Single-pipe heating system: how to heat your own house with
The choice of heating your own cottage is one of the most important stages of the design and construction of housing. It depends not only comfort and comfort in the house, but how much money will be spent on utilities. The optimal choice for buildings with a small area is a single-pipe heating system with natural circulation, the rules for the installation of which do it yourself and will be discussed below.

Species
Single-pipe heating can be designed according to several different schemes. The choice of a particular depends on your personal preferences, as well as the characteristics of the object being built.
However, any scheme of a one-pipe heating system has the following features:
- in this engineering network there is no division into the coolant supply pipelines and coolant discharge water from the radiators;
- all devices are connected in a common system in series, and the coolant, passing through the system, describes a ring;
- A closed one-pipe heating system (with a closed circle of hot water circulation) can be combined with a two-pipe one - in this case, water is supplied to the floors and removed via two channels, and the wiring is arranged one by one.
Civil engineers distinguish four varieties of one-pipe circuits, which differ in the way of installation of the pipeline connecting the boiler with radiators.
- Single pipe heating scheme with bottom pipe arrangement. In this case, the coolant flows through pipes arranged horizontally and laid along the floor (or below it), after which it rises to the installed heating panels. The advantages of this system are in easy temperature adjustment and the ability to block individual elements of the engineering network in case of accidents or for preventive maintenance.
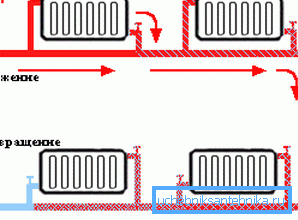
- Single pipe heating system with upper distribution. Here, the coolant, leaving the heater, immediately rises to the highest point of the network, after which it is distributed by means of pipes laid horizontally over the heating panels.
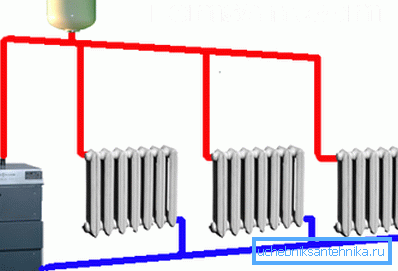
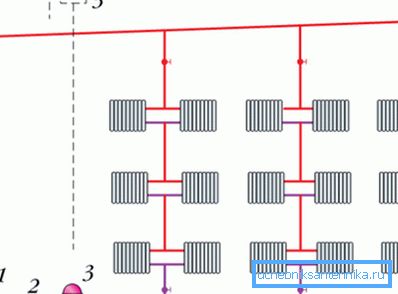
- Monotube vertical heating system. Its peculiarity is that there are no horizontally laid pipes in the rooms. Here the coolant, falling into the top point, flows vertically downwards, passing along the path through the radiators installed in the rooms.
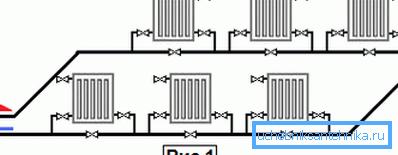
- Monotube horizontal heating system is fundamentally similar to the previous one, but here the pipes are arranged horizontally. Often this scheme is used in single-storey houses.
In addition to the varieties described above, the one-pipe scheme of the heating system is:
- with natural circulation of the coolant;
- with the forced organization of water flow.
In the first case, the flow of fluid is provided by the temperature difference and, accordingly, the density. The pressure of the cooled water flowing out of the radiators displaces the less dense and hot coolant to higher points of the pipeline, from where it spreads further.
In order for such a network to function normally, it is necessary, when installing pipes, to arrange their slope towards the boiler by 3-4 degrees. And this is not always possible in one-story buildings of great length (more than 30 meters).

The system of forced circulation is additionally equipped with a pump, which is installed in front of the entrance of the return (cold) pipeline to the boiler. In this case, the slope can be made smaller (from 0.5 to 1 degree).
Note! The scheme with natural circulation is preferable, since it is more non-volatile - its operation does not depend on the presence or absence of electricity.
In order to avoid stagnation of water during a power outage, engineers advise installing a so-called accelerating collector. This is a common vertical pipe that raises the coolant to the top of the system - at a height of at least 1.5 meters relative to radiators.
Installation
Principle of operation and elements
The one-pipe closed heating system is a ring in which all its component parts are included:
- the boiler that heats the coolant to a predetermined temperature;
- pipes through which hot water is delivered to the radiators, and after their passage to the boiler;
- heating panels;
- expansion tank.
Choosing a boiler, pay attention to the type of fuel it uses. The most economical heaters, where water is heated by gas. But for this purpose it is necessary for the gas pipeline to fit your site. In addition, solid or liquid fuel equipment, liquefied bottled gas or combination units are often used.

