Steel heating radiators: technical characteristics and
Today, heating radiators are made of various materials. Classic cast iron gives way to new, more advanced and practical options. One of them are steel batteries, which will be discussed in this article.

General provisions
Steel gives heating structures the following qualities:
Merits
- High level of heat transfer, which is carried out both by heating the air and by convection.
- Long service life. The number of possible failures is minimal when operating standards are observed.
- Simple installation instructions. Threaded or welded pipe connections are possible.

- Affordable price. The described structures are, for example, cheaper than aluminum counterparts.
- Attractive appearance. They do not need to be hidden behind curtains, blocked with furniture or covered with decorative panels. They can themselves serve as part of the interior of your home.

But it does not do, of course, without negative sides:
disadvantages
- Susceptibility to corrosive processes.
Advice: it is not recommended to use the models in question in buildings with a centralized heating system, from which all liquid is drained from within the summer period. The fact is that raw air accelerates the emergence and spread of destructive rust even more.
- Lack of durability before hydraulic impacts.
Tip: heating systems with steel batteries should be equipped with special transducers, softening the shock wave of the coolant supply, or do not use them in high-rise buildings at all. Otherwise, water hammer in a short time will destroy the entire structure of heating.
- Premature paint peeling.
Tip: it is advisable to use high-quality special paint for steel products. It will be much more economical than frequent repainting cheap.

Thus, if we carry out comparative characteristics of steel radiators with models from other materials, it will be possible to conclude that they are ideal for private houses, winning in many ways, and categorically contraindicated for installation in apartment buildings.
Kinds
There are two types of products considered:
Panel

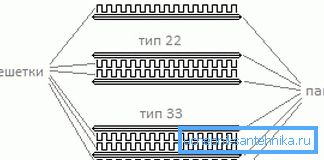
In the core of such a device are located from one to three sections, consisting of a pair of steel profiles, welded around the perimeter for joining. Plates are stamped, as a result of which vertical channels appear on them for the passage of coolant.
To increase productivity, such structures are equipped with additional elements, which causes their division into many types:
| Title | Description |
| Type 10 | Single-row model without convector and facing part |
| Type 11 | Also there is only one row without an upper grate, but with a convector |
| Type 20 | Double-row sample with air outlet grill, but without convector |
| Type 21 | Two radiators with a single convector, encased in a casing |
| Type 22 | Two-row radiator, two convectors and a cover |
| Type 30 | Three rows of radiators, convector fins absent, grille mounted on top |
| Type 33 | Three-row model with three convectors and a closed housing |
Tubular

The structure of such a radiator is iron pipes welded together. But at once it is worth noting that the final price of such products is very high, and not everyone can afford it.
Options

The following technical characteristics of heating radiators are inherent in the products under consideration:
| Parameter | Comments and value range |
| Thermal recoil | From 1200 to 1800 W, plus low inertia, thanks to which the structure warms up quickly and begins to give off heat to the room |
| Operating pressure |
this once again proves the inadmissibility of the use of steel batteries in apartment buildings, where they simply will not withstand the pressure of the common heating network |
| Permissible coolant temperature | 110-120 degrees Celsius |
| Dimensions |
|
| Steel thickness | Steel used in the manufacture of radiators can change its value from 1.15 to 1.25 mm, depending on the manufacturer. |
| Lifetime | Not less than 40 years |
| Installation | It is carried out easily, thus it is possible to use both threaded connections, and welded |
Conclusion
Radiators made of steel are an excellent choice for a private home, where you can control the flow rate of the coolant and eliminate its discharge for the summer period. They have an affordable cost, very high heat dissipation and long operational life. In high-rise buildings, frequent water hammer and periods of lack of liquid will render them unusable.

The video provided additional material relevant to the topic.
Make your choice deliberately.