What should be the scheme of connecting the heating in a
When connecting the heating in a private house, all the work is usually done independently. At the same time there are several options for connection schemes, each of which has its own strengths and weaknesses. Before embarking on the practical part, it will not be superfluous to familiarize yourself with the theory - the existing methods of connection and their brief description.

Dependent or independent scheme
An independent scheme for connecting the heating of a private house provides maximum autonomy. If in a city apartment the radiators are already hot, then in a private house a boiler will be needed to heat it, which does not have the best effect on the cost.
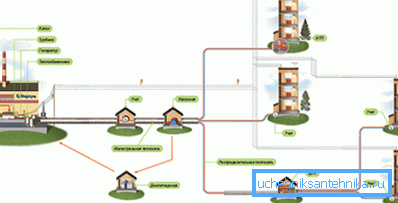
At the same time, the independent version has the advantages:
- his work can be regulated in a wide range, because all boilers are equipped with thermostats;
- heating the house becomes completely independent of the state of the heating system, given the deterioration of housing and utilities funds, this is especially important;
- can control the composition of the coolant, This allows you to extend the service life of pipes and radiators.
As for the shortcomings, it is possible to note the increased cost compared to the dependent analogue and the increased complexity of installation. In the case of the dependent option, all work comes down to laying the pipes in the apartment, installing radiators and crashing into the riser, but an independent heating circuit will additionally require the installation of a boiler, a circulation pump, thermostats, etc.
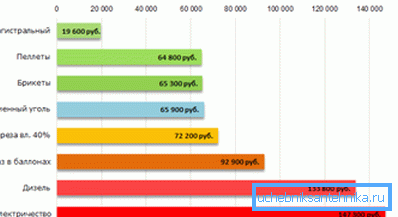
Note! Absolutely independent can only be called a version with a solid fuel boiler and natural circulation. In this case, the work will not need neither electricity nor gas, only firewood, pellets or any other type of fuel.
Which scheme is better to choose
When designing the heating system of a private house, you need to decide on:
- type of circulation (self-flowing systems can be used, or you can simply install a circulation pump);
- wiring method (one or two pipe system will be used).
Comparison of heating systems with forced and gravity circulation
By name, it is clear that in a self-flowing system, circulation occurs without the aid of a pump. Its movement occurs due to the slope of the supply and return pipes.
The movement of the coolant is as follows:
- the boiler heats up the water, it expands and a part is squeezed up along the riser;
- then, due to the pitch of the pipes, the coolant moves to the radiator, heats it and is discharged back to the boiler.
Connection scheme of the heating system with natural circulation requires:
- strict observance of slopes, it is enough to ensure a difference of the order of 3-5 mm per 1 m length;
- the use of large pipe diameters, as a result, the system is much more inertial than, for example, a centralized counterpart.
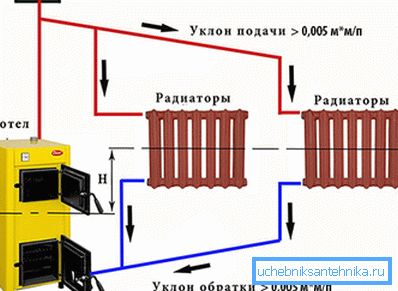
Note! If we compare the amount of coolant in the heating system with the pump and in the gravity flow, it turns out that in the first case its amount is 2.5-3.5 times more (due to the larger diameter of the pipeline).
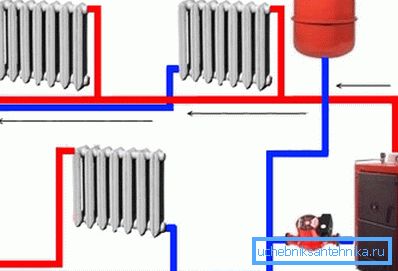
The use of a circulation pump allows you to:
- ensure a constant pressure in the system and ensure stable circulation of the coolant;
- use pipes of smaller diameter, this will reduce the required amount of coolant.
For a private house, it is also possible to have a combined water heating circuit - in normal mode, the pump circulates the coolant, and when the electricity is turned off, work will be ensured by the slope of the pipes. With this method of organizing the heating system, a bypass cuts in front of the boiler and a pump is installed on it. With the help of 2 taps, it can be turned off at any time.
