Water heating systems: how to design a quality climate
Modern heating engineers know many ways to heat homes. Comfortable temperature in the house can be created by heat fans, electric convectors, traditional wood-burning stoves, and so on. But the most economical and efficient are water heating systems with a boiler and radiators.
Continuing reading, you will learn a lot of useful information about the varieties of these engineering networks and the peculiarities of their installation by hand.
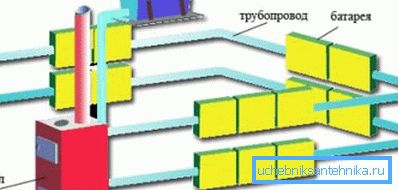
Varieties of water heating networks
The efficiency of the climate engineering system of an apartment or house depends not only on the power of the heating unit or the heat transfer coefficient of the radiator. It is equally important what type of piping is chosen for delivery of the coolant, how fluid flow and many other parameters are organized.

A more complete and detailed classification of water heating systems depending on various criteria is given in the table.
| View | Description |
| By autonomy | |
| Dependent | The coolant is heated in a centralized boiler room and is fed into the heating radiators with the help of main pipelines. This type of heating is installed in all city apartments of old buildings. |
| Independent | The heating unit is installed in the dwelling itself. It heats the water, which flows through the pipes to the radiators, where heat is exchanged with air. Then the cooled liquid flows back to the heater through the return pipe and the next cycle begins. Similar heating systems equipped the vast majority of private homes. |
| By contact with the environment | |
| Open | Such a water heating system was installed in private houses equipped with solid fuel boilers of the old design. However, there is now. The peculiarity of the considered engineering network is that the coolant circulates through pipes without excessive pressure. Part of the heating system is an open-type expansion tank, which is fixed at the highest point. |
| Closed | A sealed expansion tank of a closed type, installed in the boiler room on the return pipe, is used. The heating system is pumped with fluid under pressure. For private houses, this indicator is equal to 1 atmosphere; in dependent heating networks with centralized supply of coolant, the pressure can reach up to 6 atmospheres. |
| According to the method of organization of the coolant current | |
| Gravitational | Water heating systems, where the circulation of water occurs naturally due to the difference in pressure and density. The mass of heated water is less, so it is forced out to the upper point of the system. Then, cooling down, flows through the radiators, giving thermal energy to them. After that, the return pipe, located on a slope, returns to the boiler. |
| Forced | In this case, one of the elements of the climate network is a circulation pump. Such systems are more efficient and cost-effective. At installation it is not necessary to observe an obligatory bias of pipes. The only minus is the dependence of heating on the availability of electricity. Without it, the pump will not function (as, indeed, any of the modern boilers). |
| By the number of pipes that feed and discharge the coolant | |
| Single pipe | In all rooms, a ring is laid out of a pipe into which heating radiators run into a parallel or sequential method. The advantages include cheapness, the disadvantages - the complexity of the repair and the inability to accurately regulate the temperature in different rooms of the house. |
| Twin tube | Such a heating system, as the name implies, has two pipes: one is supplied, one is removed, the other is removed. The advantage is the ability to regulate the temperature in radiators with the help of thermostats and ease of repair (by blocking the access of water to one battery, you will not disrupt its current in other radiators). However, the price of its manufacture will be higher - for the installation will need twice as many pipes. |
| By way of laying pipes | |
| Vertical | In such a heating scheme, the coolant is fed to the upper floor, after which it flows down, passing through one heating radiator on each floor. |
| Horizontal | Here, water also flows upward through a vertical pipe, then a horizontal outlet is made from it, through which the liquid reaches all the batteries located on the same floor. |
| Combined | Such a water heating system has elements of both the first and second types. |
| By the presence of a dead end | |
| Deadlock | With this scheme, laying the supply pipe reaches the farthest radiator, there is closed with a jumper with the return line, through which water is returned back. |
| Ring | In this case, two pipes for the coolant form a sort of ring, gradually passing through all the rooms and batteries. Such a scheme is considered more effective. |
| Ray | The coolant flows from the boiler to the collector cabinet, which is connected by a pair of pipes (supply and discharge) with each radiator in the house. So you can very accurately control the microclimate in the whole building from one point. |

Note! Choosing the right heating system depends on a large number of different factors. These include the area of the house, the number of floors, the diameter of the pipes used, and so on.
Calculations and selection of a suitable scheme for water heating systems are best left to a professional engineer. He will perform a hydraulic calculation, without which the normal operation of the climate network can be forgotten.
Let us dwell in more detail on the description of heating systems with natural and forced circulation.
Types of heating by the method of circulation of water
Gravity system
Special features
The system of natural circulation of fluid in the climate network operates solely due to natural laws.
The scheme is as follows:
- when heated, water becomes lighter and rises to the top of the heating system;
- cooling down, the liquid becomes more dense and heavy, as a result of which it descends, simultaneously heating the rooms.
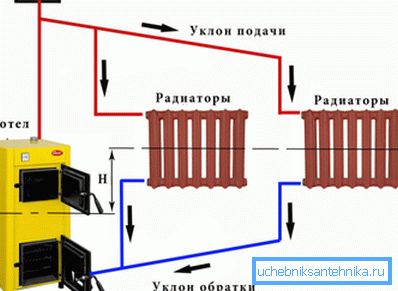
The described heating was effective only if the engineering network was mounted in such a way as to ensure the intensive circulation of fluid in it. Otherwise, the coolant will not perform the transport function entrusted to it and the heat energy generated by the installed boiler will be wasted.
When building and operating a gravity heating system, it is necessary to comply with the following requirements:
- Correctly select the diameter of the pipes connecting the boiler with the batteries, calculate their hydraulic resistance, set the total length in the vertical and horizontal plane. The necessary initial data can be obtained from the accompanying documentation for climate equipment.
- Do not allow overheating of the coolant. Water can boil, which is why pressure in pipes and radiators will increase significantly, and this will lead to breakage. To prevent this, the expansion tank, which is installed at the top of the system, helps.