The diameter of pipes depends on the length of the heating network, the type of radiators in the area of the house, the power of the boiler, and so on. Currently, the most common pipelines of various polymers.
When choosing pipes and radiators for designing a single-pipe heating system, it is necessary to take into account engineering parameters (volume of the required fluid, its pressure, temperature, diameter of pipelines, area of radiators, etc.), which must be determined in advance.
Calculation of hydraulic heating - a one-pipe system with any location of the main supplying the coolant - can be done independently or entrust this work to a specialist. The price for such a service is usually not very high.
The expansion tank is necessary to regulate the pressure of the fluid in the system and prevent its breakdown in the event of its increase. Modern heating system involves the use of a closed-type expansion tank. It consists of two chambers separated by a flexible partition. In one of them air is pumped under high pressure, the second is connected to the heating pipes.

Note! Expansion tanks of a closed type can be installed not only at the top of the system, but also in any place convenient for you, for example, a boiler room or utility room. Another advantage is that the lack of direct contact with air prevents premature corrosion of the metal parts of the heating system.
Selection of options for connecting heating panels
The one-pipe connection scheme of heating radiators provides for the flow of coolant or the construction of so-called bypasses — sections of pipes through which hot water can flow, bypassing the radiator.
In the first case, the arrangement of the riser for transporting fluid is not supposed. Water flows from the boiler and flows through each radiator: from the top to the bottom or from the near to the far. At the same time, the water temperature will gradually decrease and the lowest (far) rooms can be heated poorly.
This situation can be avoided if radiators of a smaller area are mounted at the beginning of the heating system than at the end.
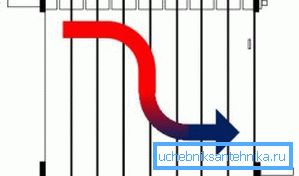
The downside of the system is rightly considered to be the inability to install shut-off valves and thermostatic valves on the pipelines, since the overlap of a single valve will result in the inoperability of the system as a whole.
In the second case, a transit pipeline, a bypass, is mounted under the heating radiator, thanks to which more efficient heating of all the rooms is provided.
Note! Bypasses must be made of pipes of smaller diameter than the main pipeline, otherwise a sufficient amount of coolant will not flow into the radiator.
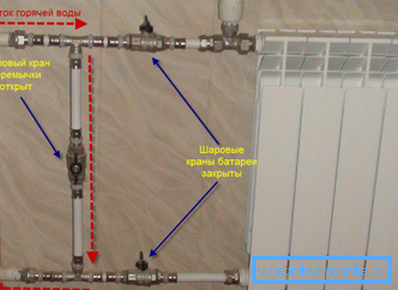
All water entry points in the heating panel, as well as bypass pipes, must be equipped with taps. This will allow you to adjust the temperature of the heating system in each room separately. In addition, in the event of an accident, it is possible to temporarily disable a particular section and repair or replace it without stopping the heating.
Installation technology
Installation of the described engineering network can be made only after the hydraulic calculation of a one-pipe heating system has been performed. It depends on it which elements will be used.
The very sequence of actions is as follows:
- In a pre-selected and prepared place, a heating boiler is installed. The instruction describing this process comes with the unit. It is advisable to entrust the installation of this equipment to a specialist of the organization where you purchased the device. He will give a guarantee on his work.
- Pipeline is being constructed. At the same time, it is necessary to mount the tees in advance at the places of installation of radiators. Be sure to ensure that all pipes are installed with a slope, otherwise the natural circulation of the coolant will be disturbed.

- In the case of installation of heating with forced water flow, you need to install an electric pump. Remember that this equipment is designed for pumping water, the temperature of which does not exceed 60 degrees. Therefore, it must be installed at the end point of the system - before the entry of the cooled coolant into the boiler.
- Next, connect the expansion tank. As already mentioned, a closed container with a membrane can be mounted anywhere, and an open one can be installed only at the highest point of the system.
- At the end of the previous stage, you can begin to fix the radiators. They are attached to the wall using complete brackets. Before marking and drilling, you should familiarize yourself with the manufacturer’s recommendations regarding installation. It is important to maintain the prescribed distances from walls, window sills, floors and other structural elements of the building.
- Heating panels are installed on the basis of your chosen scheme. Do not forget to connect valves, thermostats, plugs, valves for air bleeding, and so on.

- Before pouring the coolant, pressurized with compressed air is performed, after which the system is filled with water, a test run is made and the operating modes are adjusted.
A single-pipe vertical heating system with a lower distribution of pipes is more suitable for multi-storey private houses, with a horizontal one - for single-storeyed ones. But remember that when the area of the house is more than 200 square meters. meters and pipe lengths of more than 30 meters, you must either install powerful pumps or choose another installation scheme for the heating system.
Conclusion
Horizontal one-pipe heating system is one of the most effective ways to heat small dwellings. If you are the owner of spacious housing, it is advisable to opt for more complex but effective schemes. Their description is devoted to the video below.