted for any center distance, but this is an extra loss of time. It is much easier to take into account this nuance when buying a battery.

Battery thermal power
Regardless of what kind of heating radiators are for an apartment, it is necessary to determine the required thermal power of the device. After all, comfort in an apartment is possible only in the case when the heat input is at least equal to heat loss.
There are several calculation methods. A simple man in the street usually uses a simplified method in order to simply estimate how many sections a heating radiator should have. But when designing an autonomous heating system, a more complicated calculation may be needed (taking into account the arbitrary supply and return temperature).
Note! The calculation of the required power of the heating device with an accuracy of watt is not needed. We only need a rough value in order to determine the number of battery sections.
Such calculation options are possible:
- at the average rate of 1m2 / 100 W, that is, we simply count the area of the room and multiply by 0.1, we obtain the required power of the heating device in kW;

Note! If there are 2 or more windows in the room, the room is angular or the ceiling height exceeds 2.7 m. It is recommended to increase the result by 15-20%.
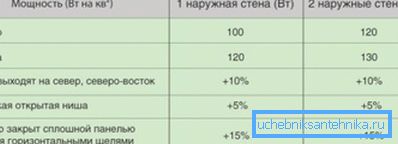
- you can go the other way - to calculate the volume of the room and given the rate of 1m3 / 41 W to calculate the required heat transfer;

- the most complicated method is dependencies that allow to calculate the real heat transfer for any temperature of the heat carrier.
The calculation instruction in this case will look like this:
- First you need to determine the temperature
?T = (T pod + Tobr) 2-Tk,
In the expression, the following notation is used: Tpod and Tobr - respectively, the coolant temperature at the inlet and at the outlet of the heating device. Tk is the air temperature in the room.
- then the actual power of the heating battery is calculated by the formula
Q = k • A •? T
k is the heat transfer rate of the radiator (depending on the material), A is the surface area. The product of these parameters is a constant for each battery. To simplify the question of how to calculate the heating radiator for an apartment, we first determine the product k • A for standard supply and return temperatures.
In this case, the thermal power of the device is known,? T is also known, is determined by k • A. After that, it is already possible to calculate the power of the heater for any temperature of the coolant.
This approach can be advised when designing an autonomous heating system, low-temperature systems can be used, for example, and the battery documentation indicates its heat output only for normal operation (90? C in flow, 70? C - return).
Selection of heating radiator
The required heat output was determined to decide the question of how to calculate sections of radiators in an apartment.
To complete the calculation you need:
- choose a suitable model of the radiator, in the technical documentation to find out the heat transfer of one section during normal operation;

- Knowing the minimum required thermal power of the device and the heat transfer of one section, it is possible to calculate how many sections will be needed as the ratio of these values.
Note! Such flexibility is inherent only in sectional radiators. If you plan to purchase a steel panel battery, then adjust the heat transfer set of sections will not work.
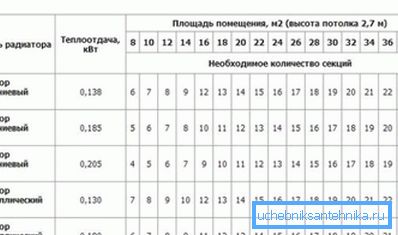
To simplify the sizing of the heater, it is possible to use ready-made tables in which, depending on the floor space, it is indicated which heater should be used. This is convenient, but it is better to inflate the result obtained a little, by 15-20 percent, and to be able to regulate the temperature just put the thermostat on the supply.
In conclusion
The selection of a heating battery for an apartment is a task that requires serious consideration. It is necessary to take into account such characteristics of the device as: thermal power, durability, tensile strength, etc.
The proposed information will help not only when selecting a radiator for thermal power, the main parameter of the heater, but also when choosing between different types of radiators.
The video in this article lists the strengths and weaknesses of popular models of radiators.