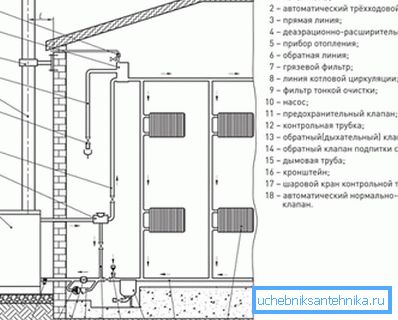
Popular schemes
To organize heating in the house in several ways:
- one pipe version - the price in this case is minimal, but in terms of efficiency, this is not the best choice. All radiators are connected in series, that is, the coolant to the last battery in the ring is fed pretty cool. This option can be considered for heating a small private house;
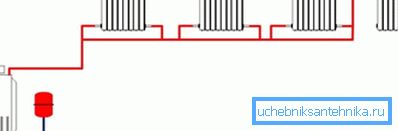
- two-pipe - flow and discharge are separated, that is, the cooled coolant is not mixed with the feed from the boiler;
- using a collector - the heating connection provides for the individual supply and removal of coolant for each radiator.
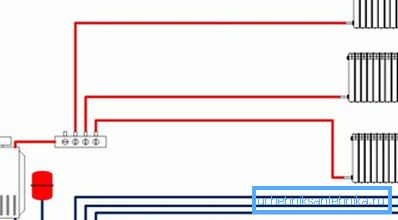
Note! When using a heating collector, material costs increase, because the need for pipes is maximum. But it is possible to regulate the temperature in the house in a wide range.
Also, the heating system can be connected in a vertical or horizontal pattern:
- with vertical wiring, the supply is organized along several risers, on each floor or several radiators are connected to the riser;
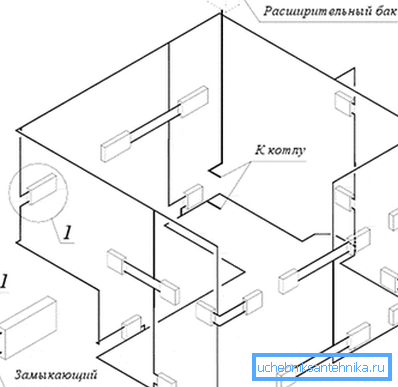
- with horizontal distribution, the riser is only 1. Horizontal pipes of small diameter are laid along the perimeter of each floor.
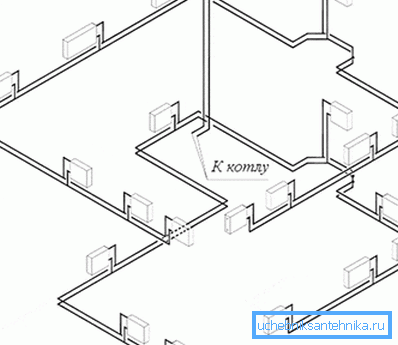
It is possible to classify heating systems in the direction of coolant movement:
- dead-end - so-called systems in which the coolant after passing through the battery begins to move in another direction;
- passing - the water moves in the same direction as before the battery.
If all the work is done by own hands, then to facilitate the start of the heating system, it is better to stop at the option with the upper filling. In this case, the supply pipe will have to bring to the attic. This will complicate maintenance a little, but the risk of air traffic is minimal.
About performance
Instructions for installation of heating in a private house includes several points:
- installation and connection of the boiler;
- installation of risers;
- floor layout;
- installation and connection of radiators;
- leak test

Of the steps listed separately, it is necessary to distinguish the installation and connection of radiators. If the radiator installation rules are not observed or the connection option is not chosen, the heating efficiency can be significantly reduced.
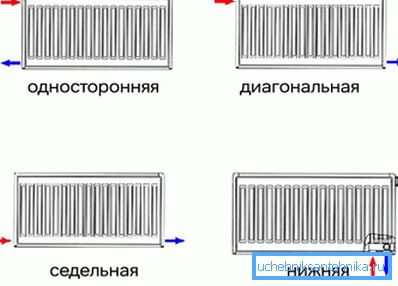
Possible options for connecting radiators:
- bottom - is considered the least effective, in which case the supply and discharge pipes are connected to the radiator at the bottom, there is a big risk that the far end of the battery simply does not warm up;
- unilateral - hot water is supplied from the upper part, and the coolant is discharged from the same side, but from the bottom;
- saddle - feed pipe is connected to the bottom of the battery, and water is drained from the other side of the radiator;
- diagonal in terms of efficiency is considered optimal.
Summarizing
For a small private house, an optimal scheme can be considered a combined one-pipe system. That is, under force majeure circumstances, the work does not stop due to natural circulation. Information about other heating schemes will be useful if you need to heat a large area. Information about other heating options will be useful if you need to heat a large area.
The video focuses on the horizontal one-pipe heating system.