What are the heating systems: water, air, warm floor and
What are the heating systems and on what grounds are they classified? We have to get acquainted with both proven long-term operation schemes used in private and apartment buildings, and with relatively new solutions that are just beginning to gain popularity. So let's get started.
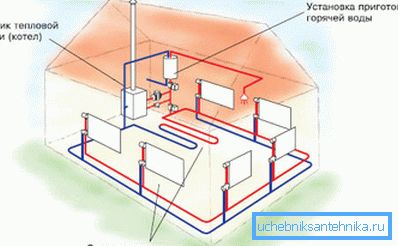
Water heating
These types of heating systems have a common feature: the heat-transfer fluid is used to transport heat from the heat source to the heaters.
Note: contrary to the name, water does not always play this role. Salt solutions, ethylene and propylene glycol, used engine oil are also used. They compare favorably with water at a much lower freezing point, which makes it possible not to be afraid of defrosting pipes and batteries.
Water type heating, in turn, can be classified according to a long series of signs.
Heat source
In this role can be:
- Boiler room or CHP. The coolant is transported to the house along two lines of the thermally insulated route (supply and return); At the entrance to the house, an elevator assembly is mounted, stabilizing the temperature parameters of the heating due to the involvement of part of the coolant in the re-circulation. The main drawback of the scheme is large heat losses during transportation.
Note! These losses are paid by the end user. Hence, there are many who want to switch from central heating to autonomous types of heating.
- Main gas. Gas boiler provides minimal heating costs (about 70 kopecks per kilowatt-hour of heat). Currently and in the near future, this is the most profitable solution. Gas in gas cylinders and gas tanks is much more expensive - from 1.8 to 2.8 rubles / KW * h.

