The basic scheme of heating and its types
Before you begin planning for autonomous heating in an apartment or a private house, you need to familiarize yourself with the concept of heating. Below we take a closer look at what it is and what are the basic concepts of heating.
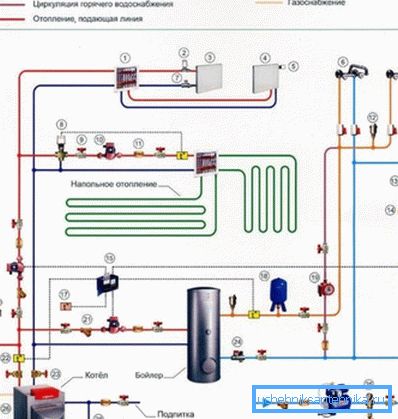
General information
Under the schematic diagram of the heating system is usually understood the simplest scheme, which indicates the main elements of water heating, combined into a single system.
The latter can be implemented in several ways, however, in any case, it includes the following elements:
- Boiler heating - provides heating fluid.
- Circulation pump or booster tank (depending on the type of system) - provides the movement of coolant in the circuit.
- Expansion tank - compensates for thermal expansion of the coolant, as well as water hammer.

- Contour - represents a closed path through which the coolant enters the radiator and then returns to the boiler.
- Heating radiators are appliances that provide room heating.
- Heat carrier is a liquid that takes heat from the boiler and transfers it to radiators. Most often, ordinary water or antifreeze is used for these purposes. The latter has a lower freezing point.
The differences in the schemes are as follows:
- In the method of circulation of the coolant;
- In the method of connecting radiators.
Below we consider the features of each of them.
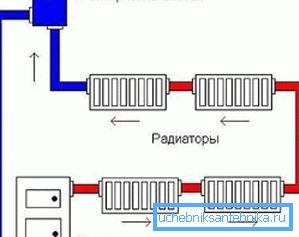
Types of schemes
According to the method of connecting radiators, heating systems are of two types:
| Single pipe | In this case, all batteries are connected to one pipe, which around the perimeter bends around the room and returns to the boiler. |
| Twin tube | The radiator of the hot coolant is supplied to the radiator and cold is discharged through different pipes. |
Each of these can be implemented with both natural circulation and forced. In addition, each option has its own advantages and disadvantages that must be considered.
Single pipe
The main advantage of one-pipe connection is its simplicity and low cost of implementation. However, it can only be used in small rooms. This is due to the fact that the batteries in this case, heat unevenly, and, with a large number, the last in the circuit devices can remain generally cold.
With natural circulation, the design is as follows:
- The contour that comes out of the boiler rises vertically upwards and connects to the booster tank.
- Next, the pipe goes down and, as mentioned above, passes around the perimeter of the room. Moreover, the contour must be mounted with a constant slight slope, which will ensure natural circulation.
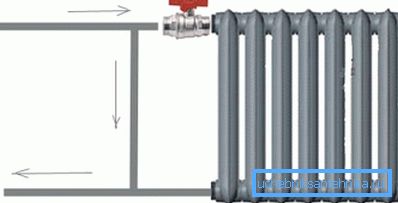
- Radiators are connected to the coolant circuit. Moreover, the binding is necessarily performed with a bypass. This allows you to separately regulate the heating of each battery, and, if necessary, dismantle the batteries without draining the coolant.
This schematic diagram of the heating system is good because the heating is non-volatile. True, this requires the use of non-volatile boiler.

As for the drawbacks, among them it is possible to distinguish a lower efficiency, since the coolant moves with a lower speed, and, accordingly, it has time to cool down. This leads to additional costs and duration of heating radiators. In addition, there are a number of requirements for installation and cross-section of the pipeline.
These deficiencies are deprived of the compulsory system, which is implemented using a circulating pump.
In this case, the connection is as follows:
- From the boiler there is a circuit to which the circulation pump is connected for heating.
- A tee is connected to the pump, which allows wiring to radiators and a surge tank.
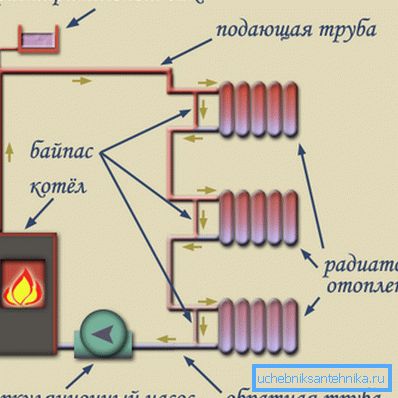
Tip! When installing the pump, you can perform a bypass and connect an expansion tank to it. Accordingly, the bypass must overlap with cranes. This will allow your hands to switch modes of natural and forced circulation.
Twin tube
This option of heating can be used in large houses and apartments. Batteries in this case can be connected both in series and in parallel. Moreover, even with a series connection of batteries, they heat up more evenly than with a single-pipe connection.
The disadvantage of this option is its higher price, since its implementation requires much more pipes. It should be noted that in this case forced circulation is most often used, since it is more difficult to provide natural circulation.
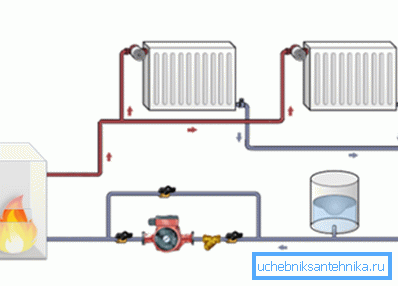
This scheme looks like this:
- From the boiler there is a circuit to which a circulation pump is connected with wiring to the expansion tank and collector (when connected in parallel).
- Further, as a rule, distributing to different rooms of a house or apartment is performed from the collector. When several radiators are connected to one circuit, the pipe is led to the last in the battery circuit.
- A return line is connected to the first outlet of the battery circuit, which is parallel to the hot circuit and is connected to the collector, as a result of which the cooled coolant flows into the boiler and heats up again.
An important advantage of this option is the ability to adjust the heating of the batteries in different rooms. Moreover, when using special electronic equipment, the maintenance of a certain temperature in the premises can be carried out automatically.
Note! We considered the simplest version of the system, since heating can include a "warm floor".
Here, in fact, all the main points of the drafting of the concept. As a rule, based on it perform a more detailed project. Detailed instructions on how to do this are available on our construction portal.
Conclusion
A schematic diagram gives an idea of the operation of the heating system and its implementation. Moreover, its choice depends on a number of conditions in which heating will be operated. From the video in this article, you can get some additional information on this topic.