Types of radiators. steel, aluminum, cast iron, bimetallic
At the moment, manufacturers offer a lot of types of heaters. Before purchasing, you need to decide which model is suitable for your home. In this article we will analyze what types of radiators exist for heating systems.

Steel batteries
These products are presented in two varieties.
Panel radiators

These converter radiators have high efficiency - about 75%. Inside the device there is one or several heating panels with convective fins.
Such devices are the most budgetary choice for a private house.
Based on the number of panels and fins, such models of radiators are produced:
- ten;
- eleven;
- 20;
- 21;
- 22;
- 33.
Advantages:
- high heat emission;
- low inertia;
- small volume of the heat carrier;
- harmlessness and environmental friendliness;
- low price
Disadvantages:
- when water is drained from the system with its own hands, oxygen begins to interact with the steel walls, which makes them rust;
- devices do not withstand strong pressure and water hammer, on the basis of this, in high-rise buildings to use them is extremely undesirable.
Tubular fixtures

Such devices are a tubular structure inside which coolant circulates. Their production is more difficult, therefore the cost is higher than panel counterparts. Batteries can be painted in a variety of colors.
Note! Stainless steel tubular radiators have the same pros and cons as panel models. The only thing - they hold more pressure.
Analogues of aluminum
Extrusion and cast radiators are made of this metal. Both types of devices are recommended for autonomous heating systems.
For utility networks, they are of little use, because do not withstand high working pressure and are subject to several types of corrosion due to poor quality of the coolant.

- Injection moldings are produced by high pressure casting. They have wide channels for coolant and thick durable walls. The device is assembled from separate sections. They can be removed as needed or added.
- Extrusion models are cheaper. Their vertical elements are extruded from aluminum on the extruder, and the collectors are cast from silumin.
Note! Such monolithic radiators are not amenable to change, because sections can not be removed and added. This is a significant disadvantage of a variety of heaters.
Instrument Features
Advantages:
- low weight due to which the batteries are easy to install, without the use of especially strong holders;
- one of the highest heat transfers among all types of radiators;
- the ability to quickly heat the room;
- efficiency, devices are often equipped with a thermostat;
- modern attractive design.
Disadvantages:
- short service life - 10-15 years.
- aluminum is chemically active, because of this, it is not resistant to corrosion and needs a high-quality heat carrier, with the exception of anodized radiators;
- if air is displaced from the coolant, hydrogen, deadly to aluminum, is generated inside the batteries;
- devices have a weak convection;
- similar radiators cannot withstand hydraulic shocks.
Pig iron appliances

Such metal radiators are divided conditionally into outdated morally Soviet-style models, modern counterparts and retro-style instruments.
We will not talk about Soviet analogs.
- Modern cast iron batteries are simple and strict in form, have a flat front surface and a neat appearance.
- Analogues in the style of "retro", including steam radiators, are produced by the method of iron casting. They have a high level of aesthetics and are able to decorate any room with them.
Advantages and disadvantages
The advantages of cast iron:
- service life of about 50 years;
- the material is passive chemically, due to which it is not susceptible to corrosion;
- heats the room with radiation (radiation), which is optimal for rooms with high ceilings;
- high level of heat capacity - the device will remain hot for a long time after the heating is turned off.
Disadvantages:
- high inertia;
- the massiveness of the products creates difficulties during their transportation and installation;
- the heavy weight of the batteries implies their durable and expensive fasteners;
- the volume of coolant is relatively large;
- The instruction warns that cast iron is fragile and not able to withstand strong water hammering.
Bimetal products
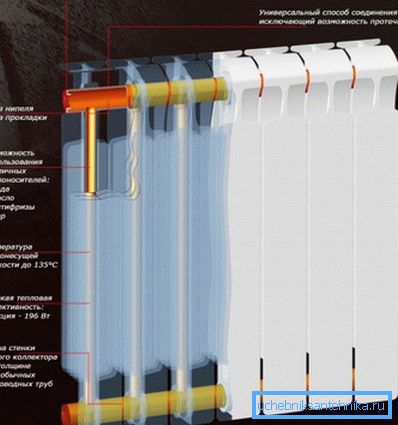
The instruments have a tubular core of copper, steel and an aluminum body. Batteries usually consist of an even number of sections.
The sizes of the units are different, there is even a low bench radiator.
- Real bimetallic devices have a tubular core of steel both horizontally and vertically. They are extremely durable and reliable. However, quite expensive.
- Analogs of pseudo-bimetallic ones are equipped only with vertical parts of channels reinforced with steel. They are cheaper, have better heat transfer, but are less resistant to corrosion, because coolant in contact with aluminum.
Product quality
Of the advantages can be identified:
- almost zero inertia;
- high heat transfer;
- bimetallic products are capable of holding the highest working pressure and very strong hydraulic shocks;
- the volume of coolant is small;
- installation of products is simple;
- their design is aesthetic;
- corrosion resistance.
Product minus: high cost.
Unusual radiators

