The amount of water in the heating radiator: documentation
The amount of coolant in the bowels of the radiators for many is an abstract value. The volume of this fluid affects the inertia of the heating system, the warm-up time and the mode of operation of the boiler. The ability to calculate the volume of water in any part of the heating system will allow you to more accurately select the rest of the equipment under it (boiler, circulation pump, etc.).

What you need to know the amount of water in the battery
Typically, radiators pay attention to the beginning or end of the heating season or during the general cleaning. At the same time, vital processes occurring inside the human being for which the coolant is responsible - most often water. Does information about how much this fluid fits into one battery, section, have any value?

It turns out that this is not the only reason:
- do not “weight” the heater, because the volume of water in the cast-iron radiator heating increases its already considerable weight;
- The installation of a heating system with a certain boiler capacity requires the calculation of the total amount of coolant, including in radiators;
- knowing that the amount of coolant in the battery is 10–12% of the heating system - all the batteries, pipes and boiler can drain the water “dry”;
- when choosing an expansion tank;
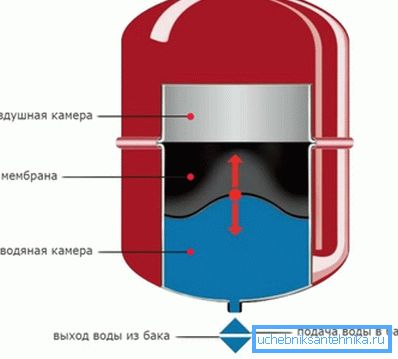
- so as not to overdo it with concentrated antifreeze, which is poured in a certain proportion with water;
- for the natural / forced circulation type, the optimum battery size is selected - big in the first case and no difference in the second.
Forced initiative
In the panel house with central heating it is not necessary to bother about such issues as filling the system with a coolant, this is the diocese of housing and communal services. But taking care of a manor or a dacha is a huge responsibility that lies completely on your shoulders. The opportunity to save time and money forces the owners to maintain thermal communications with their own hands, using sometimes non-standard methods.

For example, the lack of a centralized water supply forces the use of natural sources - wells, wells, ponds.
In order to know exactly the required amount of fluid, it is necessary to calculate in advance how much of it will be included in all composite heating systems:
- boiler;
- pipes;
- radiators.
We work with documentation
The answer to the question of how much water flows from pipe “A”, or rather, should go there, usually lies in the technical data sheet of the radiator and boiler. With pipes it is a little more difficult, but not fatal - knowing their internal diameter, on our website you can find a detailed table about the amount of water in liters / cubic meter per linear meter. The same can be said about the data on the volume of the fuel boiler or batteries.

Knowing the fullness of each meter of the pipe, find out the total “pipe” volume of the heat carrier elementary-table number multiplied by the number of meters. To do this, it is not necessary to crawl with a tape measure throughout the house, but use the project plan and ruler.
Note! On the Internet, a table of water volume in a radiator looks even more convenient. It can compare the capacity of radiators from different materials, which will give you the opportunity to choose the appropriate option.

The table below shows that the volume of water in the section of the bimetallic radiator and the aluminum one is the same. So the material does not matter, the main thing is the dimensions of the heater.
Non-permanent residence in the house requires the owners to use antifreeze. Since this pleasure is not cheap (the price for 10 liters of domestic propylene glycol "Coziness technology" reaches a thousand rubles), it is necessary to know the exact amount of non-freeze. Having determined the extreme negative threshold for the heating system, the substances are mixed in a certain proportion.
Note! Do not add antifreeze to a heating system made of galvanized pipes.

Average cheat sheet
The average data determining the volume of water in steel radiators of panel-type heating are as follows:
- model Demrad, Thermogross 11 type for every 10 cm length accounted for 0.25 liters of coolant;
- In similar models of the 22 type, this figure increases to 0.5 liters per tighter length.
Each section of the good old "cast iron" of different models has the following capacity:
- MS 140 - 1.11–1.45 l (from 5.7 to 7.1 kg);
- World Cup 1 - 0.66–0.9 l s;
- World Cup 2 - 0.7–0.95 l;
- World Cup 3 - 0.155–0.246 l;
- Konner Modern - 0.12–0.15 liters (3.5 kg).
Note! You can see how the traditional MS 140 differs from the Chinese Konner weight, which should be paid attention to if you have a floor model.

If your battery is an intricate author's thing, finding out its volume is difficult, but possible. For example, the volume of water in a steel tubular-type radiator is calculated ingeniously simply — one hole is closed by a plug, and water is poured through the second to the top.
Note! Mark the amount of liquid filled immediately or later, when you pour the contents into a bucket / bath. This method of calculation is applicable to a radiator of any complexity without documents.
In heat exchangers of a wall heating boiler, on average, from 3 to 6 liters are placed, and in floor and parapet execution - from 10 to 30 liters of water. So, having learned the amount of coolant in all the corners it reaches, you can carry out a responsible operation - calculate the volume of the expansion tank. It depends on it the optimal pressure in the system and the desired volume of coolant.

The calculation instruction assumes the use of a simple formula:
(Vс * К) / D = Vб, where
- Vс - the volume of coolant in the heating system (what was mentioned above - radiators + pipes + boiler heat exchangers);
- K - coefficient of expansion of the coolant (in water it is equal to 4%, therefore, 1.04 is used in the formula);
- D - tank expansion efficiency;
- Vb is the capacity of the expansion tank.
It is possible to find out the volume of coolant in radiators or pipes, which is close to the real figure, based on the boiler power using the formula:
x kW * 15 = VS, where
- kW - boiler power;
- figure 15 - the number of liters of water to obtain 1 kW of energy;
- VS - total system capacity.
Summarizing
The principle is better to underpower than the opposite is not applicable in heating systems, since the system airing will mean cold batteries. By calculating the volume of each structural element of the heating system using tables or experimentally, the heat consumption will become more meaningful and enjoyable. A repair or replacement of a separate fragment will no longer be a secret with seven seals.
The video in this article shows the process of pouring coolant into the heating system.