Note! No matter how right you think, to heat a house of more than 200 square meters. meters or mount pipelines longer than 30 meters and ensure the natural circulation of the coolant will not work. It will be necessary to install electric pumps, and this is already a heating system with forced water flow.
Installation procedure
Instructions for designing a gravity heating system is simple and consists of the following points:
- First you need to install the boiler. For obvious reasons, it must be installed at the lowest point of the pipelines, where all the cooled liquid from the radiators flows.

- A vertical riser is laid upwards from the boiler. The higher this pipe is, the more efficient the heating system will work. Most often, its end leads up to the attic of the house.
- An open expansion tank is placed on top.. If it is installed in the attic, do not forget to carefully insulate the container in order to avoid significant heat loss and freezing of the liquid. The membrane tank can be mounted in the boiler room, on the return pipe.
- Then the pipe layout is done.. Here it must be ensured that no heating radiator is located at the point below the boiler. The greater the height difference, the more efficient the work of the installed engineering network.
- Pipe material can be freely selected.. Remember that if a solid fuel boiler is installed in the system, the coolant can be heated to very high temperatures at which polymer pipes cannot be used. In this case, it is recommended to stay on steel.

- In other cases, plastic is more suitable, since they are not susceptible to corrosion and have a lower coefficient of hydraulic resistance.. Make sure that the internal section of the pipelines and boiler pipes used are the same. The use of pipes of smaller diameter is prohibited.
Tip! Nobody forbids to mount the inlet and outlet pipes of a larger diameter than the nozzle. For a gravitational heating system, it is even useful.
Forced circulation system
Special features
You probably already understood that the efficiency of heating depends largely on the flow rate of the coolant through all elements of the system. Therefore, climate networks with pumps pumping water are now more popular.
These are small devices that consume a minimum of electricity and work almost silently. Modern circulating pumps can change the speed of rotation of the electric motor, thanks to which it is possible to precisely control the volume of flowing hot water and, accordingly, the temperature in the rooms.
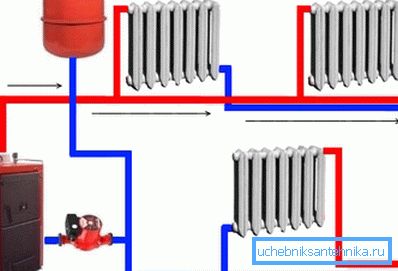
The pump increases the efficiency of the described climate system, so the fuel to maintain a normal temperature in the rooms will be spent less.
In addition, the coolant pumped by the pump, it is easier to overcome the hydraulic resistance. Consequently, for the installation of the heating system, you can use pipes of smaller diameter (but not less than the boiler nozzle).
Installation procedure
The arrangement of a heating system with forced circulation is different from the installation of a gravity network in the direction of simplification.
In particular:
- The pump is installed on the return pipe so that the liquid entering it has the lowest possible temperature.
- The heating boiler can be placed on the same level as the radiators.
- Only a membrane expansion tank can be part of the system (often it is already built into the boiler). So the fluid in the pipes will circulate under a pressure of 1-1.5 atmospheres.
- Observe the prescribed SNiP pipe slope in the case is not necessary.
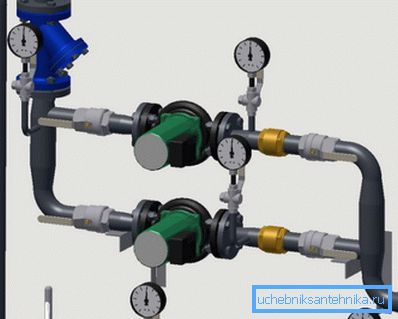
Combined heating system
In the construction of private houses often use the so-called combined heating scheme. In this case, the pipelines, radiators and the boiler are mounted according to the rules of the gravity network, but a circulating pump with a bypass (bypass) is placed on the return pipe.
This ensures the operability of the heating even in the event of a temporary power outage or breakdown of the circulation pump.
Tip! Any equipment must be connected to pipes through valves. Also a valve or bypass valve should be equipped with a bypass. In this case, you can dismantle the equipment for repair or replacement without removing the coolant from the pipes.

