Thermostat for a radiator: purpose of use, types,
When and what is the thermostat used for radiators? What designs of this device offers the modern market? How to install the thermostat correctly? In our material we will try to find answers to these and some other questions.

What it is
A thermostat is a device for maintaining a constant temperature of any medium.
With regard to heating, there are two classes of devices:
- Intended for adjusting the permeability of liner devices are used in water heating systems;
- Thermostats, intended for switching on and off electrical heating elements depending on the ambient temperature, are predictably used with various types of electric heaters - convectors, oil radiators, cable and film underfloor heating.
Note: the operation of devices of the same class can be based on different physical principles. In more detail we will get acquainted with them in the corresponding section of article.
Why do you need it
The goals of using thermostats in heating systems, in fact, are only two:
- Maintain a comfortable air temperature in a fully automatic mode, without the intervention of the owner.
- Energy savings (electric and thermal).
When weather conditions deteriorate (street temperature decreases, wind increases), heat transfer through the building envelopes increases; as the air cools in the room, the thermostat increases the heat output of the heaters. With excessive heating of the room, there is no need for excessive ventilation: the thermostat itself will reduce heat transfer to the required level.

Classification and device
Now we will start to get acquainted with different types of thermostatic devices.
Thermostatic valve
It is used in conjunction with different types of thermal heads in water heating systems. Valve operation is reduced to limiting the flow of coolant through the heater.
Structurally, it strongly resembles a choke, which, in turn, is a modification of the screw valve:
- The rod actuates the valve - flat or conical;
- The valve is lowered into the saddle and completely or partially blocks the flow of water through the hole in it.
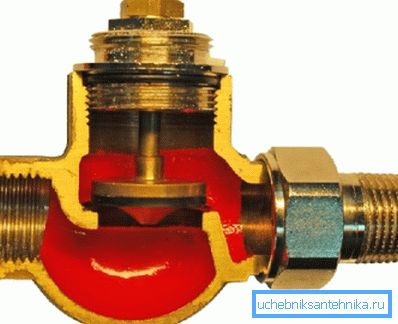
Like a screw valve, a thermostatic valve involves the movement of the medium through its body only in one direction: the coolant must flow to the saddle only and exclusively from below. The direction of movement of the coolant is always indicated by an arrow on the body.
The difference of this element of regulating valves from the throttle is that its rod is driven not by a thumbscrew but by an external regulating device - a thermostatic head.
Bellows Thermal Head
The absolute majority of thermal heads offered by the modern market belong to this type. Their dignity is a fairly affordable price, starting from about 400 rubles. Thermostatic bellows head is non-volatile; its functionality is limited by continuous adjustment of the patency of the valve while maintaining the set temperature of the medium without any cyclic fluctuations.
The principle of operation is based on a significant temperature expansion of some liquid and gaseous media: the contents of the bellows (corrugated tube in the device case) expands when heated and presses on the valve stem.
When cooling and reducing the length of the bellows, the return spring comes into play. The temperature is set by a normal thread, which displaces the stem relative to the bellows.
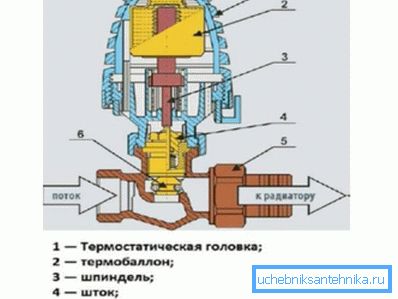
Note: heads of this type can be equipped with an external thermal sensor on a capillary tube, through which the working medium expanding in the thermal sensor enters the bellows cavity.
Electronic thermal head
Electronic radiator thermostats are much more complex:
- The thermocouple is responsible for recording the external temperature - a thermal sensor consisting of two dissimilar conductors connected in series. When the contacts between them are heated to different temperatures, a constant weak current arises in the circuit; the greater the temperature difference, the greater its value.
It is curious: in spite of the fact that electronic thermal heads are positioned as new high-tech solutions, the thermoelectric effect (Seebeck effect) underlying the principle of their operation was discovered almost two centuries ago.

- The thermostatic valve is driven by a low-power servomotor. Thanks to the gearbox, the current consumed by it is limited to 100 mA, which makes it possible to use ordinary compact galvanic cells (flat or penlight batteries) as batteries.
- Thermocouple data processing is carried out by a microcontroller. It allows programming of the daily and (sometimes) weekly cycle of temperatures: for example, at night, when the need for heat is minimal, the temperature in the room can be reduced by 2 to 3 degrees.

How do the prices for bellows and electronic thermal heads compare? Here is an excerpt from the price list for Danfoss products:
| Model | Description | Retail cost, rubles |
| RAW 5010 | Bellows Device with Liquid Filling | 698 |
| RA 2945 | Bellows Apparatus With Gas Filled Sensor | 735 |
| Living eco RA | Electronic programmable device | 2350 |
Electrical equipment thermostats
The heat-insulated floor, the electric convector or an oil radiator with the thermostat mean work at constant power; heat consumption is limited by periodic shutdowns of the device. In the role of the thermostat serves bimetallic plate - a flexible contact of two dissimilar metals with different coefficients of thermal expansion.
When a certain temperature is reached, the bimetallic plate deforms, opening the contact and interrupting the power supply to the heating elements. As it cools, the original contact form is restored, after which the power supply is resumed. By adjusting the distance between the bimetallic plate and the terminal, you can adjust the temperature of the thermostat.

The simplicity of the design provides the utmost cheapness of the device, but it also imposes restrictions on the maximum current through the thermostat: for household appliances, it is 16 amperes, which at a voltage of 220 volts corresponds to an electrical power of about 3.5 KW.
Note: the thermocouple can be either built into the device or remote. Thus, electric underfloor heating is usually used remote sensor, laid in the screed or under the finishing coating.
Installation
What rules should be followed when installing thermostats on heating with your own hands?
Despite the difference in the device devices, the instruction is universal:
- Thermostatic head or temperature sensor must be located outside the upward air flow from the radiator or connections to it. As a rule, this is achieved by horizontal installation of the head; remote sensor can be placed anywhere in the room.

- It is advisable to place the device outside the brightly lit area.. Direct sunlight will heat the case and the temperature sensor itself, affecting the accuracy of the calibration.
- Thermostatic valves, like any throttling devices, assume the presence of a bypass between the connections to the radiator. When the heaters are connected in series, the entire circuit will be throttled.

Conclusion
We hope that our miniature review of modern market offers will seem interesting and useful to the reader. Additional materials, as usual, will offer a video in this article. Successes!