The calculation of the diameter of the pipe for heating is
When it comes to installing a heating system, quite often the pipe is selected simply on the basis of the advice of friends or the recommendations of the sellers in the store. The calculation of the diameter of the pipe for heating is not always done.
Choosing a size at random, there is a risk that the heating system will work inefficiently.

The effect of diameter on the heating operation
The installation instructions for the heating system are unlikely to affect the calculation of the pipeline (also find out how to calculate the diameter of the pipe for heating).
Meanwhile, when moving through a pipe, the coolant encounters several types of resistance, and this should be taken into account when selecting a standard size:
- wall friction. Due to this, part of the speed is lost;
- loss of speed when cornering. Wiring around the apartment cannot be performed without turns (besides, are there turns at an angle of 90?);
- diameter change. If you try to use different sizes when wiring to the apartment, then resistance to flow will also be observed in the places of conjugation of different sizes.
Note! The narrowing of the diameter of the heating pipe is undesirable. When wiring around the house you need to use the same size. An exception is allowed in the case of a large length of the circulation loop, in which case it is possible to increase the speed of the coolant by decreasing D.
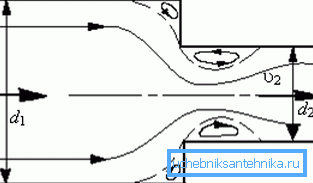
As for the pipeline itself, its main characteristic affecting the movement of the coolant can be called the internal diameter (D). The smaller it is, the greater the pressure, and vice versa — as Dw grows, the pressure in the system drops. This should be taken into account when selecting the diameter of the pipe for heating.
A common mistake of amateur plumbers is associated with this phenomenon. They are sure that if you take a larger size, then more heat carrier will pass through the radiators and the room warms up faster.
In fact, the effect will be the opposite - due to the pressure drop, the batteries will remain cool. In this case, the installation of a more powerful circulating pump can help out, but the price of such a solution is high, it is much easier to choose the right diameter.

An example of the calculation of the heating system
As a rule, a simplified calculation is performed based on such parameters as the volume of the room, the level of its insulation, the flow rate of the coolant and the temperature difference in the inlet and outlet pipelines.
The diameter of the pipe for heating with forced circulation is determined in the following sequence:
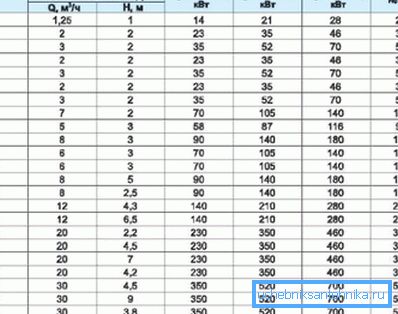
- the total amount of heat that must be supplied to the room is determined (heat output, kW); you can also focus on the table data;
- asking the speed of water movement, determine the optimal D.
Thermal power calculation
As an example, there will be a standard room with dimensions of 4.8 x5.0 x3.0 m. Heating circuit with forced circulation, it is necessary to calculate the diameter of the heating pipes for wiring around the apartment. The basic formula is as follows:
in the formula, the following notation is used:
- V is the volume of the room. In the example, it is equal to 3.8 • 4.0 • 3.0 = 45.6m3;
- ?t is the difference between the temperature in the street and in the room. In the example, taken 53? C;
- K is a special coefficient determining the degree of insulation of a building. In general, its value is in the range of 0.6-0.9 (effective thermal insulation is used, the floor and roof are insulated, at least double-glazed windows are installed) to 3-4 (buildings without thermal insulation, for example, cabins). In the example, an intermediate variant is used - the apartment has standard thermal insulation (K = 1.0 - 1.9), it is accepted K = 1.1.
The total heat output should be 45.6 • 53 • 1.1 / 860 = 3.09 kW.
You can use tabular data.
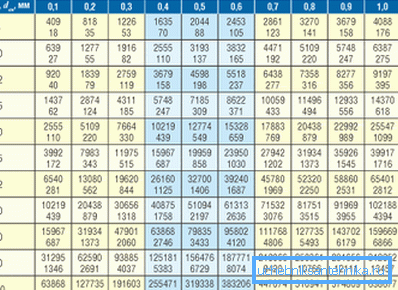
Diameter determination
The diameter of the heating pipes is determined by the formula
Where are used the notation:
- ?t– temperature difference of the coolant in the supply and discharge pipelines. Considering that water is supplied at a temperature of about 90-95? C, and it has time to cool down to 65-70? C, the temperature difference can be taken as equal to 20? C;
- v –speed of water movement. It is undesirable for it to exceed 1.5 m / s, and the minimum permissible threshold is 0.25 m / s. It is recommended to stop at an intermediate speed of 0.8 - 1.3 m / s.
Note! The wrong choice of pipe diameter for heating can lead to a drop in speed below the minimum threshold, which in turn will cause air traffic jams. As a result, the work efficiency will become zero.
The value of Dвн in the example will be v354 • (0.86 • 3.09 / 20) / 1.3 = 36.18 mm. If you pay attention to the sizes, for example, PP pipeline, it is clear that there is simply no such Dвн. In this case, just choose the closest diameter of the propylene pipes for heating.
In this example, you can choose PN25 with Dv 33.2 mm, this will lead to a slight increase in the speed of the coolant, but it will still remain within acceptable limits.
Features of heating systems with natural circulation
Their main difference is that they do not use a circulation pump to create pressure. The liquid moves by gravity, after heating it is pushed upward, then passes through radiators, cools and returns to the boiler.
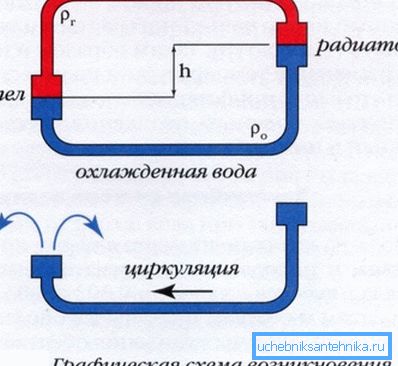
In comparison with systems with forced circulation, the diameter of pipes for heating with natural circulation should be larger. The basis of the calculation in this case is that the circulating pressure exceeds the friction losses and local resistances.
In order not to calculate the value of the circulation pressure each time, there are special tables compiled for different temperature differences. For example, if the length of the pipeline from the boiler to the radiator is 4.0 m, and the temperature difference is 20 ° C (70 ° C in the outlet and 90 ° C in the supply), then the circulation pressure will be 488 Pa. Based on this, the speed of the coolant is selected by changing D.
When performing calculations with their own hands, a verification calculation is also required. That is, the calculations are carried out in the reverse order, the purpose of the test is to establish whether the losses due to friction and local resistance do not exceed the circulating pressure.
Summarizing
The calculation of the heating pipeline is a very important task at the design stage. The information in the article will allow you to independently calculate the heating system, so that a comfortable microclimate in the house is guaranteed (see also the article Which pipes for heating are better: an analysis of the 4 most common options).
On the video in this article, the calculation of the pipeline is carried out at an acceptable speed.