In the same way, outdated heating systems are modernized. You just need to make a sidebar with a pump and the efficiency of the climate network will increase significantly.
Types of heating by the method of distributing pipes
Single pipe
Such a heating system provides for the installation of a single pipe through which the coolant is supplied to the radiators, and returns back to the boiler. In this trunk line, heating radiators are connected in series or in parallel, where heat exchange takes place.
The advantage of such a scheme is cheapness. You will need a minimum number of pipes and various fittings.
But you can’t call an effective and convenient system, as it has several significant drawbacks:
- it is impossible to manually or with the help of thermal valves to adjust the volume of coolant falling into each battery, therefore, to set the desired temperature in each individual room will not work;
- the amount of heat energy transferred to radiators will decrease as the batteries move away from the boiler, therefore, the farthest (lower) rooms will be heated worse.
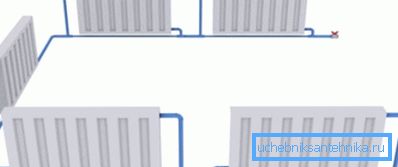
To circumvent some of the limitations of the described system by installing a bypass - a bypass pipe - connecting the inlet and outlet nozzles of the radiator directly. In this case, opening and closing the shut-off and regulating valves, you can not only set a comfortable temperature of the battery, but also make (if necessary) dismantle and repair it without stopping the operation of the entire heating network.
Double-tube vertical with lower wiring
The main difference between a single-pipe layout and a two-pipe layout is the presence of two pipelines: the first is supplied with hot heat transfer fluid to the radiators, the second water is drained off and delivered back to the boiler.
Thanks to this scheme, it is possible to regulate the volume of liquid entering each battery and to achieve the most comfortable temperature in the rooms.
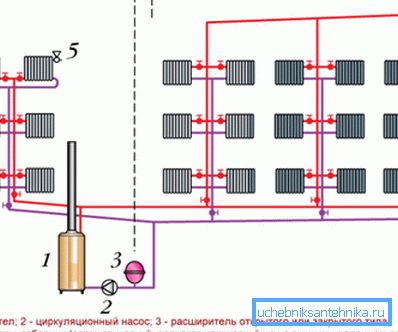
One of the options is a two-pipe system with vertical risers and a lower arrangement of feed pipes.
Its features are as follows:
- At the lowest level of the system from the heating boiler lay pipelines connected to the heating device.
- From these highways, they let up risers that raise the coolant to the highest point of the system and deliver it to the heating radiators on each floor.
- Then, through the other pipe, the cooled liquid is returned for repeated heating cycle.
The disadvantage of this solution is the danger of airing the system.
It is necessary to provide devices to remove air from the pipes and radiator:
- air tube rising to the top of the system;
- open-type expansion tank or diaphragm device with special air valve;
- Mayevsky's cranes mounted at the top of each battery.

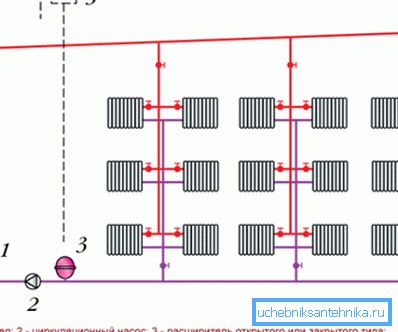
Double-tube vertical with top wiring
In this case, the distribution of fluid occurs at the highest point of the system - in the attic or under the ceiling of the upper floor. The coolant is delivered there by a vertical pipe, then flows through the horizontal pipelines into the batteries.
An expansion tank is also needed here, but it is better to use an airtight one so that the water pressure can be increased than to increase the heating efficiency.
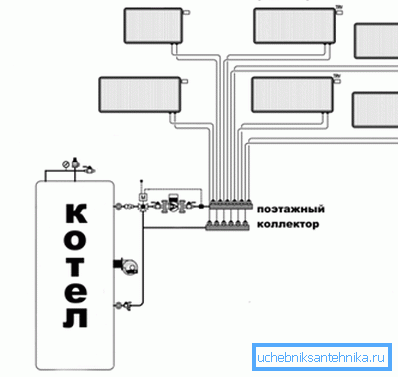
Twin tube horizontal
This type of liquid distribution through pipes is most common in the construction of private houses and cottages. The peculiarity here is that in order to ensure the flow of water, it is imperative to install a circulating pump, since it will not be possible to achieve the desired speed of water movement in a natural way.
Pipes are laid according to one of several schemes:
- Deadlock. The advantage of this method is quite economical use of pipes. Minus - a significant length of the system, which complicates its precise adjustment.
- Passing. In such a system, the length of the heating circuits is shorter, making them easier to adjust. However, the cost of buying pipes and installation work increases significantly.
- Collector. In this case, each radiator is connected via pipes to two dies - supply and discharge. The most effective network, but the cost of its installation is higher than all the others. In addition, you need to provide a hidden pipe laying, as it is not aesthetic to build such a number along the walls.
Conclusion
As you can see, there is a huge selection of different options for arranging the climate system. The choice of the desired scheme depends not only on your desire and the amount of money, but also on the engineering capabilities. Therefore, technical calculation of climate networks is so important.
This issue is dedicated to the video in this material.