Types of radiators: convection, radiation, water,
To ensure the most comfortable microclimate in our homes and apartments today are used a variety of types of radiators. There are several types of devices on the market, and they all differ not only in appearance, but also in design features as well as in operational parameters.
In our article we will describe what are the heating devices, noting the strengths and weaknesses of the main functional groups.

Work basics
Convection or radiation?
The main difference between devices used for space heating is the principle of their heat transfer.
According to this principle, convectors, radiators themselves, as well as devices of mixed type are distinguished.
- Convection radiator is a system that operates due to air movement.. Cold air enters the lower part of the device, then it passes through a heat-exchanging grid, where it is heated when it comes in contact with heating elements or pipes with hot water, and then goes through holes in the upper part of the structure.
- Sometimes there is not enough natural convection for efficient heat exchange, and a fan is installed at the bottom of the convector., providing forced circulation.

- The radiator principle is implemented differently.. The coolant moves inside the device and transfers heat energy to the walls of the battery. When heated, the walls radiate heat into the surrounding space, due to which the air temperature rises.
- Mixed devices combine the features of convectors and "clean" radiators.. An example of such a system may be a panel steel heater, to the body of which heat exchanger plates are additionally welded, which play the role of convection fins.

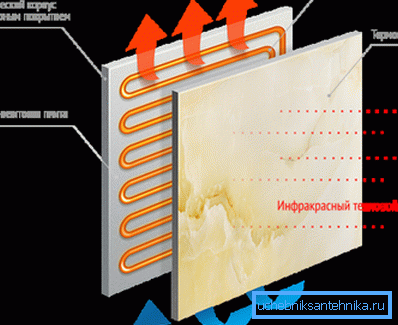
- In a separate group, it is worthwhile to single out the units that function due to infrared radiation.. The infrared radiator, powered by electricity, heats not the air, but the surrounding objects; therefore, experts consider these products to be more economical.
Note! When installing infrared heaters, it is very important to arrange them correctly, since in the dead zone it will almost always be pretty cool, because the air is heated there only by secondary radiation and residual heat.
Water or electricity
Next you need to deal with the type of coolant.
There are two options - water or electricity.
- Water batteries are known to all of us. They are devices of several pipes or tanks, through which the medium heated to a certain temperature circulates (not necessarily water - it can be steam, antifreeze, and a water-alcohol mixture). The coolant gives energy to the walls of the pipes and heat transfer plates, and they, in turn, heat the room.

- The principles of operation of electric radiators are more diverse. They can use either a liquid coolant based on mineral oil, or direct heating of air as it passes through red-hot spirals or plates (like most electric convectors). In any case, the system consumes a lot of electricity, but at the same time provides a quick warm-up of air.
- Special mention deserve inverter radiators. They allow you to control the heating process in automatic mode: when the temperature set by the user is reached, the heating element is not turned off, but goes into reduced power mode, saving resources. This becomes possible due to the presence in the design of an AC-DC converter (inverter).
Note! Very often, inverter systems are used for integrated climate control, i.e. not only for heating, but also for air conditioning.
Body material
The efficiency of its work depends on the material from which the structure is made. For water batteries, this is primarily due to the difference in thermal conductivity of metals, as well as other performance characteristics.

Today on the market are such options:
- Products made of cast iron - the traditional version, which is gradually obsolete. They are distinguished by low heat emission, high inertia (they heat up slowly, cool slowly), and a considerable margin of safety.
- Steel structures - panel and plate radiators. The thermal conductivity of steel products is higher than that of cast iron, but they are more susceptible to corrosion.
- Aluminum - the most profitable in terms of heat transfer. At the same time, aluminum does not differ in hydraulic stability; in addition, it does not tolerate prolonged contact with alkaline water.

- Bimetallic devices (sometimes the erroneous name "biometric radiator" is found) is a complex of steel or copper pipes with aluminum heat exchangers. Combine the advantages of steel and aluminum models, with virtually no functional drawbacks. The main disadvantage was the high price, but good heat dissipation and significant service life allow to put up with the high cost of products of this type.
If we talk about electric heaters, they are most often made of steel, and for the production of protective shells silumin and heat-resistant polymers can be used.
A separate group consists of products with ceramic elements. The ceramic radiator provides uniform distribution of heat, since the front plate made of baked clay with stabilizing and reinforcing additives plays the role of a kind of filter that equalizes and directs the flow of infrared waves.
Design features
Sectional and panel products
The form and features of the device can also be distinguished by different types of heating radiators.
Here comes to the fore the type of design:
- If the body of the product is assembled from the same type of elements within which the coolant circulates, then this battery is called sectional. Cast-iron, aluminum and bimetallic models have a sectional design. It allows you to select the desired number of heating fins, adjusting the power of the device in a greater or lesser direction.

- Steel heaters are most often produced by stamping a single steel sheet. Since they have a monolithic structure, they are called panel. To change the size of such a battery does not work, so you need to initially select a product with a suitable performance and dimensions.
Note! If you need a hygienic radiator, i.e. model that is resistant to regular processing in the process of wet cleaning, then you just need a steel panel device with the smoothest front surface.
- Tubular structures (copper and steel) stand apart. They are contours of thin tubes, which are interconnected by a welded method. Externally, these tubes look like separate sections, but the design is received non-separable.

Installation method
If you plan to install the heaters yourself, then one of the most important classification points for you will be the type of installation. According to this parameter, these types of structures are distinguished:

| Variety | Key features |
| Wall mounted |
|
| Outdoor | This includes two groups of devices:
|
| Embedded | Built-in heating radiators are usually installed in floor niches along windows or thresholds:
|
| Portable |
|

Conclusion
As can be seen from the above description, all types of radiators have their own characteristics. The choice of available models is very wide, because, in order not to get confused, you should carefully study the above information, as well as watch the video in this article, which contains a large amount of additional information on this issue.