External sewer networks: structure and regulatory
How does the waste system work outside the house? What materials are used for its construction? Are there any building codes for external sewer networks? Let's try to figure it out.

Device: just about complicated
First, let's find out how everything works.
After leaving the sewage system at home, liquid effluents enter the well. A typical scheme of connecting the walls of the well with the release is extremely simple: the pipe passes through a hole in the reinforced concrete ring; the entrance is sealed with a cement-sand mortar.
The bottom of the well is a concrete tray that directs the drains to the connecting pipe between the wells. As a rule, the number of wells corresponds to the number of entrances of an apartment building. The direction of movement of the wastewater is selected taking into account the terrain relief.
Captain Obviousness suggests: in the absence of a slope or the need to force drains to move in the direction of elevation of the terrain, the movement of drains can be achieved by varying the depth of the wells. In addition, in some cases, sewage sites are pressured; Fecal pumps are responsible for the recovery of sewage.

As the sewage flows merge, the diameter of the pipes connecting the wells increases. All discharges of a district or several districts of the city are combined in a collector - the Biggest Pipe, which carries the contents to the treatment plant. There, the wastewater is filtered, disinfected and discharged to the relief or to any local water body.
What materials are used in the construction of various sewage facilities?
- The traditional material for the walls of wells - red ceramic brick - about half a century ago, reinforced concrete rings were replaced; now they are gradually being replaced by polyethylene and polypropylene wells.
- Pipes are made of cast iron and plastics - polyethylene, polypropylene and polyvinyl chloride. Asbestos cement, ceramics and reinforced concrete are less commonly used.
- Reinforced concrete and ceramic pipes are used for the construction of collectors. In addition to them, in many cities you can find collectors with brick arches and monolithic reinforced concrete structures.

Regulatory requirements
We have to study two documents that are directly related to the topics of interest to us.
- The SNiP on the external water supply and sewage networks has the number 3.05.04-85 and was put into operation in 1986.
- In addition, the laying of external sewage networks is governed by a set of rules SP 32.13330.2012. It is declared as an updated version of the SNiP 2.04.03-85 issued simultaneously with the previous one.
Let's select the key points from the text.
SNiP 3.05.04-85
Laying of external networks of water supply and sewage with the use of bell-shaped pipes on the terrain with a slope is performed with their orientation up the slope of the socket.
The straightness of the sewage section between the wells is checked with a mirror for clearance. The horizontal tolerance is not more than a quarter of the diameter, or not more than 5 cm in each side; vertical deviations are not allowed. Inspection of each section is carried out twice - before and after backfilling of the pipeline.
The deviation of the top of the sewer pipe from the design position can not exceed 30 millimeters, regardless of the length of the site.

Pipe fittings are centered when laying, so that the gap width is constant.
During breaks in laying, the ends of the pipes are muffled.
Joints with socket seals cannot be joined frozen.
Cast iron pipes
Cast iron pipe flange connections are sealed with a cabol (tarred or bituminized hemp). It is desirable to protect the seal with an asbestos cement lock. In addition, sealants and rubber o-rings are allowed.
The depth of embedding of the socket is regulated by the document.
| Diameter of pipes, mm | Depth of seal, mm | ||
| Kabolka | Cabol and asbestos cement lock | Sealant | |
| 65-200 | 35 | thirty | 50 |
| 250-400 | 45 | 35 | 60 |
| 600-1000 | 50 | 40 | 70 |
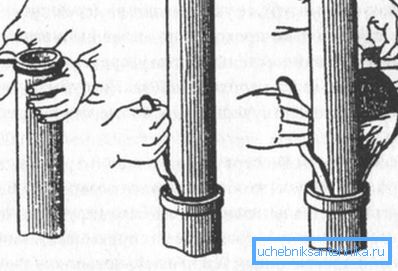
Asbestos cement pipes
The size of the gap between the ends of the joined pipes is:
- With a diameter up to 300 mm - 5 mm.
- With a diameter over 300 mm - 10 mm.
Before connecting the sewer pipe coupler should make a mark indicating the initial and working position of the coupling.
The joints of the asbestos-cement section with the cast-iron one are made using cast-iron fittings.
Concrete and reinforced concrete pipes
They are used primarily for storm sewers.

The size of the gap between the end face and the thrust surface at the socket connection is:
- For pressure sewage with a diameter of up to a meter - 12-15 mm, over a meter - 18-22.
- For free-flow sewage with a diameter of 700 mm - 8-12 mm, over 700 mm - 18-22.
- For seam connections - up to 25 mm regardless of diameter.
- Methods of sealing joints are similar to those described for cast iron pipes - with one amendment: the use of only polysulfide sealants is recommended. The depth of embedding is regulated in this case as well:
| Diameter, mm | Depth of seal, mm | ||
| Kabolka | Cabol with asbestos cement lock | Sealant | |
| 100-150 | 25 | 25 | 35 |
| 200-250 | 40 | 40 | 40 |
| 400-600 | 50 | 50 | 50 |
| 800-1600 | 55 | 55 | 70 |
| 2400 | 70 | 70 | 95 |
Please note: for drainpipes, the socket can be fully sealed with cement grade B7.5. When preparing the solution with your own hands, 5.24 parts of sand are taken for 1 part of cement.
Ceramics
The gap between the ends with a diameter of up to 300 mm is 5-7 mm, with large diameters - 8-10.