In addition to the products described above, manufacturers also produce not quite ordinary analogues.
Plastic batteries
These are, for example, plastic heating radiators. If you face the challenge of austerity, this option is optimal. The only condition - the temperature of the coolant in the system should not exceed +80 ?.
Such low-temperature batteries are easy to install and use, resistant to wear, weigh little and stand.
Floor-mounted convectors
Such convection heaters hide in the floor. They consist of a box, a heat exchanger and a decorating grid. The tubular core for the coolant is steel or copper, aluminum convective fins. A similar structure has a three-row radiator, which is the basis of an automobile stove.
Advantages:
- the device is optimal for panoramic glazing;
- it is durable with a simple design and low weight;
- not afraid of corrosion;
- does not take place;
- heats the room evenly.
Minuses:
- considerable length of the device;
- when using it can not use forced ventilation;
- small heat transfer;
- inefficiency
Plinth convectors

The plinth radiator (warm plinth) is a low convector (height 20-25 cm, depth 10 cm) mounted along the lower perimeter of the walls.
Advantages:
- saving space and fuel (up to 40%);
- the ability to control the temperature using thermostats;
- automatic overheating protection;
- heats the room evenly.
Disadvantages:
- the device is adjacent to the walls, as a result, their lining can be deformed;
- high price.
Product Specifications
The bottom table shows the main technical parameters of the described types of radiators.
| Type of radiator | Thermal power, watt | Working pressure bar | Maximum coolant temperature, degrees | Acidity of the coolant (pH), units |
| Steel panel | 1200-1600 (total) | 6-10 | 110-120 | 8.3-9.5 |
| Steel tubular | 1200-1600 (total) | 8-15 | 110-120 | 8.3-9.5 |
| Aluminum | 82-212 (section) | 6-16 | 110 | 7-8 |
| Cast iron | 100-160 (section) | 9-16 | 110 | Irrelevant |
| Bimetallic | 150-200 | 20-65 | 130 | Irrelevant |
| Sexual convector | 130-10000 (total) | 10-16 | 110-130 | Irrelevant |
| Plinth convector | 500-1500 (total) | sixteen | 130 | Irrelevant |
Stand alone portable models

The portable types of radiators described below are powered by the electrical grid.
They can serve as a supplement to the main heating system or be a heater in a small room, shop, office, etc.
- Oil radiator, as the name suggests, uses technical oil as heat carrier. This is an excellent choice for space heating up to 30 m ?. It has a small weight. It can be moved from place to place, as needed.
- Quartz heater - This is a monolithic slab made of a special solution on a filler of quartz sand. Its heating element is an alloy of nickel and chromium. It is completely poured into the stove.

- Mikatermichesky The radiator is made using a unique technology. It consists of non-metallic heating plates, covered with a thin layer of mica.
Note! The heater transmits most of the thermal energy (80%) in the form of infrared radiation, beneficial to our health. The remaining 20% comes from normal thermal radiation.
Conclusion
At the moment, there are many types of heating radiators. They are made from different materials, have different designs and specifications.
They should be chosen on the basis of the conditions in the dwelling and features of the heating system. The video in this article will complement our review with visual information.