Types of radiators: what is the functional difference?
For arrangement of the system of centralized heating of the room today are used a variety of types of heating batteries. They are distinguished not only by the material of manufacture, but also by the configuration, dimensions, and the principle of operation.
In our article we will look at the main types of heaters, focusing on their pros and cons.

Convector or radiator?
One of the most important parameters by which the classification of heating products is carried out is the principle of air heating.
Convectors and radiators are distinguished by this parameter:
- When using any of these structures, the principle of air heating remains the same: the heat carrier (most often water) is heated in a boiler room or an autonomous device, through pipes it enters the room and enters the heating battery. Passing through the pipes of the battery, the water gives a part of the temperature to the surrounding air, heating it.

- In the convective principle of heating, heat transfer occurs when air passes through heated surfaces, taking away some of their thermal energy.. It is for this reason that the convectors have a rather complicated construction, which significantly increases the area for heat exchange.
Note! Convective heating is more efficient as the room temperature rises faster. At the same time, energy costs will also be higher.
- The radiator works according to a different principle: the coolant from the inside heats the surface of the battery, which radiates heat into the surrounding space. The process is rather slow, but at the same time radiator type batteries (especially cast iron, made of metal with high heat capacity) do not cool for a long time, maintaining an optimal microclimate.

Most often, radiators are used in our apartments. At the same time, where fast heating is critical, the instruction recommends installing convectors as more efficient devices.
Note! Convective-type batteries can be electric, which makes them easier to move and install in a new place: it is much easier to stretch the wire to the outlet than to supply a pipe with hot water.
Design features
Prefabricated and panel products
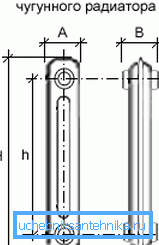
All types of radiators used today are not able to boast of a special variety of designs:
- Cast iron, aluminum and bimetallic products often have a sectional structure.. This means that each battery consists of individual elements, the number of which can be changed depending on the performance needs of the entire system. In this case, the design provides for the possibility of installing additional sections without the use of special devices, i.e. installation is carried out on regular fastenings.
- Steel radiators and convectors are often produced as monoblock panels.. Inside they are also divided into sections, but the connection of parts is carried out in the factory. On the one hand, this provides an increase in the tightness of all joints, and on the other hand, it somewhat reduces the possibilities for selecting equipment for specific performance parameters.

However, in practice (especially - if the installation of the system is done by hand), they usually use radiators of the configuration that suits the price and parameters of heat transfer. Just when buying panel models, their power is rounded up, providing the system with the necessary reserve.
Advantages and disadvantages of different materials

However, the most important parameter is the material from which the radiator is made. You can compare the pros and cons of various devices by analyzing the table below:
| Variety | Merits | disadvantages |
| Cast iron |
|
|
| Steel |
|
|
| Aluminum |
|
|
| Bimetallic |
|
|
| Copper |
|
|
As you can see, any kind of battery has advantages and disadvantages. That is why the material should be chosen, based on your requirements and financial possibilities: of course, bimetallic or aluminum radiators are more modern, but in some cases such expenses will be simply unnecessary.
Conclusion
To maintain an optimal microclimate, a variety of heating structures and their types can be used - radiator and convector type radiators, products made of various materials, etc. The range of such details is very extensive, and the above tips, as well as video material in our article, will help you to understand it.