To seal the sockets can be used:
- Already familiar to us a cabol with a lock device made of cement mortar class B7.5.
- Asphalt mastic (at temperatures of effluents not higher than 40 ° C).
- Polysulfide sealants.
Instructions for the selection of the depth of the seal is present here:
| Diameter, mm | Depth of seal, mm | ||
| Kabolka | Kabolka with lock | Mastic, sealant | |
| 160-300 | thirty | thirty | 40 |
| 350-600 | thirty | 38 | 45 |
Plastics
In recent years, plastic sewage systems have substantially forced competing solutions to make room. The main reason for its popularity is the price: let's say PVC pipes are cheaper than cast iron 3-5 times.
The installation instructions in the SNiP refer to pipes made of polyethylene and polyvinyl chloride.
- The joints of polyethylene pipelines are made by the method of contact welding butt or socket. At the same time, different types of polyethylene (HDPE and LDPE) cannot be interconnected.

- Construction of external water supply and sewage networks using polyethylene pipes and fittings can be carried out at temperatures not lower than +10 C. In the cold, welding is performed in a warmed room (for example, in a mobile tent heated with a diesel heat gun).
- The welding site must be protected from dust and contact with snow or rain.
- PVC piping connected by glue or using rubber seals. For bonding used gipk-127 glue. The gluing place should not be subjected to mechanical stress for 15 minutes; hydraulic tests are carried out no earlier than a day.
An important point: the temperature at which bonding is performed is also limited. It should be +5 - +35 degrees.
Tests
How are outdoor water and sewage networks tested?
Pressure pipelines are tested hydraulically by pumping water. However, if there are technical difficulties with its submission, some pipelines may be tested by air.
In which cases are pneumatic tests permissible?
- With a working pressure of asbestos-cement, reinforced concrete and cast-iron pipelines up to 5 atmospheres.

- With a working pressure of underground steel pipes up to 16 atmospheres, above-ground - up to 3. However, the laying of sewage with steel pipes is the rarest exception.
Reference: an overpressure of 1 atmosphere (1 kg / cm2) raises the water column to a height of 10 meters. Thus, air can be tested pressure sewage with a height difference of up to 50 meters.
Tests are performed in two stages:
- After joining all the joints and partially filling it with soil (up to half the vertical diameter). In this connection must be available for inspection.
- After the final backfill, a repeated test is carried out - already in the presence of the customer and representatives of the operating organization.
What with non-pressure pipelines, which mostly include sewage?
If to simplify the formulations given in the document, the leak test can be carried out in two ways:
- At low groundwater levels (in dry soils) the pipeline is filled with water. Its level should not fall during the test.
- When high groundwater, on the contrary, the lack of water in the pipes will indicate tightness.
As agreed with the customer, the testing of the pipeline can be selective.

SP 32.13330.2012
What requirements must meet the external sewer network according to SP 32.13330.2012?
When designing a sewage system, the possibility of using treated effluent for water supply of production and irrigation of farmland or landscaping should be considered.
When connecting to the sewer network of enterprises outside their territory, control wells are constructed.
In some cases it is necessary to provide for the installation of a waste meter:
- If the enterprise has no centralized water supply or is supplied with water from several sources;

- If the production process implies an imbalance between water consumption and discharge of more than five percent.
It is allowed to combine the drains of several enterprises, but only after they pass the control wells.
The degree of sewage treatment is regulated by municipal services. In case of non-compliance of wastewater with these requirements, the work on their preliminary treatment is assigned to the enterprise.
Drains from some territories cannot be discharged into storm sewers without prior cleaning.
The list includes:
- Industrial zones of enterprises;
- Carpool;
- Gas stations;
- Construction sites;
- Bus stations and car parks;
- Shopping centers;
- Warehouses.
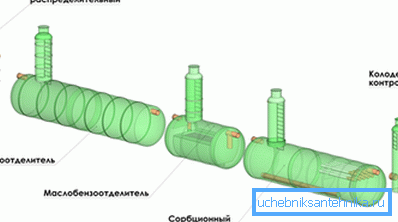
To ensure the smooth operation of the sewage document a number of measures are strongly recommended:
- Duplication of energy sources in pressure areas. As a backup source can be used as an autonomous power plant or battery.
- Duplication of communications and the device of bypass lines to solve the problem of salvo discharges.
- The device buffer tanks, again filled with salvo discharge and pumped out later in normal mode.
- Sectioning of sewers with the possibility of sectional decommissioning for repair or maintenance.
The smallest diameters of pipes for gravity drainage are determined by the serviced object:
| An object | Smallest diameter, mm |
| Street network for domestic wastewater | 200 |
| Intra quarterly network for domestic wastewater | 150 |
| Storm street network | 250 |
| Storm Intra Network | 200 |
| Street network in settlements with a daily water consumption of less than 300 m3 | 150 |
| Industrial network | 150 |

Conclusion
We hope that the information and regulatory references will be useful to the reader. As usual, additional materials on outdoor sewage can be found in the video in this article. Successes!