The degree-day of the heating period: calculation, reference
What is this concept - degree day of the heating period? What is it used for and how is it calculated? In the article we have to answer these questions and get acquainted with some statistical data that are directly related to our calculations.

Definitions
First, we will deal with the terminology.
- The heating period is the time of the central heating operation.. It starts when the average temperature of the outdoor air for the last five days is kept at +8 C or lower. When in spring the average temperature for a five-day week exceeds +8 - the season ends.
Useful: when calculating the duration of the heating season, a somewhat simplified scheme is usually used. Take the total number of days with temperatures below +8 C.
- Degree-day is a conventional concept corresponding to the difference between temperatures in a heated room and on the street one degree during the day.. It is used as a measure of heat in public utilities. The cost of heat is not determined by the absolute value of the temperature, but by their delta: to maintain the room at +30 at 0 C outside the window, you need to spend as much heat as at maintaining +15 at -15 outside.
- Finally, the degree of the day of the heating period (GOSP) indicate the temperature delta between the room and the street throughout the season..
Formula
Using your own hands, it is more than easy to calculate the HSTP if you own certain statistical data. The formula for calculating the parameter is of the form HOSP = (T1-T2) * Z.
In it:
- T1 - indoor temperature.
- T2 - the average temperature for the entire heating season (average daily temperature is +8 and below).
- Z is the number of days with an average daily temperature of +8 or less degrees per year.
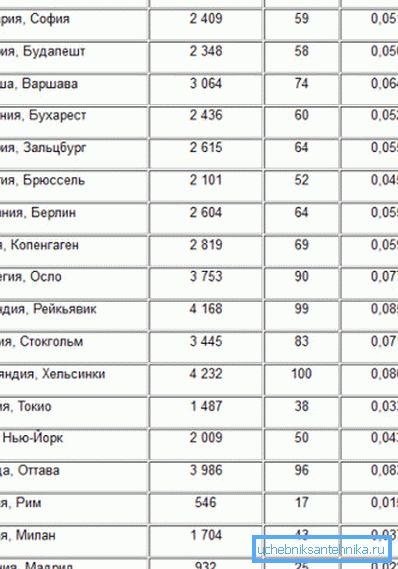
Reference Values
Yes, the calculation instructions are simple; but for its implementation we lack some reference data. Hurry to fill the shortage. (See also the article Calculation of heating: features.)
Room temperature
Its recommended values are easy to find in existing SNiP.
| The room | The temperature norm, С |
| Living room in regions with lower winter temperatures above -31 ° C | +18 |
| Same for corner and end rooms | +20 |
| Living room in regions with lower winter temperatures below -31 | +20 |
| Same for corner and end rooms | +22 |
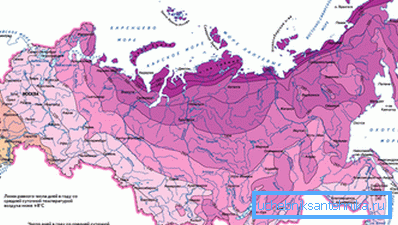
Outdoor temperature and season duration
For the convenience of the reader, we will put at his disposal statistics for the years 1966 - 1980 for some cities of Russia. It is clear that for the nearest settlements to them the values will be close to those given.
| City | Duration of the heating season | The average temperature of the heating season |
| Abakan | 225 | -8.4 |
| Anadyr | 311 | -10.5 |
| Arkhangelsk | 253 | -4.4 |
| Barnaul | 221 | -7.7 |
| Belgorod | 191 | -1.9 |
| Birobidzhan | 219 | -10.4 |
| Bodaybo | 254 | -13.9 |
| Bryansk | 205 | -2.3 |
| Velikiy Novgorod | 221 | -2.3 |
| Verkhoyansk | 279 | -24.1 |
| Vladivostok | 196 | -3.9 |
| Volgograd | 177 | -2.4 |
| Voronezh | 196 | -3.1 |
| Derbent | 138 | +3.7 |
| Yekaterinburg | 230 | -6 |
| Zeya | 238 | -13.8 |
| Izhevsk | 222 | -5.6 |
| Irkutsk | 240 | -8.5 |
| Kaliningrad | 193 | 1.1 |
| Kemerovo | 231 | -8.3 |
| Komsomolsk-on-Amur | 223 | -10.8 |
| Krasnoyarsk | 234 | -7.1 |
| Makhachkala | 148 | +2.7 |
| Moscow | 214 | -3.1 |
| Novosibirsk | 230 | -8.7 |
| Oymyakon | 286 | -24.3 |
| Omsk | 221 | -8.4 |
| Permian | 229 | -5.9 |
| Rostov-on-Don | 171 | -0.6 |
| St. Petersburg | 220 | -1.8 |
| Sovetskaya Gavan | 243 | -6 |
| Taganrog | 167 | -0.4 |
| Tynda | 258 | -14.7 |
| Khabarovsk | 211 | -9.3 |
| Chelyabinsk | 218 | -6.5 |
| Yakutsk | 256 | -20.6 |
Calculation example
As an example, let's calculate the GSOP for a couple of cities.
The average temperature of the heating season in Derbent is +3.7 degrees. In the room of an apartment building, you must maintain +18 C. Heating will be turned on for 138 days. (See also the article Calculation of heating radiators: features.)
The calculation will be in the form of a GOSP = (18-3.7) * 138 = 1973.4
Now let's calculate the same parameter for Verkhoyansk, which, along with Oymyakon, disputes the title of the cold pole of the continent.

An average temperature of -24.1 is combined with a heating operation duration of 279 days. At the same time, according to sanitary standards in apartments located in the center of the house, it is necessary to maintain +20 C: the lower peak of the temperature differs significantly from -31 C, and not in the direction of heat.
GOSP = (20 - -24,1) * 279 = 12303.
Truly, from the southern mountains to the northern seas
Why do you need it
So, we have learned to count a certain parameter. And what to do with the resulting value? The most obvious area of application is the estimated cost of heating. However, the GOPP influences one more thing - the quality of building insulation.
The colder the winter, the higher the requirements of SNiP 23-02-2003 Thermal protection of buildings imposes on this very protection.

In order to make the dependence more visual, it is worth mentioning one adjacent concept - heat transfer resistance, normalized by the above mentioned SNiP. It is measured in m2xC / W: the less watts of thermal energy is transferred through a square meter of the wall when the temperature difference on its sides is 1 degree, the better it resists heat leakage.
Here are some normalized heat transfer resistances for regions with different GPSL.
- For the GSOP 2000 (Stavropol, Astrakhan Region) the minimum thermal resistance of the walls is 2.1 m2 * C / W.
- For GSOP 4000 (Volgograd and Belgorod regions) - 2.8.
- GOSP 6000 (Moscow and Leningrad regions) - 3.5.
- GOSP 8000 (Magadan) - 4.2.
- GOSP 10,000 (Chukotka) - 4.9.
- GOSP 12000 (Some areas of Yakutia, including the Verkhoyansk mentioned by us) - 5.6.
Pay attention: the SNiP is normalized by the thermal resistance of not only walls, but also floors, and even windows. The price of a deviation from the normalized values is a significant excess of heat.

Conclusion
We hope that we were able to answer all the questions that have accumulated in the reader. The video attached to the article, as usual, will offer additional thematic information. Successes in designing!