Vacuum heating radiators - a fair assessment of high
Relatively recently, an alternative to the usual radiators appeared on the market - vacuum radiators. Marketers in the estimates of these devices are not shy and in unison declare that this is almost a revolution in the field of home heating.
The novelty looks very interesting, so you should pay more attention to it.

Device and principle of operation
The design and principle of operation of a classic heating battery is familiar to everyone - water passes through separate sections and heats the metal. The vacuum heating radiator looks, and works, a little differently.
The vacuum battery looks like a normal register - that is, two tubes in the upper and lower parts are connected by hollow ribs. The upper tube is tightly sealed, and through the lower the pipeline passes through which the heat carrier will flow (the pipe in the pipe). To ensure uniform heating, a low-boiling lithium-bromide liquid is poured inside the heater.
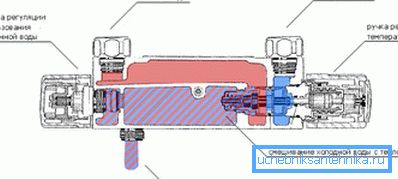
Note! Air is pumped out of the internal space for greater efficiency of the device. So any violation of the integrity of the battery will reduce the efficiency of work at times.
The novelty works according to the following scheme:
- after the start of operation of the heating system, water flows into the lower pipe;
- the lithium-bromide mixture boils already at a temperature of about 30-35? C (this contributes to reduced pressure);
- after the transition to the gaseous state, the entire section is evenly warmed up, in the upper part the gases cool down, turn into liquid and descend to the lower part of the section, the cycle repeats.
Note! If a conventional radiator can operate in a wide range of temperatures, then the vacuum in this matter is more capricious. So, if the coolant is heated up too much, and all the liquid in the battery evaporates, then the efficiency of the radiator will decrease by an order of magnitude. At the same time, at a very low temperature, the liquid will evaporate very badly.
Truth and fiction about vacuum radiators
In the case of devices of this type, quite often the actual heating efficiency turns out to be much worse than the advertising promises. For many, the question arises as to whether this is the cause - improper installation, a violation of the process technology, or perhaps vacuum heating radiators do not have any serious advantages over conventional batteries.
What manufacturers promise
According to marketers, such devices have the following advantages:
- heating the room already at a temperature of about +35? С. For comparison - with ordinary heating water should be heated to a temperature of about + 85-90? С;
- a much smaller volume of coolant, which is located in the radiator, is entered into the asset. In vacuum devices, the volume of coolant does not exceed 500 ml, while in a conventional steel or cast iron radiator in only one section there is 350 ml of water;
- due to the fact that the coolant does not pass during operation through the entire radiator, the battery does not become dirty with time, which means that the heat transfer does not deteriorate;
- hydraulic resistance is less;
- heating uniformity at height;
- The main advantage is usually called saving heating costs.. In the descriptions for different models, they usually call a number close to 30%, that is, in theory, costs are reduced by 1/3.
As for the shortcomings, it is usually noted:
- high cost - somewhat higher compared to conventional batteries; the price is explained by the complicated design;
- quiet crackling when boiling liquid evaporates;
- the fact that effective work is possible only in a relatively narrow range of coolant temperatures.
What is silent advertising
If in reality the situation looked the same as marketers draw it, then vacuum batteries would already occupy a fair share of the market. However, so far this is not happening, and sales growth leaves much to be desired.
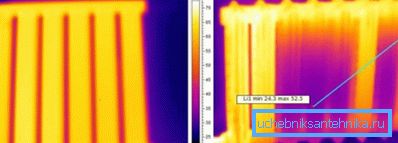
The efficiency of home heating depends mainly on the quality of insulation (affects heat loss), the working temperature of the heat carrier and the surface area of the radiator (finning area). A battery is only an “intermediary”, which is necessary in order to transfer the thermal energy received from the coolant into the air.

Vacuum radiators heat up almost instantly, but you need to understand that the heating rate does not play a special role in heating. The cast-iron “heavyweight” will heat up in a few minutes, but when comparing a particular difference, it will not be noticeable.
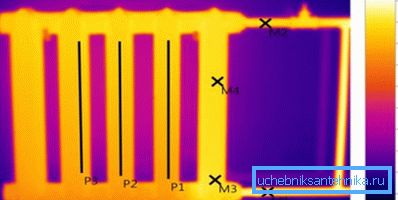
In terms of such a parameter as the surface area, they sometimes lose to traditional heating radiators altogether. And this directly affects the efficiency of heating, because the balance between heat loss and the flow of heat into the room must be maintained.
As for the advantage in the form of a smaller amount of coolant, this makes the heating system simply less inertial, that is, the water cools faster. This means that the boiler will have to be turned on more times.
Installation and operation practices
As for the installation by hand, it is practically no different from the installation of conventional radiators.
It is only necessary to take into account a couple of features:
- Before installing it, you need to shake it left and right so that the liquid in it does not accumulate in the upper tube;
- It is forbidden to install vacuum devices with conventional radiators.
The installation instructions in this case consist of the usual operations:
- installation of fixtures on the wall;
- hanging radiator;
- pipe connection to the bottom;
- leak test
An interesting result of operation is shown in the table:
| Type of | Aluminum | Vacuum |
| Electricity consumption, kW | 0.782 | 0.356 |
| Starting temperature,? С | 24 | 25 |
| The final temperature,? С | 40 | 32 |
A small cabin was heated, the thermo-relay was set at 80? С.
It can be seen that for an hour of work, the aluminum battery heated the room by 16? C, and the vacuum one - by 7? C, while at the same time spending half the electricity. An interesting relationship is half the efficiency and half the power consumption. If we add the fins to the vacuum battery, then the results would most likely be equal.
Summarizing
New products should be treated with caution and vacuum batteries are no exception to this rule. Despite the loud advertising, the effectiveness of the use of such devices raises serious doubts. Quite often, traditional radiators are at least as good as vacuum counterparts (see also the article Geothermal Heating at Home — Features and Device).
The video shows an example of a heating system using a vacuum radiator.