- Firewood, coal. Costs are slightly higher (1.1 - 1.4 rubles / KW * H). The main drawback is the low autonomy of the boilers: they require periodic fuel loading and ash removal.
- Diesel fuel boiler, on the contrary, it does not require the owner’s attention for weeks. The disadvantages include the need to store a large amount of fuel, smell, a high level of noise during the operation of the solar burner and the high cost of heat (3.2 rubles / KW * h).
- Finally, electric boilers of all kinds. (Tenovy, induction and electrode) are most convenient in operation and safe. They do not require frequent maintenance or removal of combustion products. For all the good you have to pay; in this case, quite specific money at the rate of about 3.6 - 3.8 rubles per kilowatt-hour.
Coolant circulation
It can be natural and forced.
| Circulation type | Description |
| Natural (gravitational) | Heating the water in the heat exchanger of the boiler reduces its density. Having expanded, the hot coolant is forced out with colder water into the upper part of the circuit. Returning to the boiler through the heating devices, the water gives off excess heat. |
| Forced | The movement of water is provided by the operation of the circulation pump with a constant or adjustable capacity. |
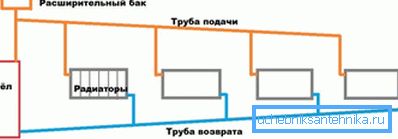
Useful: practiced installation schemes that can work in both modes. In this case, the inset of the pump into the filling of large (from the DN 32) diameter is supplied with a bypass. It is needed so that the restriction of the pipeline does not reduce the already low hydraulic head in the natural circulation mode.
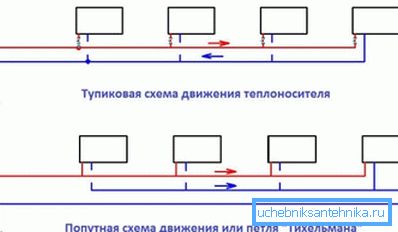
The direction of movement of the coolant
It can be deadlock and passing.
- The dead-end type of the heating system implies that in different parts of the circuit the coolant moves in opposite directions.
- Following traffic means that water, antifreeze, oil, etc. are not in any point of the circuit. do not change the direction of movement to the opposite.
Top and bottom bottling
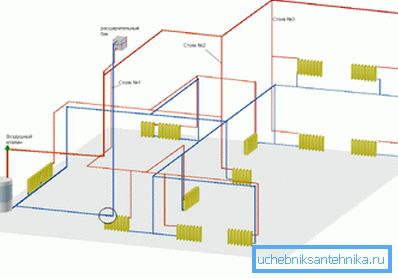
Everything is simple here: the scheme with the upper filling assumes that the heating supply bed (the horizontal branch of the pipeline connecting the risers) is in the attic, and the return flow bed is in the basement.
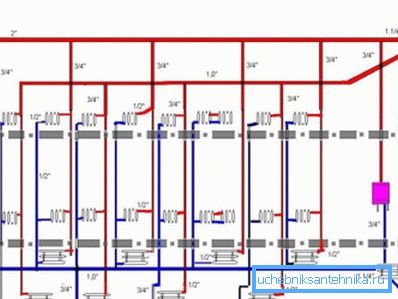
In the case of lower bottling, respectively, both plank houses are divorced in the basement. The risers are connected in pairs; each pair is connected by a jumper on the top floor of the house or in the basement.
Layout
Separate the vertical and horizontal wiring; the terms, it seems, are intuitively understandable and do not need comments. It is worth, however, to clarify that in the real world, the combined types of heating systems are more common. For example, in a typical apartment building, the riser is a vertical layout, but the bottling is horizontal.
Connection of heating devices
On this basis, single-pipe and two-pipe circuits are distinguished.
- In the first case, the filling is a ring between the inlet and outlet pipes of the boiler or house valves of the elevator assembly. Heating devices tear it apart or, which is much more reasonable, crash parallel to the bottling.
- The second scheme implies that each radiator or convector is a jumper between the supply and return filling.
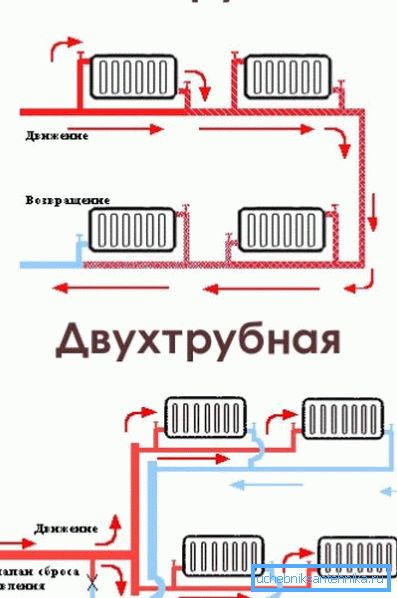
Note: in general, a two-pipe circuit requires throttling each instrument and balancing the system when started using chokes. The instruction is connected with the fact that otherwise the whole circulation will go through the devices closest to the boiler or elevator, which is fraught with defrosting of long-range radiators.
Exotic
What is the heating in addition to the usual and widely used schemes with a liquid coolant?
Airy
In the role of the coolant serves ordinary air. Since its specific heat capacity is small, large volumes have to be transported; Air heating systems are often combined with ventilation.
The solution is interesting in the absence of heating devices in the interior. The main disadvantage is that the hidden installation of air ducts is possible only at the stage of construction or major repairs of the house.

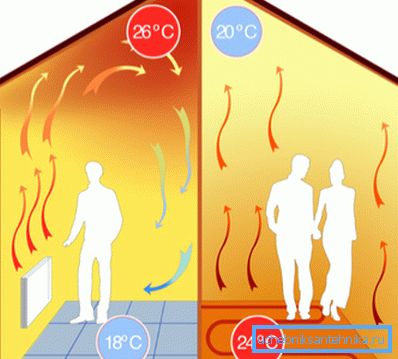
Warm floor
In the role of the heater serves the entire surface of the floor. For this purpose, a pipe with heat carrier, a heating cable or a film heater is placed in the screed or under the finishing coating. The work can easily be done by hand, without the involvement of specialists.
Heated floor is interesting for its efficiency. No, the price of a kilowatt-hour of heat does not change: it depends only on the heat source. Savings are achieved by more efficient temperature distribution and less leakage through the ceiling.
Infrared
Most of the heat is transferred from the heating element to objects and people in the room due to thermal radiation, and not convection. Since the heaters directly affect the temperature receptors of the inhabitants of the house, the temperature in the room can be reduced to 15-16C without the slightest discomfort. Hence again energy savings.

Conclusion
Of course, our miniature review of possible solutions in the field of heating does not claim to be complete. The attached video will complement it with useful and educational materials. Successes!